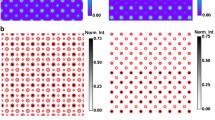
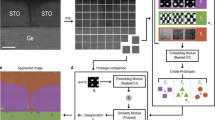
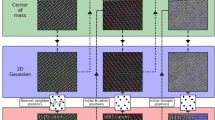
Abstract
In the fields of nanoscience and nanotechnology, it is important to be able to functionalize surfaces chemically for a wide variety of applications. Scanning tunneling microscopes (STMs) are important instruments in this area used to measure the surface structure and chemistry with better than molecular resolution. Self-assembly is frequently used to create monolayers that redefine the surface chemistry in just a single-molecule-thick layer (Love et al. in Chem Rev 105(4):1103–1170, 2005; Nuzzo and Allara in J Am Chem Soc 105(13):4481–4483, 1983; Smith et al. in Prog Surf Sci 75(1):1–68, 2004). Indeed, STM images reveal rich information about the structure of self-assembled monolayers since they convey chemical and physical properties of the studied material. In order to assist in and to enhance the analysis of STM and other images (Thomas et al. in ACS Nano 10(5):5446–5451, 2016; Thomas et al. in ACS Nano 9(5):4734–4742, 2015), we propose and demonstrate an image processing framework that produces two image segmentations: One is based on intensities (apparent heights in STM images) and the other is based on textural patterns. The proposed framework begins with a cartoon + texture decomposition, which separates an image into its cartoon and texture components. Afterward, the cartoon image is segmented by a modified multiphase version of the local Chan–Vese model (Wang et al. in Pattern Recognit 43(3):603–618, 2010), while the texture image is segmented by a combination of 2D empirical wavelet transform and a clustering algorithm. Overall, our proposed framework contains several new features, specifically in presenting a new application of cartoon + texture decomposition and of the empirical wavelet transforms and in developing a specialized framework to segment STM images and other data. To demonstrate the potential of our approach, we apply it to raw STM images of various monolayers and present their corresponding segmentation results.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosio L, Tortorelli VM (1990) Approximation of functional depending on jumps by elliptic functional via t-convergence. Commun Pure Appl Math 43(8):999–1036
Arivazhagan S, Ganesan L (2003) Texture segmentation using wavelet transform. Pattern Recognit Lett 24(16):3197–3203
Arivazhagan S, Ganesan L, Kumar TS (2006) Texture classification using curvelet statistical and co-occurrence features. In: ICPR 2006. 18th international conference on pattern recognition, 2006, vol 2, pp 938–941. IEEE
Arthur D, Vassilvitskii S (2007) K-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. In: Proceedings of the 18th annual ACM-SIAM symposium on discrete algorithms
Averbuch A, Coifman RR, Donoho DL, Elad M, Israeli M (2006) Fast and accurate polar Fourier transform. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 21(2):145–167
Averbuch A, Coifman RR, Donoho DL, Israeli M, Shkolnisky Y (2008) A framework for discrete integral transformations I-the pseudopolar Fourier transform. SIAM J Sci Comput 30(2):764–784
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, Peleato B, Eckstein J et al (2011) Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found Trends® Mach Learn 3(1):1–122
Buades A, Le T, Morel JM, Vese L (2011) Cartoon + texture image decomposition. Image processing on line 1
Buades A, Lisani JL (2016) Directional filters for cartoon + texture image decomposition. Image Process Line 6:75–88
Buades A, Lisani JL (2016) Directional filters for color cartoon + texture image and video decomposition. J Math Imag Vis 55(1):125–135
Bumm LA, Arnold JJ, Cygan MT, Dunbar TD, Burgin TP, Jones L, Allara DL, Tour JM, Weiss PS (1996) Are single molecular wires conducting? Science 271:1705–1707
Candes E, Demanet L, Donoho D, Ying L (2006) Fast discrete curvelet transforms. Multiscale Model Simul 5(3):861–899
Candes EJ, Donoho DL (2005) Continuous curvelet transform: I. Resolution of the wavefront set. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 19(2):162–197
Chambolle A (2004) An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications. J Math Imag Vis 20(1):89–97
Chan TF, Esedoglu S (2005) Aspects of total variation regularized \({L}_1\) function approximation. SIAM J Appl Math 65:1817–1837
Chan TF, Sandberg BY, Vese LA (2000) Active contours without edges for vector-valued images. J Vis Commun Image Represent 11(2):130–141
Claridge SA, Liao WS, Thomas JC, Zhao Y, Cao HH, Cheunkar S, Serino AC, Andrews AM, Weiss PS (2013) From the bottom up: dimensional control and characterization in molecular monolayers. Chem Soc Rev 42(7):2725–2745
Dameron AA, Charles LF, Weiss PS (2005) Structures and displacement of 1-adamantanethiol self-assembled monolayers on Au 111. J Am Chem Soc 127(24):8697–8704
Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D (2014) Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62(3):531–544
Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D (2015) Two-dimensional variational mode decomposition. In: International workshop on energy minimization methods in computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 197–208. Springer
Dunn D, Higgins WE (1995) Optimal gabor filters for texture segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 4(7):947–964
Dunn D, Higgins WE, Wakeley J (1994) Texture segmentation using 2-d gabor elementary functions. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 16(2):130–149
Dunn D.F, Higgins W.E (1993) Optimal gabor-filter design for texture segmentation. In: 1993 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 1993. ICASSP-93., vol 5, pp 37–40. IEEE
Esedoglu S, Tsai YHR (2006) Threshold dynamics for the piecewise constant Mumford-Shah functional. J Comput Phys 211(1):367–384
Fowlkes C, Belongie S, Chung F, Malik J (2004) Spectral grouping using the Nyström method. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(2):214–225
Gabay D, Mercier B (1976) A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximation. Comput Math Appl 2(1):17–40
Garcia-Cardona C, Merkurjev E, Bertozzi AL, Flenner A, Percus AG (2014) Multiclass data segmentation using diffuse interface methods on graphs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 36(8):1600–1613
Gethers ML, Thomas JC, Jiang S, Weiss NO, Duan X, Goddard WA III, Weiss PS (2015) Holey graphene as a weed barrier for molecules. ACS Nano 9(11):10909–10915
Getreuer P (2012) Chan-Vese segmentation. Image Process Line 2:214–224
Gilles J (2013) Empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Signal Process 61(16):3999–4010. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2013.2265222
Gilles J, Heal K (2014) A parameterless scale-space approach to find meaningful modes in histograms-application to image and spectrum segmentation. Int J Wavel Multiresolut Inf Process 12(6):14500441–145004417. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219691314500441
Gilles J, Tran G, Osher S (2014) 2D empirical transforms. Wavelets, ridgelets and curvelets revisited. SIAM J Imag Sci 7(1):157–186. https://doi.org/10.1137/130923774
Glowinski R, Marroco A (1975) Sur l’approximation, par éléments finis d’ordre un, et la résolution, par pénalisation-dualité d’une classe de problèmes de dirichlet non linéaires. Revue française d’automatique, informatique, recherche opérationnelle. Analyse numérique 9(R2): 41–76
Gooding JJ, Mearns F, Yang W, Liu J (2003) Self-assembled monolayers into the 21st century: recent advances and applications. Electroanalysis 15(2):81–96
Guttentag AI, Barr KK, Song TB, Bui KV, Fauman JN, Torres LF, Kes DD, Ciomaga A, Gilles J, Sullivan NF, Yang Y, Allara DL, Zharnikov M, Weiss PS (2016) Hexagons to ribbons: flipping cyanide on Au \(\{\)111\(\}\). J Am Chem Soc 138(48):15580–15586
Guttentag AI, Wachter T, Barr KK, Abendroth JM, Song TB, Sullivan NF, Yang Y, Allara DL, Zharnikov M, Weiss PS (2016) Surface structure and electron transfer dynamics of the self-assembly of cyanide on Au \(\{\)111\(\}\). J Phys Chem C 120(47):26736–26746
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I (1973) Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 3(6):610–621
Huang Y, De Bortoli V, Zhou F, Gilles J (2018) Review of wavelet-based unsupervised texture segmentation, advantage of adaptive wavelets. IET Image Process 12(9):1626–1638
Jain AK, Farrokhnia F (1991) Unsupervised texture segmentation using gabor filters. Pattern Recognit 24(12):1167–1186
Kim M, Hohman JN, Cao Y, Houk KN, Ma H, Jen AKY, Weiss PS (2011) Creating favorable geometries for directing organic photoreactions in alkanethiolate monolayers. Science 331(6022):1312–1315
Kim M, Hohman JN, Serino AC, Weiss PS (2010) Structural manipulation of hydrogen-bonding networks in amide-containing alkanethiolate monolayers via electrochemical processing. J Phys Chem C 114(46):19744–19751
Labate D, Lim W-Q, Kutyniok G, Weiss G (2005) Sparse multidimensional representation using shearlets. In: Wavelets XI, vol 5914. International Society for Optics and Photonics
Love JC, Estroff LA, Kriebel JK, Nuzzo RG, Whitesides GM (2005) Self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on metals as a form of nanotechnology. Chem Rev 105(4):1103–1170
March R (1992) Visual reconstruction with discontinuities using variational methods. Image Vis Comput 10(1):30–38
Merkurjev E, Garcia-Cardona C, Bertozzi AL, Flenner A, Percus AG (2014) Diffuse interface methods for multiclass segmentation of high-dimensional data. Appl Math Lett 33:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aml.2014.02.008
Merriman B, Bence J.K, Osher S (1992) Diffusion generated motion by mean curvature. In: Proceedings of the geometry center workshop
