Abstract
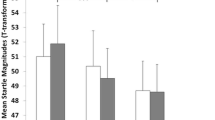
The dopamine transporter (DAT) and the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) both terminate synaptic dopamine action. Here, we investigated the influence of two polymorphisms in the respective genes: DAT1 (SLC6A3) VNTR and COMT val158met (rs4680). Startle magnitudes to intense noise bursts as measured with the eye blink response were recorded during the presentation of pictures of three valence conditions (unpleasant, pleasant and neutral) and during baseline without additional pictorial stimulation in a sample of healthy older adults (N = 94). There was a significant Bonferroni corrected main effect of COMT genotype on the overall startle responses, with met/met homozygotes showing the highest and participants with the val/val genotype showing the lowest startle response, while participants with the val/met genotype displayed intermediate reactions. There was also a DAT1 VNTR main effect, which, after Bonferroni correction, still showed a tendency toward significance with carriers of at least one 9-repeat (R) allele showing smaller overall startle responses compared to 10R/10R homozygotes. Thus, older adult carriers of COMT variants, which result in lower enzyme activity and therefore probably enhanced dopamine signaling, showed stronger startle activity. Although the functional significance of DAT1 VNTR is less defined, our results point to a potential influence of SLC6A3 on startle magnitude.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhadad SS, Lipp OV, Purkis HM (2008) Modality-specific attentional startle modulation during continuous performance tasks: a brief time is sufficient. Psychophysiology 45(6):1068–1078. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2008.00705.x
Anokhin AP, Golosheykin S, Heath AC (2007) Genetic and environmental influences on emotion-modulated startle reflex: a twin study. Psychophysiology 44(1):106–112. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2006.00486.x
Armbruster D, Moser DA, Strobel A, Hensch T, Kirschbaum C, Lesch KP, Brocke B (2009) Serotonin transporter gene variation and stressful life events impact processing of fear and anxiety. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12(3):393–401. doi:10.1017/S1461145708009565
Armbruster D, Mueller A, Strobel A, Kirschbaum C, Lesch KP, Brocke B (2010) Influence of functional tryptophan hydroxylase 2 gene variation and sex on the startle response in children, young adults, and older adults. Biol Psychology 83(3):214–221. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2009.12.010
Bäckman L, Nyberg L, Lindenberger U, Li SC, Farde L (2006) The correlative triad among aging, dopamine, and cognition: current status and future prospects. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30(6):791–807. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.06.005
Bäckman L, Lindenberger U, Li SC, Nyberg L (2011) Linking cognitive aging to alterations in dopamine neurotransmitter functioning: recent data and future avenues. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:670–677. doi:S0149-7634(09)00205-X
Barnett JH, Jones PB, Robbins TW, Muller U (2007) Effects of the catechol-o-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism on executive function: a meta-analysis of the Wisconsin Card Sort test in schizophrenia and healthy controls. Mol Psychiatry 12(5):502–509. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001973
Barr CS, Newman TK, Schwandt M, Shannon C, Dvoskin RL, Lindell SG, Taubman J, Thompson B, Champoux M, Lesch KP, Goldman D, Suomi SJ, Higley JD (2004) Sexual dichotomy of an interaction between early adversity and the serotonin transporter gene promoter variant in rhesus macaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(33):12358–12363. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403763101
Bilder RM, Volavka J, Lachman HM, Grace AA (2004) The catechol-o-methyltransferase polymorphism: relations to the tonic-phasic dopamine hypothesis and neuropsychiatric phenotypes. Neuropsychopharmacology 29(11):1943–1961. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300542
