Abstract
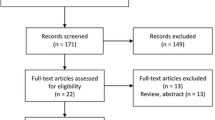
In rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, cardiovascular disease is frequently one of the leading causes of mortality or morbidity. Studies have shown that acute systemic inflammation and chronic systemic vasculitis are associated with endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerotic plaque formation, subsequently leading to cardiovascular disease. This meta-analysis aimed to explore the association of subclinical atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. A comprehensive search of the MEDLINE and Embase databases was performed from date of inception through August 2017. The inclusion criterion was observational studies evaluating the association between primary Sjogren’s syndrome, subclinical atherosclerosis, and arterial stiffness by measuring pulse wave velocity (PWV) and intima–media thickness (IMT). Definitions of PSS and methods to assess PWV and IMT were recorded for each study. Different locations of IMT were evaluated including common carotid, internal carotid, and femoral arteries. The pooled mean difference (MD) of PWV and IMT and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated using a random-effect meta-analysis. The between-study heterogeneity of effect size was quantified using the Q statistic and I2. Data were extracted from eight observational studies involving 767 subjects. Pooled result demonstrated a significant increase in PWV in patients who have PSS compared with controls (MD = 1.30 m/s; 95% CI 0.48–2.12; p value = 0.002; I2 = 85%). Patients with PSS also have higher IMT (MD = 0.08 mm; 95% CI 0.04–0.11; p value < 0.01; I2 = 72%). Our study suggests that PSS is associated with arterial stiffness and subclinical atherosclerosis. Further studies need to be conducted to find the correlation of subclinical atherosclerosis in PSS with the cardiovascular event, the pathophysiological changes of arterial stiffness in PSS, and the benefit of statins, because controlling cardiovascular risk factors or disease activity could potentially help avoid progression of atherosclerosis to overt cardiovascular disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gyongyosi M, Pokorny G, Jambrik Z, Kovacs L, Kovacs A, Makula E, Csanady M (1996) Cardiac manifestations in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 55(7):450–454
Sung MJ, Park SH, Kim SK, Lee YS, Park CY, Choe JY (2011) Complete atrioventricular block in adult Sjogren's syndrome with anti-Ro autoantibody. Korean J Intern Med 26(2):213–215
Scofield RH (2011) Vasculitis in Sjogren's syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep 13(6):482–488
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283(15):2008–2012
Shiboski SC, Shiboski CH, Criswell L, Baer A, Challacombe S, Lanfranchi H et al (2012) American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjogren's syndrome: a data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjogren's International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64(4):475–487
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE et al (2002) Classification criteria for Sjogren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European consensus group. Ann Rheum Dis 61(6):554–558
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25(9):603–605
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13
Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T (2014) Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol 14:135
Higgins JPT, Green S (eds) (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from http://handbook.cochrane.org
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Sterne JA, Egger M (2001) Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. J Clin Epidemiol 54(10):1046–1055
Akyel A, Tavil Y, Yayla C, Tufan A, Kaya A, Tezcan ME, Ozturk MA, Boyaci B (2012) Endothelial dysfunction in primary Sjogren syndrome. West Indian Med J 61(9):870–872
Atzeni F, Sarzi-Puttini P, Signorello MC, Gianturco L, Stella D, Boccassini L et al (2014) New parameters for identifying subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome: a pilot study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32(3):361–368
Gravani F, Papadaki I, Antypa E, Nezos A, Masselou K, Ioakeimidis D, Koutsilieris M, Moutsopoulos HM, Mavragani CP (2015) Subclinical atherosclerosis and impaired bone health in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome: prevalence, clinical and laboratory associations. Arthritis Res Ther 17(1):99
Sabio JM, Sanchez-Berna I, Martinez-Bordonado J, Vargas-Hitos JA, Navarrete-Navarrete N, Exposito Ruiz M et al (2015) Prevalence of and factors associated with increased arterial stiffness in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 67(4):554–562
Vaudo G, Bocci EB, Shoenfeld Y, Schillaci G, Wu R, Del Papa N et al (2005) Precocious intima-media thickening in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 52(12):3890–3897