Merriman B, Bence JK, Osher SJ (1994) Motion of multiple junctions: a level set approach. J Comput Phys 112(2):334–363
Meyer Y (2001) Oscillating Patterns in Image Processing and Nonlinear Evolution Equations: The Fifteenth Dean Jacqueline B. Lewis Memorial Lectures. American Mathematical Society, Boston, MA, US
Modica L (1987) The gradient theory of phase transitions and the minimal interface criterion. Arch Ration Mech Anal 98(2):123–142
Modica L, Mortola S (1977) Un esempio di \(\Gamma\)-convergenza. Bollettino della Unione Matematica Italiana B 14(5):285–299
Mumford D, Shah J (1989) Optimal approximations by piecewise smooth functions and associated variational problems. Commun Pure Appl Math 42(5):577–685
Nuzzo RG, Allara DL (1983) Adsorption of bifunctional organic disulfides on gold surfaces. J Am Chem Soc 105(13):4481–4483
Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Maenpaa T (2002) Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(7):971–987
Osher S, Sethian JA (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79(1):12–49
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9(1):62–66
Poirier GE (1997) Characterization of organosulfur molecular monolayers on Au (111) using scanning tunneling microscopy. Chem Rev 97(4):1117–1128
Rudin LI, Osher S, Fatemi E (1992) Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenom 60(1–4):259–268
Shen L, Yin Q (2009) Texture classification using curvelet transform. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on information processing (ISIP09), pp 319–324. Citeseer
Smith RK, Lewis PA, Weiss PS (2004) Patterning self-assembled monolayers. Progress Surf Sci 75(1):1–68
Strang G (1993) Wavelet transforms versus fourier transforms. Bull Am Math Soc 28(2):288–305
Thomas JC, Goronzy DP, Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D, Gilles J, Osher SJ, Bertozzi AL, Weiss PS (2016) Mapping buried hydrogen-bonding networks. ACS Nano 10(5):5446–5451
Thomas JC, Goronzy DP, Serino AC, Auluck HS, Irving OR, Jimenez-Izal E, Deirmenjian JM, Machacek J, Sautet P, Alexandrova AN et al (2018) Acid-base control of valency within carboranedithiol self-assembled monolayers: molecules do the can-can. ACS Nano 12(3):2211–2221
Thomas JC, Schwartz JJ, Hohman JN, Claridge SA, Auluck HS, Serino AC, Spokoyny AM, Tran G, Kelly KF, Mirkin CA, Gilles J, Osher SJ, Weiss PS (2015) Defect-tolerant aligned dipoles within two-dimensional plastic lattices. ACS Nano 9(5):4734–4742
Unser M (1995) Texture classification and segmentation using wavelet frames. IEEE Trans Image Process 4(11):1549–1560
Vese LA, Chan TF (1997) Reduced non-convex functional approximations for image restoration and segmentation. UCLA CAM Reports pp 97–56
Vese LA, Chan TF (2002) A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and Shah model. Int J Comput Vis 50(3):271–293
Wang XF, Huang DS, Xu H (2010) An efficient local Chan-Vese model for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit 43(3):603–618
Weldon TP, Higgins WE, Dunn DF (1996) Efficient gabor filter design for texture segmentation. Pattern Recognit 29(12):2005–2015
Yugay D, Goronzy DP, Kawakami LM, Claridge SA, Song TB, Yan Z, Xie YH, Gilles J, Yang Y, Weiss PS (2016) Copper ion binding site in \(\beta\)-amyloid peptide. Nano Lett 16(10):6282–6289
Zhang H, Fritts J.E, Goldman S.A (2003) An entropy-based objective evaluation method for image segmentation. In: Storage and Retrieval Methods and Applications for Multimedia 2004, vol 5307, pp. 38–50. International Society for Optics and Photonics
Zhang H, Fritts JE, Goldman SA (2008) Image segmentation evaluation: a survey of unsupervised methods. Comput Vis Image Underst 110(2):260–280
Zosso D, An J, Stevick J, Takaki N, Weiss M, Slaughter LS, Cao HH, Weiss PS, Bertozzi AL (2017) Image segmentation with dynamic artifacts detection and bias correction. Inverse Probl Imaging 11(3):577–600
Zosso D, Dragomiretskiy K, Bertozzi AL, Weiss PS (2017) Two-dimensional compact variational mode decomposition. J Math Image Vis 58(2):294–320
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the W.M. Keck Foundation Center for Leveraging Sparsity. The self-assembly and STM imaging were supported by the US Department of Energy (Grant #DE-SC-1037004). L. Torres Mandiola was partially supported by NSF DMS-1312361. K. Bui, J. Fauman, and D. Kes were partially supported by NSF DMS-1045536. A. Bertozzi was supported by Simons Math + X Investigator Award Number 510776. The authors thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments in improving the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bui, K., Fauman, J., Kes, D. et al. Segmentation of scanning tunneling microscopy images using variational methods and empirical wavelets. Pattern Anal Applic 23, 625–651 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-019-00824-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-019-00824-0