Blasi G, Mattay VS, Bertolino A, Elvevag B, Callicott JH, Das S, Kolachana BS, Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Weinberger DR (2005) Effect of catechol-o-methyltransferase val158met genotype on attentional control. J Neurosci 25(20):5038–5045. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0476-05.2005
Blumenthal TD, Cuthbert BN, Filion DL, Hackley S, Lipp OV, van Boxtel A (2005) Committee report: guidelines for human startle eyeblink electromyographic studies. Psychophysiology 42(1):1–15. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2005.00271.x
Brocke B, Armbruster D, Muller J, Hensch T, Jacob CP, Lesch KP, Kirschbaum C, Strobel A (2006) Serotonin transporter gene variation impacts innate fear processing: acoustic startle response and emotional startle. Mol Psychiatry 11(12):1106–1112. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001908
Carstensen LL, Mikels JA (2005) At the intersection of emotion and cognition—aging and the positivity effect. Curr Direct Psychol Sci 14(3):117–121. doi:10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00348.x
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, McClay J, Mill J, Martin J, Braithwaite A, Poulton R (2003) Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 301(5631):386–389. doi:10.1126/science.1083968
Chen J, Lipska BK, Halim N, Ma QD, Matsumoto M, Melhem S, Kolachana BS, Hyde TM, Herman MM, Apud J, Egan MF, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR (2004) Functional analysis of genetic variation in catechol-o-methyltransferase (comt): effects on mRNA, protein, and enzyme activity in postmortem human brain. Am J Hum Genet 75(5):807–821. doi:10.1086/425589
Congdon E, Constable RT, Lesch KP, Canli T (2009) Influence of SLC6A3 and comt variation on neural activation during response inhibition. Biol Psychol 81(3):144–152. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2009.03.005
Davis M, Falls WA, Campeau S, Kim M (1993) Fear-potentiated startle: a neural and pharmacological analysis. Behav Brain Res 58(1–2):175–198. doi:10.1016/0166-4328(93)90102-V
Diamond A (2007) Consequences of variations in genes that affect dopamine in prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 17(Suppl 1):i161–i170. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm082
Drabant EM, Hariri AR, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Munoz KE, Mattay VS, Kolachana BS, Egan MF, Weinberger DR (2006) Catechol o-methyltransferase val158met genotype and neural mechanisms related to affective arousal and regulation. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63(12):1396–1406. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.12.1396
Dreher JC, Kohn P, Kolachana B, Weinberger DR, Berman KF (2009) Variation in dopamine genes influences responsivity of the human reward system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(2):617–622. doi:10.1073/pnas.0805517106
Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Callicott JH, Mazzanti CM, Straub RE, Goldman D, Weinberger DR (2001) Effect of COMT Val108/158 Met genotype on frontal lobe function and risk for schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(12):6917–6922. doi:10.1073/pnas.111134598
Ekman P, Friesen WV (1976) Pictures of facial affect. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto
Ellwanger J, Geyer MA, Braff DL (2003) The relationship of age to prepulse inhibition and habituation of the acoustic startle response. Biol Psychol 62(3):175–195. doi:10.1016/S0301-0511(02)00126-6
Enoch MA, Xu K, Ferro E, Harris CR, Goldman D (2003) Genetic origins of anxiety in women: a role for a functional catechol-o-methyltransferase polymorphism. Psychiatr Genet 13(1):33–41. doi:10.1097/01.ypg.0000054709.85338.c3
Ettinger U, Kumari V, Collier DA, Powell J, Luzi S, Michel TM, Zedomi O, Williams SC (2008) Catechol-o-methyltransferase (comt) val158met genotype is associated with bold response as a function of task characteristic. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(13):3046–3057. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301658
Faraone SV, Perlis RH, Doyle AE, Smoller JW, Goralnick JJ, Holmgren MA, Sklar P (2005) Molecular genetics of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 57(11):1313–1323. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.024
