Abstract
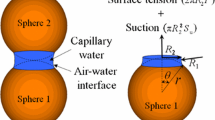
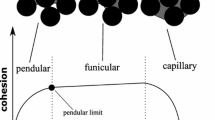
This paper discusses the coupled effects of capillary suction and fabric on the behavior of partially saturated granular materials at pendular state when discrete liquid bridges form around particle contacts. Experimental results show that the soil–water characteristic curves of granular materials are affected by the internal structure formed during reconstitution of the specimen. The effect of capillary suction on the shear strength of moist sand varies with the direction of shearing relative to the bedding plane which is generally perpendicular to the major principal direction of the fabric tensor. When treating capillary attraction as interparticle forces at particle contacts, a micromechanics analysis shows that the coupling between capillary-attracting forces and fabric results in an additional stress tensor, which describes the anisotropic effect of capillary suction on the behavior of moist sand.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso E.E., Gens A., Josa A.: A constitutive model for partially saturated soils. Geotechnique 40(3), 405–430 (1990)
Alonso-Marroquin, F., Luding, S., Herrmann, H.J., Vardoulakis, I.: Role of the anisotropy in the elastoplastic response of a polygonal packing. Phys. Rev. E, 51, 051304, 1–18 (2005)
Baker R., Frydman S.: Unsaturated soil mechanics: critical review of physical foundations. Eng. Geol. 106(1–2), 26–39 (2009)
Benahmed N., Canou J., Dupla J.-C.: Structure initiale et propriétés de liquéfaction statique d’un sable. Comptes Rendus Mecanique—C R MEC 332(11), 887–894 (2004)
Bishop A.W.: The principle of effective stress. Teknisk Ukeblad 106(39), 859–863 (1959)
Cambou, B., Jean, M., Radjaï, F.: Micromechanics of Granular Materials. ISTE Ltd., London, UK (2009)
Cho G.C., Santamarina J.C.: Unsaturated particulate materials—particle-level studies. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 127(1), 84–96 (2001)
Christoffersen J., Mehrabadi M.M., Nemat-Nasser S.J.: A micromechanical description of granular material behavior. J. Appl. Mech. 48, 339–344 (1981)
Coleman J.D.: Stress strain relations for partly saturated soil. Correspondence. Geotechnique 12(4), 348–350 (1962)
Fredlund D.G., Morgenstern N.R.: Stress state variables and unsaturated soils. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. ASCE 103(GT5), 447–466 (1977)
Gili J.A., Alonso E.E.: Microstructural deformation mechanisms of unsaturated granular soils. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 26, 433–468 (2002)
Guo P.: Modified direct shear test for anisotropic strength of sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron Eng. 134(9), 1311–1318 (2008)
Guo P., Stolle D.F.E.: On the failure of granular materials with fabric effects. Soils Found. 45(4), 1–12 (2005)
Hicher P.-Y., Chang C.S.: A microstructural elastoplastic model for unsaturated granular materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 2304–2323 (2007)
Higo Y., Oka F., Kimoto S., Sanagawa T., Matsushima Y.: Study of strain localization and microstructure changes in partially saturated sand during triaxial tests using microfocus X-ray CT. Soils Found. 51(1), 95–111 (2011)
Houlsby G.T.: The work input to an unsaturated granular material. Geotechnique 47(1), 193–196 (1997)
Ishihara, K.: Liquefaction and flow failure during earthquakes. Geotechnique 43(3), 351–415 (1993)
Kanatani K.: Distribution of directional data and fabric tensors. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 22, 149–164 (1984)
Kawai K., Karube D., Kato S.: The model of water retention curve considering effects of void ratio. In: Rahardjo, H., Toll, D.G., Leong, E.C. (eds) Unsaturated Soils for Asia, pp. 329–334. Balkema, Rotterdam (2000)
Koliji A., Laloui L., Cuisinier O., Vulliet L.: Suction induced effects on the fabric of a structured soil. Trans. Porous Med. 64, 261–278 (2006)
Kruyt N.P.: Contact forces in anisotropic frictional granular materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40, 3537–3556 (2003)
Lewis R.W., Schrefler B.A.: The Finite Element Method in the Deformation and Consolidation of Porous Media. Wiley, Chichester (1987)
Li X.S.: Effective stress in unsaturated soil: a microstructural analysis. Geotechnique 53(2), 273–277 (2003)
Likos W.J., Lu N.: Hysteresis of capillary stress in unsaturated granular soil. J. Eng. Mech. 130(6), 646–655 (2004)
Masin D.: Predicting the dependency of a degree of saturation on void ratio and suction using effective stress principle for unsaturated soils. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 34, 73–90 (2010)
