Abstract
Objectives
Our aim was to investigate the prevalence value of a high-avidity antinuclear antibody (ANA) of the IgG isotype (HA IgG ANA) compared with that of ANAs of other isotypes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to assess the associations of HA IgG ANA with the activity of SLE and lupus nephritis.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed clinical and laboratory data from subjects. Blood samples were acquired from 101 SLE patients, 67 patients with other autoimmune diseases, and 65 healthy donors. The levels of HA IgG ANA and other isotype ANAs were measured by indirect immunofluorescence (IIF). The prevalence and diagnosis value of HA IgG ANA and other antibodies in SLE patient were tested. The advantage of HA IgG ANA compared with HA anti-dsDNA antibodies IgG (HA dsDNA IgG) was verified by ELISA. We monitored the relative avidity indexes (RAIs) of HA IgG ANA and HA dsDNA IgG at 3 time points after the start of treatment in the same individuals with SLE.
Results
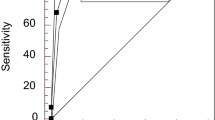
The prevalence of HA IgG ANA was significantly higher in active cases than in inactive cases of SLE and LN, which is consistent with data for IgG ANAs, anti-dsDNA IgG antibodies, low C3 levels, low C4 levels, and anti-C1q antibodies. HA IgG ANA showed moderate sensitivity and specificity (80% and 81.3%) for discriminating active and inactive SLE cases. However, HA IgG ANA showed no significant differences among the different clinical manifestations of SLE. Compared with that of HA dsDNA IgG, the RAI of HA IgG ANA was positively related to SLEDAI scores after treatment at 0, 1, and 3 months (r = 0.6813, p = 0.0026; r = 0.5972, p = 0.0114; r = 0.4817, p = 0.0474).
Conclusions
First, we demonstrated that HA IgG ANA was a reliable diagnostic tool in SLE patients. Furthermore, HA IgG ANA was supposed to be more appropriate for identifying the activity of SLE compared with HA dsDNA IgG. In summary, HA IgG ANA may be a new biomarker for diagnosing SLE and identifying SLE activity.
Key Points • We first introduced the concept of a “high-avidity IgG ANA (HA IgG ANA)” that could distinguish between the early stage of SLE and SLE that had been active for some time. • The relative avidity indexes (RAIs) of HA IgG ANA and HA dsDNA IgG were presented and applied here to evaluate the avidities of antibodies involved in SLE. • In our study, we confirmed the value of HA IgG ANA in diagnosing SLE. In addition, HA IgG ANA was more appropriate for identifying the activity of SLE than was HA dsDNA IgG. • In conclusion, HA IgG ANA could be a potential biomarker for the assessment of the prognosis of SLE activity. |


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damoiseaux J, Andrade LEC, Carballo OG, Conrad K, Francescantonio PLC, Fritzler MJ, de la Torre IG, Herold M, Klotz W, Cruvinel WD, Mimori T, von Muhlen C, Satoh M, Chan EK (2019) Clinical relevance of HEp-2 indirect immunofluorescent patterns: the International Consensus on ANA patterns (ICAP) perspective. Ann Rheum Dis 78(7):879–889
Aringer M, Costenbader KH, Brinks R, Boumpas D, Daikh D, Jayne D, Kamen D, Mosca M, Ramseygoldman R, Smolen JS (2018) OP0020 Validation of new systemic lupus erythematosus classification criteria. Annual European Congress of Rheumatology, EULAR 2018, Amsterdam, 13–16 June 2018; 2018
Swaak T, Smeenk R (1985) Detection of anti-DSDNA as a diagnostic tool - a prospective study in 441 non-systemic lupus-erythematosus patients anti-DSDNA antibody (anti-DSDNA). Ann Rheum Dis 44(4):245–251
Lopez-Hoyos M, Cabeza R, Martinez-Taboada VM, Crespo J, SanSegundo D, Blanco R, Lopez-Escribano H, Pena M, Rodriguez-Valverde V (2005) Clinical disease activity and titers of anti-dsDNA antibodies measured by an automated immunofluorescence assay in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 14(7):505–509
Compagno M, Jacobsen S, Rekvig OP, Truedsson L, Heegaard NH, Nossent J, Jonsen A, Jacobsen RS, Eilertsen GO, Sturfelt G, Bengtsson AA (2013) Low diagnostic and predictive value of anti-dsDNA antibodies in unselected patients with recent onset of rheumatic symptoms: results from a long-term follow-up Scandinavian multicentre study. Scand J Rheumatol 42(4):311–316
Arbuckle MR, James JA, Kohlhase KF, Rubertone MV, Dennis GJ, Harley JB (2001) Development of anti-dsDNA autoantibodies prior to clinical diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol 54(1–2):211–219
Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, Dennis GJ, James JA, Harley JB (2003) Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349(16):1526–1533
Nossent JC, Huysen V, Smeenk RJ, Swaak AJ (1989) Low avidity antibodies to double stranded DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal study of their clinical significance. Ann Rheum Dis 48(8):677–682