Filion DL, Dawson ME, Schell AM (1998) The psychological significance of human startle eyeblink modification: a review. Biol Psychol 47(1):1–43. doi:10.1016/S0301-0511(97)00020-3
Fischer H, Sandblom J, Gavazzeni J, Fransson P, Wright CI, Backman L (2005) Age-differential patterns of brain activation during perception of angry faces. Neurosci Lett 386(2):99–104. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.06.002
Ford JM, Roth WT, Isaacks BG, White PM, Hood SH, Pfefferbaum A (1995) Elderly men and women are less responsive to startling noises: N1, P3 and blink evidence. Biol Psychol 39(2–3):57–80. doi:10.1016/0301-0511(94)00959-2
Fuke S, Suo S, Takahashi N, Koike H, Sasagawa N, Ishiura S (2001) The VNTR polymorphism of the human dopamine transporter (DAT1) gene affects gene expression. Pharmacogenomics J 1(2):152–156
Goldberg TE, Egan MF, Gscheidle T, Coppola R, Weickert T, Kolachana BS, Goldman D, Weinberger DR (2003) Executive subprocesses in working memory: relationship to catechol-o-methyltransferase val158met genotype and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60(9):889–896. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.60.9.889
Goldman D, Oroszi G, Ducci F (2005) The genetics of addictions: uncovering the genes. Nat Rev Genet 6(7):521–532. doi:10.1038/nrg1635
Haraldsson HM, Ettinger U, Magnusdottir BB, Sigmundsson T, Sigurdsson E, Ingason A, Petursson H (2010) Catechol-o-methyltransferase val 158 met polymorphism and antisaccade eye movements in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 36(1):157–164. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbn064
Heinz A, Goldman D, Jones DW, Palmour R, Hommer D, Gorey JG, Lee KS, Linnoila M, Weinberger DR (2000) Genotype influences in vivo dopamine transporter availability in human striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology 22(2):133–139. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00099-8
Hünnerkopf R, Strobel A, Gutknecht L, Brocke B, Lesch KP (2007) Interaction between BDNF Val66Met and dopamine transporter gene variation influences anxiety-related traits. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(12):2552–2560. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301383
Isaacowitz DM, Wadlinger HA, Goren D, Wilson HR (2006) Is there an age-related positivity effect in visual attention? A comparison of two methodologies. Emotion 6(3):511–516. doi:10.1037/1528-3542.6.3.511
Jacobsen LK, Staley JK, Zoghbi SS, Seibyl JP, Kosten TR, Innis RB, Gelernter J (2000) Prediction of dopamine transporter binding availability by genotype: a preliminary report. Am J Psychiatry 157(10):1700–1703
Joober R, Gauthier J, Lal S, Bloom D, Lalonde P, Rouleau G, Benkelfat C, Labelle A (2002) Catechol-o-methyltransferase val-108/158-met gene variants associated with performance on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59(7):662–663
Karoum F, Chrapusta SJ, Egan MF (1994) 3-methoxytyramine is the major metabolite of released dopamine in the rat frontal cortex: Reassessment of the effects of antipsychotics on the dynamics of dopamine release and metabolism in the frontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and striatum by a simple two pool model. J Neurochem 63(3):972–979. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63030972.x
Koch M (1999) The neurobiology of startle. Prog Neurobiol 59(2):107–128. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(98)00098-7
Lachman ME (2004) Development in midlife. Annu Rev Psychol 55:305–331. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.141521
Lang PJ (1980) Behavioral treatment and bio-behavioral assessment: computer applications. In: Sidowski JB, Johnson JH, Williams TA (eds) Technology in mental health care delivery systems. Ablex, Norwood, pp 119–137
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (1990) Emotion, attention, and the startle reflex. Psychol Rev 97:377–395
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (1999) International affective picture system (IAPS): instruction manual and affective ratings. Technical report a-4, Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida, Gainesville
