Summary
Background. In deep brain stimulation the way to define and localize the optimal target for the individual patient is still under debate. The objective of our study was to investigate the reliability of atlas derived data by comparing them with direct targeting on MR images.
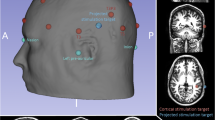
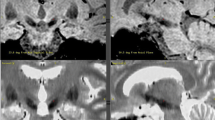
Method. We investigated 28 STN targets in 14 volunteers. The stereotactic coordinates of the dorso-lateral subthalamic nucleus (STN), were determined in 5 different ways for both STNs of each individual volunteer: 1. directly, on axial T2WI spin echo slices, 2. directly, on coronal T2WI spin echo slices and after fusion of data sets: 3. indirectly, on an axial atlas plate, 4. indirectly, on a coronal atlas plate, 5. indirectly, 12 mm lateral, 3 mm posterior and 3 mm inferior to mid-AC-PC.
Findings. The differences between MRI derived targets on axial vs. coronal slices were not statistically significant. After detection of the atlas derived targets the resulting x-coordinates were found more lateral than after direct detection on both, axial and coronal T2-weighted images (p<0.001). On axial images y-coordinates were located more anterior (p=0.240) on atlas derived targets and more posterior when target localizations were compared on coronal slices (p<0.001). z-Coordinates were more superior after atlas targeting compared to MRI targeting (p<0.001). Differences up to 6.21 mm occurred.
Conclusions. Despite the limitations concerning image distortions and slice thickness, direct target planning on MRI, regarding our results, is more reliable than targeting solely based on atlas derived data. Only MRI gives us detailed information about the individual configurations of central structures in every single patient. However, targets, which are not detectable on MRI like the nucleus ventralis intermedius have to be planned using stereotactic atlas information. In these cases intra-operative micro-electrode recording might help to better define the target region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RL Alterman BA Kall H Cohen PJ Kelly (1995) ArticleTitleStereotactic ventrolateral thalamotomy: is ventriculography necessary? Neurosurgery 37 IssueID4 717–721 Occurrence Handle8559301
RL Alterman GT Reiter J Shils B Skolnick JE Arle M Lesutis T Simuni A Colcher M Stern H Hurtig (1999) ArticleTitleTargeting for thalamic deep brain stimulator implantation without computer guidance: assessment of targeting accuracy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 72 IssueID2–4 150–153 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000029718
BP Bejjani D Dormont B Pidoux J Yelnik P Damier I Arnulf AM Bonnet C Marsault Y Agid J Philippon P Cornu (2000) ArticleTitleBilateral subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson’s disease by using three-dimensional stereotactic magnetic resonance imaging and electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 92 IssueID4 615–625 Occurrence Handle10761650
Benabid AL, Pollack P, Benazzouz A et al (1998) Grenoble Guidelines for deep brain stimulation, in First European Symposium on Stimulation in Parkinson Disease. Université Joseph Fourier de Grenoble, Grenoble, France, p 13
Benabid AL, Krack PP, Benazzouz A, Limousin P, Koudsie A, Pollak P (2000) Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson’s disease: methodologic aspects and clinical criteria. Neurology 55(12) [Suppl] 6: 40–44
Benabid AL, Koudsie A, Benazzouz A, Vercueil L, Fraix V, Chabardes S, Lebas JF, Pollak P, (2001) Deep brain stimulation of the corpus luysi (subthalamic nucleus) and other targets in Parkinson’s disease. Extension to new indications such as dystonia and epilepsy. J Neurol 248 [Suppl] 3: III37–III47
JD Carlson RP Iacono (1999) ArticleTitleElectrophysiological versus image-based targeting in the posteroventral pallidotomy. Comput Aided Surg 4 IssueID2 93–100 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0150(1999)4:2<93::AID-IGS4>3.0.CO;2-S Occurrence Handle10494139
E Cuny D Guehl P Burbaud C Gross V Dousset A Rougier (2002) ArticleTitleLack of agreement between direct magnetic resonance imaging and statistical determination of a subthalamic target: the role of electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 97 IssueID3 591–597 Occurrence Handle12296643
D Dormont P Cornu B Pidoux AM Bonnet A Biondi C Oppenheim D Hasboun P Damier E Cuchet J Philippon Y Agid C Marsault (1997) ArticleTitleChronic thalamic stimulation with three-dimensional MR stereotactic guidance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18 IssueID6 1093–1107 Occurrence Handle9194437