Zardi EM, Basta F, Afeltra A (2016) Levels of vitamin D, disease activity and subclinical atherosclerosis in post-menopausal women with Sjogren's syndrome: does a link exist? In Vivo 30(5):721–725
Zardi EM, Sambataro G, Basta F, Margiotta DP, Afeltra AM (2014) Subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in elderly patients with primary Sjogren syndrome: a duplex Doppler sonographic study. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 27(4):645–651
Sezis Demirci M, Karabulut G, Gungor O, Celtik A, Ok E, Kabasakal YI (2016) There an increased arterial stiffness in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome? Intern Med 55(5):455–459
Valim V, Gerdts E, Jonsson R, Ferreira GA, Brokstad KA, Brun JG et al (2016) Atherosclerosis in Sjogren's syndrome: evidence, possible mechanisms and knowledge gaps. Clin Exp Rheumatol 34(1):133–142
Rongen GA, van Ingen I, Kok M, Vonkeman H, Janssen M, Jansen TL (2018) Vasodilator function worsens after cessation of tumour necrosis factor inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis only if a flare occurs. Clin Rheumatol 37(4):909–916
Izzo JL Jr (2004) Arterial stiffness and the systolic hypertension syndrome. Curr Opin Cardiol 19(4):341–352
Davies JI, Struthers AD (2003) Pulse wave analysis and pulse wave velocity: a critical review of their strengths and weaknesses. J Hypertens 21(3):463–472
Mattace-Raso FU, van der Cammen TJ, Hofman A, van Popele NM, Bos ML, Schalekamp MA et al (2006) Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: the Rotterdam study. Circulation 113(5):657–663
Imura T, Yamamoto K, Kanamori K, Mikami T, Yasuda H (1986) Non-invasive ultrasonic measurement of the elastic properties of the human abdominal aorta. Cardiovasc Res 20(3):208–214
Kurum T, Yildiz M, Soy M, Ozbay G, Alimgil L, Tuzun B (2005) Arterial distensibility as determined by carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity in patients with Behcet's disease. Clin Rheumatol 24(2):134–138
Chiang CH, Liu CJ, Chen PJ, Huang CC, Hsu CY, Chan WL, Huang PH, Chen TJ, Lin SJ, Chen JW, Leu HB (2014) Primary Sjogren's syndrome and risk of ischemic stroke: a nationwide study. Clin Rheumatol 33(7):931–937
Chiang CH, Liu CJ, Chen PJ, Leu HB, Hsu CY, Huang PH et al (2013) Primary Sjogren's syndrome and the risk of acute myocardial infarction: a nationwide study. Zhonghua Minguo Xin Zang Xue Hui Za Zhi 29(2):124–131
Kang JH, Lin HC (2010) Comorbidities in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome: a registry-based case-control study. J Rheumatol 37(6):1188–1194
Ramagopalan SV, Pakpoor J, Seminog O, Goldacre R, Graham L, Goldacre MJ (2013) Risk of subarachnoid haemorrhage in people admitted to hospital with selected immune-mediated diseases: record-linkage studies. BMC Neurol 13:176
Zoller B, Li X, Sundquist J, Sundquist K (2012) Risk of subsequent ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in patients hospitalized for immune-mediated diseases: a nationwide follow-up study from Sweden. BMC Neurol 12:41
Bartoloni E, Baldini C, Schillaci G, Quartuccio L, Priori R, Carubbi F, Bini V, Alunno A, Bombardieri S, de Vita S, Valesini G, Giacomelli R, Gerli R (2015) Cardiovascular disease risk burden in primary Sjogren's syndrome: results of a population-based multicentre cohort study. J Intern Med 278(2):185–192
Hansson GK (2005) Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 352(16):1685–1695
Krasnokutsky S, Romero AG, Bang D, Pike VC, Shah B, Igel TF, Dektiarev I, Guo Y, Zhong J, Katz SD, Pillinger MH (2018) Impaired arterial responsiveness in untreated gout patients compared with healthy non-gout controls: association with serum urate and C-reactive protein. Clin Rheumatol 37(7):1903–1911
Biesbroek PS, Heslinga SC, van de Ven PM, Peters MJL, Amier RP, Konings TC, Maroules CD, Ayers C, Joshi PH, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van Halm VP, van Rossum AC, Nurmohamed MT, Nijveldt R (2018) Assessment of aortic stiffness in patients with ankylosing spondylitis using cardiovascular magnetic resonance. In: Clin Rheumatol, vol 37, pp 2151–2159
Cicek OF, Bayram NA, Ayhan H, Erten S, Aslan AN, Sari C et al (2014) Assessment of the relationship between aortic stiffness and left ventricular functions with echocardiography in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Int J Rheum Dis 17(6):658–663
Mariette X, Criswell LA (2018) Primary Sjogren's syndrome. N Engl J Med 378(10):931–939
Nocturne G, Cornec D, Seror R, Mariette X (2016) Use of biologics in Sjogren's syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 42(3):407–417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 11 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yong, W.C., Sanguankeo, A. & Upala, S. Association between primary Sjogren’s syndrome, arterial stiffness, and subclinical atherosclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 38, 447–455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4265-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4265-1