Mulilis J.P., Seed H.B., Chan C.K., Mitchell J.K., Arulanandan K.: Effects of sample preparation on sand liquefaction. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. ASCE 103(2), 91–108 (1977)
Mitarai N., Nori F.: Wet granular materials. Adv. Phys. 55(1–2), 1–45 (2006)
Mani R., Kadau D., Herrmann H.J.: liquid migration in sheared unsaturated granular media. Granul. Matter 15(4), 447–454 (2013)
Nemat-Masset S.: A micromechanically-based constitutive model for frictional deformation of granular materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48, 1541–1563 (2000)
Nuth M., Laloui L.: Advances in modelling hysteretic water retention curve in deformable soils. Comput. Geotech. 35(6), 835–844 (2008)
Oda M.: Co-ordination number and its relation to shear strength of granular material. Soils Found. 17(2), 29–42 (1977)
Ouadfel H., Rothenburg L.: Stress-force-fabric relationship for assemblies of ellipsoids. Mech. Mater. 33(4), 201–221 (2001)
Pietruszczak S., Mroz Z.: On failure criteria for anisotropic cohesive-frictional materials. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 25, 509–524 (2001)
Pietruszczak S., Mroz Z.: Formulation of anisotropic failure criteria incorporating a microstructure tensor. Comput. Geotech. 26, 105–112 (2000)
Pietruszczak S., Pande G.N.: On the mechanics of partially saturated soils. Comput. Geotech. 12, 55–71 (1991)
Radjaï, F.: Particle-scale origins of shear strength in granular media. In: Evolution, vol. 1. Van Nostrand Reinhold, p. ix, 290. http://arxiv.org/abs/0810.4722 (2008)
Radjaï F., Richefeu V.: Bond anisotropy and cohesion of wet granular materials. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 136(1909), 5123–5138 (2009)
Radjaï F., Troadec H., Roux S.: Key features of granular plasticity. In: Antony, S.J., Hoyle, W., Ding, Y. (eds.) Granular Materials: Fundamentals and Applications, pp. 157–184. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge (2004)
Richefeu, V., El Youssoufi, M.S., Radjaï, F.: Shear strength properties of wet granular materials. Phys. Rev. E 73, 051304, 1–11 (2006)
Richefeu V., El Youssoufi M.S., Azéma E., Radjaï F.: Force transmission in dry and wet granular media. Powder Technol. 190(1), 258–263 (2009)
Rothenburg L., Bathurst R.J.: Analytical study of induced anisotropy in idealized granular materials. Géotechnique 39(4), 601–614 (1989)
Satake M.: Fabric tensor in granular materials. In: Vermeer, P.A., Luger, H.J. (eds.) Deformation and Failure of Granular Materials, pp. 63–68. Balkema, Rotterdam (1982)
Scholtès L., Hicher P.-Y., Chareyre B., Nicot F., Darve F.: On the capillary stress tensor in wet granular materials. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 33(10), 1289–1313 (2009)
Scholtès L., Chareyre B., Nicot F., Darve F.: Micromechanics of granular materials with capillary effects. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 47(1), 64–75 (2009)
Scholtès L., Chareyre B., Nicot F., Darve F.: Discrete modelling of capillary mechanisms in multi-phase granular media. Comput. Modeling Eng. Sci. 52(3), 297–318 (2009)
Simms P.H., Yanful E.K.: Measurement and estimation of pore shrinkage and pore distribution in a clayey till during soil-water characteristic curve tests. Can. Geotech. J. 38(4), 741–754 (2001)
Thomson P.R., Wong R.C.K.: Specimen nonuniformities in water-pluviated and moist-tamped sands under undrained triaxial compression and extension. Can. Geotech. J. 45(7), 939–956 (2008)
Thornton C.: Numerical simulation of deviatoric shear deformation of granular media. Géotechnique 50(1), 43–53 (2000)
Tokunaga, T.K., Olson, K.R., Wan, J.: Conditions necessary for capillary hysteresis in porous media: tests of grain-size and surface tension influences. Water Resour. Res. W05111, doi:10.1029/2003WR002908 (2004)
Wang J., Dove J.E., Gutierrez M.S.: Discrete-continuum analysis of shear banding in the direct shear test. Géotechnique 57(6), 513–526 (2007)
Zhou, A.N., Sheng, D., Carter, J.P.: Modelling the dependency of soil-water characteristic curves on initial density. In: Jotisankas, A., Sawangsuriya, A., Soralump, S., Mairaing, W. (eds.) Unsaturated Soils: Theory and Practice 2011, pp. 385–390. Kasetsart University, Thailand (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, P. Coupled effects of capillary suction and fabric on the strength of moist granular materials. Acta Mech 225, 2261–2275 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-014-1124-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-014-1124-2