F Duffner H Schiffbauer S Breit S Friese D Freudenstein (2002) ArticleTitleRelevance of image fusion for target point determination in functional neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144 IssueID5 445–451 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007010200065
A Forster MS Eljamel TR Varma M Tulley M Latimer (1999) ArticleTitleAudit of neurophysiological recording during movement disorder surgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 72 IssueID2–4 154–156 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000029719 Occurrence Handle10853071
RE Gross WJ Lombardi WD Hutchison S Narula JA Saint-Cyr JO Dostrovsky RR Tasker AE Lang AM Lozano (1999) ArticleTitleVariability in lesion location after microelectrode-guided pallidotomy for Parkinson’s disease: anatomical, physiological, and technical factors that determine lesion distribution. J Neurosurg 90 IssueID3 468–477 Occurrence Handle10067915
Guridi J, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Lozano AM, Moro E, Albanese A, Nuttin B, Gybels J, Ramos E, Obeso JA (2000) Targeting the basal ganglia for deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 55(12) [Suppl] 6: 21–28
W Hamel B Schrader D Weinert J Herzog J Volkmann G Deuschl D Muller HM Mehdorn (2002) ArticleTitleMRI- and skull x-ray-based approaches to evaluate the position of deep brain stimulation electrode contacts – a technical note. Zentralbl Neurochir 63 IssueID2 65–69 Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-2002-33976 Occurrence Handle12224032
PE Holtzheimer Suffix3rd DW Roberts TM Darcey (1999) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography for target localization in functional stereotactic neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 45 IssueID2 290–297 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199908000-00018 Occurrence Handle10449073
JL Houeto ML Welter PB Bejjani S Tezenas du Montcel AM Bonnet V Mesnage S Navarro B Pidoux D Dormont P Cornu Y Agid (2003) ArticleTitleSubthalamic stimulation in Parkinson disease: intraoperative predictive factors. Arch Neurol 60 IssueID5 690–694 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archneur.60.5.690 Occurrence Handle12756132
Hutchison WD (1998) Microelectrode techniques and findings of globus pallidus. In: Krauss JK, Grossman RG, Jankovic J (eds) Pallidal surgery for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and movement disorders. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 135–152
BA Kall SJ Goerss PJ Kelly (1992) ArticleTitleA new multimodality correlative imaging technique for VOP/VIM (VL) thalamotomy procedures. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 58 IssueID1–4 45–51 Occurrence Handle1439348
Kelly PJ (1988) Contemporary stereotactic ventralis lateral thalamotomy in the treatment of Parkinsonian tremor and other movement disorders. In: Heilbrun MP (ed) Stereotactic neurosurgery. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 133–148
DL Kirschman B Milligan S Wilkinson J Overman L Wetzel S Batnitzky K Lyons R Pahwah WC Koller MA Gordon (2000) ArticleTitlePallidotomy microelectrode targeting: neurophysiology-based target refinement. Neurosurgery 46 IssueID3 613–622 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200003000-00018 Occurrence Handle10719858
JK Krauss RK Simpson SuffixJr WG Ondo T Pohle JM Burgunder J Jankovic (2001) ArticleTitleConcepts and methods in chronic thalamic stimulation for treatment of tremor: technique and application. Neurosurgery 48 IssueID3 535–541 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200103000-00015 Occurrence Handle11270543
MM Lanotte M Rizzone B Bergamasco G Faccani A Melcarne L Lopiano (2002) ArticleTitleDeep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus: anatomical, neurophysiological, and outcome correlations with the effects of stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72 IssueID1 53–58 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.72.1.53 Occurrence Handle11784826
M Merello A Cammarota D Cerquetti RC Leiguarda (2000) ArticleTitleMismatch between electrophysiologically defined and ventriculography based theoretical targets for posteroventral pallidotomy in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69 IssueID6 787–791 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.69.6.787 Occurrence Handle11080233
F Mobin AA De Salles EJ Behnke R Frysinger (1999) ArticleTitleCorrelation between MRI-based stereotactic thalamic deep brain stimulation electrode placement, macroelectrode stimulation and clinical response to tremor control. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 72 IssueID2–4 225–232 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000029730 Occurrence Handle10853082
