Abstract
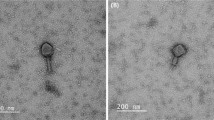
Escherichia coli is an important opportunistic pathogen. It can cause sepsis and severe infection. The application of lytic bacteriophages to treat infectious diseases is an alternative to antibiotics. A lytic Escherichia coli phage, designated IME-EC2, was isolated from hospital sewage. Transmission electron microscopy revealed that IME-EC2 to be a member of the family Podoviridae. It had a 60-nm head and a 15-nm tail. Here, we present the complete genome sequence of this phage, which consists of 41,510 bp with an overall G+C content of 59.2 %. A total of 60 coding sequences (CDS) were identified, and the phage genome does not contain any tRNA genes. Forty percent of the unknown CDSs are unique to IME-EC2. This phage does not show significant similarity to other phages at the DNA level, which suggests that IME-EC2 could be a novel phage. One of the unique features identified in the IME-EC2 genome was a gene coding for a putative colanic-acid-degrading protein, which could allow the phage to degrade bacterial capsule and biofilms. Another unique feature is that IME-EC2 does not contain a terminase small subunit, which suggests that this phage may have a unique packaging mechanism. The present work provides novel information on phages and shows that this lytic phage or its products could be exploited to destroy bacterial biofilms and pathogenic E. coli.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azaïez SRC, Fliss I, Simard RE, Moineau S (1998) Monoclonal antibodies raised against native major capsid proteins of lactococcal c2-like bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4255–4259
Bachrach U, Friedmann A (1971) Practical procedures for the purification of bacterial viruses. Appl Microbiol 22:706–715
Bamford DH, Grimes JM, Stuart DI (2005) What does structure tell us about virus evolution? Curr Opin Struct Biol 15:655–663
Bateman A, Bycroft M (2000) The structure of a LysM domain from E. coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D (MltD). J Mol Biol 299:1113–1119
Brüssow H (2005) Phage therapy: the Escherichia coli experience. Microbiology 151:2133–2140
Briers Y, Volckaert G, Cornelissen A, Lagaert S, Michiels CW, Hertveldt K, Lavigne R (2007) Muralytic activity and modular structure of the endolysins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages φKZ and EL. Mol Microbiol 65:1334–1344
Buist G, Steen A, Kok J, Kuipers OP (2008) LysM, a widely distributed protein motif for binding to (peptido) glycans. Mol Microbiol 68:838–847
Calendar R, Abedon ST (2005) The bacteriophages. Oxford University Press, UK
Catalano C (2000) The terminase enzyme from bacteriophage lambda: a DNA-packaging machine. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 57:128–148
Chibeu A, Ceyssens PJ, Hertveldt K, Volckaert G, Cornelis P, Matthijs S, Lavigne R (2009) The adsorption of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage phiKMV is dependent on expression regulation of type IV pili genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 296:210–218
Darling AE, Mau B, Perna NT (2010) progressiveMauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS One 5:e11147
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard J-F, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M (2008) Phylogeny. fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W465–W469
Donate LE, Herranz L, Secilla JP, Carazo J, Fujisawa H, Carrascosa J (1988) Bacteriophage T3 connector: three-dimensional structure and comparison with other viral head-tail connecting regions. J Mol Biol 201:91–100
Eppler K, Wyckoff E, Goates J, Parr R, Casjens S (1991) Nucleotide sequence of the bacteriophage P22 genes required for DNA packaging. Virology 183:519–538
Foster SJ (1991) Cloning, expression, sequence analysis and biochemical characterization of an autolytic amidase of Bacillus subtilis 168 trpC2. J Gen Microbiol 137:1987–1998
Hambly E, Tétart F, Desplats C, Wilson WH, Krisch HM, Mann NH (2001) A conserved genetic module that encodes the major virion components in both the coliphage T4 and the marine cyanophage S-PM2. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:11411–11416
Hughes K, Sutherland I, Clark J, Jones M (1998) Bacteriophage and associated polysaccharide depolymerases––novel tools for study of bacterial biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 85:583–590
