Abstract
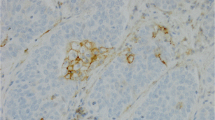
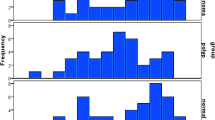
Survivin is expressed in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of various types of malignant tumor cells. Cytoplasmic survivin functions as an apoptosis inhibitor, while nuclear survivin is indispensable for complete mitosis completion. To investigate the effect of cigarette smoking on the survivin expression in lung adenocarcinomas at the early developmental stage, we examined the expression of nuclear and cytoplasmic survivin in pathological Stage IA lung adenocarcinomas resected from 38 non-smokers and 44 smokers (current smokers and ex-smokers) using an immunohistochemical method. Labeling indices of nuclear survivin in tumors of smokers were significantly greater than those of non-smokers. The labeling index of nuclear survivin was above 3 % in only 1 (2.6 %) of the 38 tumors of the non-smokers, while the labeling indices in 19 (43.2 %) of 44 tumors of the smokers were above 3 % with a significantly greater frequency. There was no significant difference in the labeling index of nuclear survivin between current smokers and ex-smokers. There was no significant difference in the labeling index of cytoplasmic survivin between tumors of the non-smokers and the smokers. The present results show that cigarette smoking is associated with the higher nuclear surviving expression in lung adenocarcinomas at the early stage, suggesting that cigarette smoking affects the nuclear survivin expression in lung adenocarcinomas at the early developmental stage.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NES:
-
Nuclear export signal
References
Li F, Yang J, Ramnath N, Javle MM, Tan D (2005) Nuclear or cytoplasmic expression of survivin: What is the significance? Int J Cancer 114:509–512
Li F, Ling X (2006) Survivin study: an update of “what is the next wave”? J Cell Physiol 208:476–486
Stauber RH, Mann W, Knauer SK (2007) Nuclear and cytoplasmic survivin: molecular mechanism, prognostic, and therapeutic potential. Cancer Res 67:5999–6002
Devesa SS, Bray F, Vizcaino AP, Parkin DM (2005) International lung cancer trends by histologic type: male:female differences diminishing and adenocarcinoma rates rising. Int J Cancer 117:294–299
Khuder SA (2001) Effect of cigarette smoking on major histological types of lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 31:39–48
Dasgupta P, Kinkade R, Joshi B, Decook C, Haura E, Chellappan S (2006) Nicotine inhibits apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs by up-regulating XIAP and survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6332–6337
Jin Q, Menter DG, Mao L, Hong WK, Lee HY (2008) Survivin expression in normal human bronchial epithelial cells: an early and critical step in tumorigenesis induced by tobacco exposure. Carcinogenesis 29:1614–1622
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V, Sobin L, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer International Staging Committee, Participating Institutions (2007) The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (7th) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol 2:706–714
Maeda R, Yoshida J, Ishii G, Hishida T, Nishimura M, Nagai K (2012) Influence of cigarette smoking on survival and tumor invasiveness in clinical stage IA lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg 93:1626–1632
Shinohara ET, Gonzalez A, Massion PP, Chen H, Li M, Freyer AS, Olson SJ, Andersen JJ, Shyr Y, Carbone DP, Johnson DH, Hallahan DE, Lu B (2005) Nuclear survivin predicts recurrence and poor survival in patients with resected nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 103:1685–1692
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirano, H., Maeda, H., Takeuchi, Y. et al. Association of cigarette smoking with the expression of nuclear survivin in pathological Stage IA lung adenocarcinomas. Med Mol Morphol 47, 196–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-013-0061-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-013-0061-9