D Nandi M Chir X Liu P Bain S Parkin C Joint J Winter J Stein R Scott R Gregory T Aziz (2002) ArticleTitleElectrophysiological confirmation of the zona incerta as a target for surgical treatment of disabling involuntary arm movements in multiple sclerosis: use of local field potentials. J Clin Neurosci 9 IssueID1 64–68 Occurrence Handle10.1054/jocn.2001.1012 Occurrence Handle11749021
K Niemann I van Nieuwenhofen (1999) ArticleTitleOne atlas – three anatomies: relationships of the Schaltenbrand and Wahren microscopic data. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141 IssueID10 1025–1038 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007010050479
NK Patel P Heywood K O’Sullivan S Love SS Gill (2002) ArticleTitleMRI-directed subthalamic nucleus surgery for Parkinson’s disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 78 IssueID3–4 132–145 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000068964 Occurrence Handle12652038
MC Rodriguez-Oroz M Rodriguez J Guridi K Mewes V Chockkman J Vitek MR DeLong JA Obeso (2001) ArticleTitleThe subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease: somatotopic organization and physiological characteristics. Brain 124 IssueIDPt 9 1777–1790 Occurrence Handle10.1093/brain/124.9.1777 Occurrence Handle11522580
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W (1977) Atlas for stereotaxy of the human brain. Georg Thieme, New York
PR Schuurman RM de Bie CB Majoie JD Speelman DA Bosch (1999) ArticleTitleA prospective comparison between three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging and ventriculography for target-coordinate determination in frame-based functional stereotactic neurosurgery. J Neurosurg 91 IssueID6 911–914 Occurrence Handle10584834
PA Starr JL Vitek M DeLong RA Bakay (1999) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance imaging-based stereotactic localization of the globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus. Neurosurgery 44 IssueID2 303–313 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199902000-00031 Occurrence Handle9932883
PA Starr (2002) ArticleTitlePlacement of deep brain stimulators into the subthalamic nucleus or Globus pallidus internus: technical approach. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 79 IssueID3–4 118–145 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000070828 Occurrence Handle12890973
D Sterio A Beric M Dogali E Fazzini G Alfaro O Devinsky (1994) ArticleTitleNeurophysiological properties of pallidal neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 35 IssueID5 586–591 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ana.410350512 Occurrence Handle8179304
D Sterio M Zonenshayn AY Mogilner AR Rezai K Kiprovski PJ Kelly A Beric (2002) ArticleTitleNeurophysiological refinement of subthalamic nucleus targeting. Neurosurgery 50 IssueID1 58–67 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200201000-00012 Occurrence Handle11844235
E Taub (2000) ArticleTitleMathematical theory of stereotactic coordinate transformation: elimination of rotational targeting error by addition of a third reference point. J Neurosurg 92 IssueID5 884–888 Occurrence Handle10794308
PV Theodosopoulos WJ Marks SuffixJr C Christine PA Starr (2003) ArticleTitleLocations of movement-related cells in the human subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18 IssueID7 791–798 Occurrence Handle10.1002/mds.10446 Occurrence Handle12815658
N Vayssiere S Hemm M Zanca MC Picot A Bonafe L Cif P Frerebeau P Coubes (2000) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance imaging stereotactic target localization for deep brain stimulation in dystonic children. J Neurosurg 93 IssueID5 784–790 Occurrence Handle11059658
JL Vitek RA Bakay T Hashimoto Y Kaneoke K Mewes JY Zhang D Rye P Starr M Baron R Turner MR DeLong (1998) ArticleTitleMicroelectrode-guided pallidotomy: technical approach and its application in medically intractable Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosurg 88 IssueID6 1027–1043 Occurrence Handle9609298
M Zonenshayn AR Rezai AY Mogilner A Beric D Sterio PJ Kelly (2000) ArticleTitleComparison of anatomic and neurophysiological methods for subthalamic nucleus targeting. Neurosurgery 47 IssueID2 282–292 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200008000-00005 Occurrence Handle10942001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlaier, J., Schoedel, P., Lange, M. et al. Reliability of atlas-derived coordinates in deep brain stimulation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147, 1175–1180 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0606-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0606-3