King AM, Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ, Carstens EB (2012) Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Elsevier
Kropinski AM, Waddell T, Meng J, Franklin K, Ackermann H-W, Ahmed R, Mazzocco A, Yates J, Lingohr EJ, Johnson RP (2013) The host-range, genomics and proteomics of Escherichia coli O157: H7 bacteriophage rV5. Virology J 10:76
Lhuillier S, Gallopin M, Gilquin B, Brasilès S, Lancelot N, Letellier G, Gilles M, Dethan G, Orlova EV, Couprie J (2009) Structure of bacteriophage SPP1 head-to-tail connection reveals mechanism for viral DNA gating. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:8507–8512
Li X, Heyer W-D (2008) Homologous recombination in DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance. Cell Res 18:99–113
Liew KW, Alvarez AM (1981) Biological and morphological characterization of Xanthomonas campestris bacteriophages. Phytopathology 71:269–273
Loessner MJ, Krause IB, Henle T, Scherer S (1994) Structural proteins and DNA characteristics of 14 Listeria typing bacteriophages. J Gen Virol 75:701
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:0955–0964
Meyer F, Paarmann D, D’Souza M, Olson R, Glass EM, Kubal M, Paczian T, Rodriguez A, Stevens R, Wilke A (2008) The metagenomics RAST server––a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform 9:386
Miller ES, Kutter E, Mosig G, Arisaka F, Kunisawa T, Rüger W (2003) Bacteriophage T4 genome. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:86–156
Otawa K, Lee SH, Yamazoe A, Onuki M, Satoh H, Mino T (2007) Abundance, diversity, and dynamics of viruses on microorganisms in activated sludge processes. Microb Ecol 53:143–152
Park M, Lee J-H, Shin H, Kim M, Choi J, Kang D-H, Heu S, Ryu S (2012) Characterization and comparative genomic analysis of a novel bacteriophage, SFP10, simultaneously inhibiting both Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli O157: H7. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:58–69
Petrovski S, Seviour RJ, Tillett D (2011) Genome sequence and characterization of the Tsukamurella bacteriophage TPA2. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1389–1398
Petrovski S, Seviour RJ, Tillett D (2013) Genome sequence and characterization of a Rhodococcus equi phage REQ1. Virus genes 46:588–590
Rao VB, Feiss M (2008) The bacteriophage DNA packaging motor. Annu Rev Genet 42:647–681
Saha S, Raghava GP (2007) BTXpred: prediction of bacterial toxins. In Silico Biol 7:405–412
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, vol 1. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp 6.4–6.11
Santos SB, Kropinski AM, Ceyssens P-J, Ackermann H-W, Villegas A, Lavigne R, Krylov VN, Carvalho CM, Ferreira EC, Azeredo J (2011) Genomic and proteomic characterization of the broad-host-range Salmonella phage PVP-SE1: creation of a new phage genus. J Virol 85:11265–11273
Stothard P, Wishart DS (2005) Circular genome visualization and exploration using CGView. Bioinformatics 21:537–539
Valpuesta J, Fujisawa H, Marco S, Carazo J, Carrascosa J (1992) Three-dimensional structure of T3 connector purified from overexpressing bacteria. J Mol Biol 224:103–112
Withey S, Cartmell E, Avery L, Stephenson T (2005) Bacteriophages—potential for application in wastewater treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 339:1–18
Zuber S, Boissin-Delaporte C, Michot L, Iversen C, Diep B, Brüssow H, Breeuwer P (2008) Decreasing Enterobacter sakazakii (Cronobacter spp.) food contamination level with bacteriophages: prospects and problems. Microb Biotechnol 1:532–543
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Hi-Tech Research and Development (863) Program of China (No. 2012AA022003 and No. 2014AA021402), China Mega-Project on Major Drug Development (No. 2011ZX09401-023), China Mega-Project on Infectious Disease Prevention (No. 2013ZX10004-605, No. 2013ZX10004-607, No. 2013ZX10004-217, and No. 2011ZX10004-001) and State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and BioSecurity Program (No. SKLPBS1113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Hua and X. An have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, Y., An, X., Pei, G. et al. Characterization of the morphology and genome of an Escherichia coli podovirus. Arch Virol 159, 3249–3256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2189-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2189-x