Lang UE, Bajbouj M, Sander T, Gallinat J (2007) Gender-dependent association of the functional catechol-o-methyltransferase val158met genotype with sensation seeking personality trait. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(9):1950–1955. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301335
Leaton RN, Cranney J (1990) Potentiation of the acoustic startle response by a conditioned stimulus paired with acoustic startle stimulus in rats. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 16(3):279–287
Li J, Ji L (2005) Adjusting multiple testing in multilocus analyses using the eigenvalues of a correlation matrix. Heredity 95(3):221–227. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6800717
Ludewig K, Ludewig S, Seitz A, Obrist M, Geyer MA, Vollenweider FX (2003) The acoustic startle reflex and its modulation: effects of age and gender in humans. Biol Psychol 63(3):311–323. doi:10.1016/S0301-0511(03)00074-7
Lynch DR, Mozley PD, Sokol S, Maas NM, Balcer LJ, Siderowf AD (2003) Lack of effect of polymorphisms in dopamine metabolism related genes on imaging of TRODAT-1 in striatum of asymptomatic volunteers and patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18(7):804–812. doi:10.1002/mds.10430
Malhotra AK, Kestler LJ, Mazzanti C, Bates JA, Goldberg T, Goldman D (2002) A functional polymorphism in the COMT gene and performance on a test of prefrontal cognition. Am J Psychiatry 159(4):652–654
Martinez D, Gelernter J, Abi-Dargham A, van Dyck CH, Kegeles L, Innis RB, Laruelle M (2001) The variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism of the dopamine transporter gene is not associated with significant change in dopamine transporter phenotype in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 24(5):553–560. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00216-5
Mather M, Carstensen LL (2003) Aging and attentional biases for emotional faces. Psychol Sci 14(5):409–415. doi:10.1111/1467-9280.01455
Mather M, Canli T, English T, Whitfield S, Wais P, Ochsner K, Gabrieli JD, Carstensen LL (2004) Amygdala responses to emotionally valenced stimuli in older and younger adults. Psychol Sci 15(4):259–263. doi:10.1111/j.0956-7976.2004.00662.x
Matsumoto M, Weickert CS, Beltaifa S, Kolachana B, Chen J, Hyde TM, Herman MM, Weinberger DR, Kleinman JE (2003) Catechol o-methyltransferase (COMT) MRNA expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 28(8):1521–1530. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300218
McClearn GE (2006) Contextual genetics. Trends Genet 22(6):314–319. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2006.04.005
Michelhaugh SK, Fiskerstrand C, Lovejoy E, Bannon MJ, Quinn JP (2001) The dopamine transporter gene (SLC6A3) variable number of tandem repeats domain enhances transcription in dopamine neurons. J Neurochem 79(5):1033–1038. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00647.x
Mier D, Kirsch P, Meyer-Lindenberg A (2010) Neural substrates of pleiotropic action of genetic variation in COMT: a meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 15(9):918–927. doi:10.1038/mp.2009.36
Mignone F, Gissi C, Liuni S, Pesole G (2002) Untranslated regions of mRNAs. Genome Biol 3 (3):REVIEWS0004. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-3-reviews0004
Mikels JA, Larkin GR, Reuter-Lorenz PA, Cartensen LL (2005) Divergent trajectories in the aging mind: changes in working memory for affective versus visual information with age. Psychol Aging 20(4):542–553. doi:10.1037/0882-7974.20.4.542
Mill J, Asherson P, Browes C, D’Souza U, Craig I (2002) Expression of the dopamine transporter gene is regulated by the 3′ UTR VNTR: evidence from brain and lymphocytes using quantitative RT-PCR. Am J Med Genet 114(8):975–979. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.10948
Miller GM, Madras BK (2002) Polymorphisms in the 3′-untranslated region of human and monkey dopamine transporter genes affect reporter gene expression. Mol Psychiatry 7(1):44–55. doi:10.1038/sj/mp/4000921
Montag C, Buckholtz JW, Hartmann P, Merz M, Burk C, Hennig J, Reuter M (2008) COMT genetic variation affects fear processing: psychophysiological evidence. Behav Neurosci 122(4):901–909. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.122.4.901
Munafo MR, Bowes L, Clark TG, Flint J (2005) Lack of association of the COMT (val158/108 met) gene and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of case–control studies. Mol Psychiatry 10(8):765–770. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001664
Murphy NA, Isaacowitz DM (2008) Preferences for emotional information in older and younger adults: a meta-analysis of memory and attention tasks. Psychol Aging 23(2):263–286. doi:10.1037/0882-7974.23.2.263
Nagel IE, Chicherio C, Li SC, von Oertzen T, Sander T, Villringer A, Heekeren HR, Backman L, Lindenberger U (2008) Human aging magnifies genetic effects on executive functioning and working memory. Front Hum Neurosci 2:1–8. doi:10.3389/neuro.09.001.2008
Nicodemus KK, Kolachana BS, Vakkalanka R, Straub RE, Giegling I, Egan MF, Rujescu D, Weinberger DR (2007) Evidence for statistical epistasis between catechol-o-methyltransferase (COMT) and polymorphisms in RGS4, G72 (DAOA), GRM3, and DISC1: influence on risk of schizophrenia. Hum Genet 120(6):889–906. doi:10.1007/s00439-006-0257-3
Nieoullon A, Coquerel A (2003) Dopamine: a key regulator to adapt action, emotion, motivation and cognition. Curr Opin Neurol 16(Suppl 2):S3–S9
Nyholt DR (2004) A simple correction for multiple testing for single-nucleotide polymorphisms in linkage disequilibrium with each other. Am J Hum Genet 74(4):765–769. doi:10.1086/383251
Olsson CA, Anney RJ, Lotfi-Miri M, Byrnes GB, Williamson R, Patton GC (2005) Association between the COMT val158met polymorphism and propensity to anxiety in an Australian population-based longitudinal study of adolescent health. Psychiatr Genet 15(2):109–115. doi:00041444-200506000-00007
Papaleo F, Crawley JN, Song J, Lipska BK, Pickel J, Weinberger DR, Chen J (2008) Genetic dissection of the role of catechol-o-methyltransferase in cognition and stress reactivity in mice. J Neurosci 28(35):8709–8723. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2077-08.2008
Pauli P, Conzelmann A, Mucha RF, Weyers P, Baehne CG, Fallgatter AJ, Jacob CP, Lesch KP (2010) Affect-modulated startle reflex and dopamine D4 receptor gene variation. Psychophysiology 47(1):25–33. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00923.x
Quednow BB, Schmechtig A, Ettinger U, Petrovsky N, Collier DA, Vollenweider FX, Wagner M, Kumari V (2009) Sensorimotor gating depends on polymorphisms of the serotonin-2A receptor and catechol-o-methyltransferase, but not on neuregulin-1 Arg38Gln genotype: a replication study. Biol Psychiatry 66(6):614–620. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.05.007
Reuter M, Hennig J (2005) Association of the functional catechol-o-methyltransferase val158met polymorphism with the personality trait of extraversion. Neuroreport 16(10):1135–1138. doi:00001756-200507130-00020
Rollo CD (2009) Dopamine and aging: intersecting facets. Neurochem Res 34(4):601–629. doi:10.1007/s11064-008-9858-7
Rommelse NN, Altink ME, Arias-Vasquez A, Buschgens CJ, Fliers E, Faraone SV, Buitelaar JK, Sergeant JA, Franke B, Oosterlaan J (2008) A review and analysis of the relationship between neuropsychological measures and DAT1 in ADHD. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B(8):1536–1546. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30848
Roussos P, Giakoumaki SG, Rogdaki M, Pavlakis S, Frangou S, Bitsios P (2008) Prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex depends on the catechol o-methyltransferase val158met gene polymorphism. Psychol Med 38(11):1651–1658. doi:10.1017/S0033291708002912
Ruffman T, Henry JD, Livingstone V, Phillips LH (2008) A meta-analytic review of emotion recognition and aging: Implications for neuropsychological models of aging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32(4):863–881. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.01.001
Sesack SR, Hawrylak VA, Matus C, Guido MA, Levey AI (1998) Dopamine axon varicosities in the prelimbic division of the rat prefrontal cortex exhibit sparse immunoreactivity for the dopamine transporter. J Neurosci 18(7):2697–2708
Smith DP, Hillman CH, Duley AR (2005) Influences of age on emotional reactivity during picture processing. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 60(1):P49–P56. doi:10.1093/geronb/60.1.P49
Smolka MN, Schumann G, Wrase J, Grusser SM, Flor H, Mann K, Braus DF, Goldman D, Buchel C, Heinz A (2005) Catechol-o-methyltransferase val158met genotype affects processing of emotional stimuli in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 25(4):836–842. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1792-04.2005
Smolka MN, Buhler M, Schumann G, Klein S, Hu XZ, Moayer M, Zimmer A, Wrase J, Flor H, Mann K, Braus DF, Goldman D, Heinz A (2007) Gene–gene effects on central processing of aversive stimuli. Mol Psychiatry 12(3):307–317. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001946
Stefanis NC, Van Os J, Avramopoulos D, Smyrnis N, Evdokimidis I, Hantoumi I, Stefanis CN (2004) Variation in catechol-o-methyltransferase val158 met genotype associated with schizotypy but not cognition: A population study in 543 young men. Biol Psychiatry 56(7):510–515. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.06.038
Stein MB, Fallin MD, Schork NJ, Gelernter J (2005) COMT polymorphisms and anxiety-related personality traits. Neuropsychopharmacology 30(11):2092–2102. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300787
Tenhunen J, Salminen M, Jalanko A, Ukkonen S, Ulmanen I (1993) Structure of the rat catechol-o-methyltransferase gene: Separate promoters are used to produce mRNAs for soluble and membrane-bound forms of the enzyme. DNA Cell Biol 12(3):253–263. doi:10.1089/dna.1993.12.253
Tunbridge EM, Bannerman DM, Sharp T, Harrison PJ (2004) Catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibition improves set-shifting performance and elevates stimulated dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 24(23):5331–5335. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1124-04.2004
Tunbridge EM, Harrison PJ, Weinberger DR (2006) Catechol-o-methyltransferase, cognition, and psychosis: Val158met and beyond. Biol Psychiatry 60(2):141–151. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.10.024
van Dyck CH, Malison RT, Jacobsen LK, Seibyl JP, Staley JK, Laruelle M, Baldwin RM, Innis RB, Gelernter J (2005) Increased dopamine transporter availability associated with the 9-repeat allele of the SLC6A3 gene. J Nucl Med 46(5):745–751
Varty GB, Hauger RL, Geyer MA (1998) Aging effects on the startle response and startle plasticity in Fischer F344 rats. Neurobiol Aging 19(3):243–251. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(98)00053-0
Vrana SR, Spence EL, Lang PJ (1988) The startle probe response: a new measure of emotion? J Abnorm Psychol 97(4):487–491. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.97.4.487
Weinshilboum RM, Otterness DM, Szumlanski CL (1999) Methylation pharmacogenetics: Catechol o-methyltransferase, thiopurine methyltransferase, and histamine N-methyltransferase. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:19–52. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.39.1.19
Winterer G, Musso F, Vucurevic G, Stoeter P, Konrad A, Seker B, Gallinat J, Dahmen N, Weinberger DR (2006) COMT genotype predicts bold signal and noise characteristics in prefrontal circuits. Neuroimage 32(4):1722–1732. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.058
Woo JM, Yoon KS, Choi YH, Oh KS, Lee YS, Yu BH (2004) The association between panic disorder and the l/l genotype of catechol-o-methyltransferase. J Psychiatr Res 38(4):365–370. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2004.01.001
Yang B, Chan RC, Jing J, Li T, Sham P, Chen RY (2007) A meta-analysis of association studies between the 10-repeat allele of a Vntr polymorphism in the 3’-Utr of dopamine transporter gene and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 144B(4):541–550. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30453
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KI 537/20-1, 20-3) and SFB 581, KFO 125 and SFB TTR 58 to K.P.L. We would like to thank Nicole Steigerwald and Nicole Döring for their excellent technical assistance in DNA sample processing and genotyping, and U. Buhss for excellent work in processing and analyzing the EMG data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armbruster, D., Mueller, A., Strobel, A. et al. Variation in genes involved in dopamine clearance influence the startle response in older adults. J Neural Transm 118, 1281–1292 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-011-0625-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-011-0625-6