Ghirardello A, Doria A, Zampieri S, Tarricone E, Tozzoli R, Villalta D, Bizzaro N, Piccoli A, Gambari PF (2004) Antinucleosome antibodies in SLE: a two-year follow-up study of 101 patients. J Autoimmun 22(3):235–240
Pisetsky DS (2016) Anti-DNA antibodies--quintessential biomarkers of SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12(2):102–110
Berden JH (1997) Lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 52(2):538–558
Sui M, Lin Q, Xu Z, Han X, Xie R, Jia X, Guo X, Zhang W, Guan X, Ren H (2013) Simultaneous positivity for anti-DNA, anti-nucleosome and anti-histone antibodies is a marker for more severe lupus nephritis. J Clin Immunol 33(2):378–387
Cortes-Hernandez J, Ordi-Ros J, Labrador M, Bujan S, Balada E, Segarra A, Vilardell-Tarres M (2004) Antihistone and anti-double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid antibodies are associated with renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med 116(3):165–173
Steward MW (1981) The biolgoical significance of antibody affinity. Immunol Today 2(7):134–140
Hedman K, Hietala J, Tiilikainen A, Hartikainen-Sorri AL, Raiha K, Suni J, Vaananen P, Pietilainen M (1989) Maturation of immunoglobulin G avidity after rubella vaccination studied by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (avidity-ELISA) and by haemolysis typing. J Med Virol 27(4):293–298
Suh-Lailam BB, Chiaro TR, Davis KW, Wilson AR, Tebo AE (2011) Evaluation of a high avidity anti-dsDNA IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4(8):748–754
Oliveira RC, Oliveira IS, Santiago MB, Atta M, Atta AM (2015) High avidity dsDNA autoantibodies in Brazilian women with systemic lupus erythematosus: correlation with active disease and renal dysfunction. J Immunol Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/814748
Kim HA, Jeon JY, Choi GS, Sung JM, Kim MJ, Yun JM, Suh CF (2008) The antichromatin antibodies can be useful as a diagnostic tool and disease activity marker of systemic lupus erythematosus in Koreans. Clin Immunol 128(2):277–283
Atta AM, Santiago MB, Guerra FG, Pereira MM, Sousa Atta ML (2010) Autoimmune response of IgE antibodies to cellular self-antigens in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 152(4):401–406
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35(6):630–640
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1725
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25(11):1271–1277
Walravens M (1987) Systemic diseases and the detection of antinuclear and anticytoplasmic antibodies. An historical review. Clin Rheumatol 6(Suppl 1):9–17
Kumar Y, Bhatia A, Minz RW (2009) Antinuclear antibodies and their detection methods in diagnosis of connective tissue diseases: a journey revisited. Diagn Pathol 4:1
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcon GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR, Bruce IN, Isenberg D, Wallace DJ, Nived O, Sturfelt G, Ramsey-Goldman R, Bae SC, Hanly JG, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Clarke A, Aranow C, Manzi S, Urowitz M, Gladman D, Kalunian K, Costner M, Werth VP, Zoma A, Bernatsky S, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA, Jacobsen S, Buyon JP, Maddison P, Dooley MA, van Vollenhoven RF, Ginzler E, Stoll T, Peschken C, Jorizzo JL, Callen JP, Lim SS, Fessler BJ, Inanc M, Kamen DL, Rahman A, Steinsson K, Franks AG Jr, Sigler L, Hameed S, Fang H, Pham N, Brey R, Weisman MH, McGwin G Jr, Magder LS (2012) Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2677–2686
Ray SK, Putterman C, Diamond B (1996) Pathogenic autoantibodies are routinely generated during the response to foreign antigen: a paradigm for autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(5):2019–2024
Atta AM, Pereira MM, Santiago M, Sousa-Atta ML (2009) Anti-dsDNA antibodies in Brazilian patients of mainly African descent with systemic lupus erythematosus: lack of association with lupus nephritis. Clin Rheumatol 28(6):693–697
Jia Y, Zhao LL, Wang CY, Shang J, Miao Y, Dong YY, Zhao ZZ (2018) Anti-Double-Stranded DNA Isotypes and anti-C1q antibody improve the diagnostic specificity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4528547
Wang W, Li JM (2011) Predominance of IgG1 and IgG3 subclasses of autoantibodies to peptidylarginine deiminase 4 in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 30(4):563–567
Kim AHJ, Strand V, Sen DP, Fu Q, Mathis NL, Schmidt MJ, Bruchas RR, Staten NR, Olson PK, Stiening CM, Atkinson JP (2019) Association of blood concentrations of complement split product iC3b and serum C3 with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 71(3):420–430
Birmingham DJ, Irshaid F, Nagaraja HN, Zou X, Tsao BP, Wu H, Yu CY, Hebert LA, Rovin BH (2010) The complex nature of serum C3 and C4 as biomarkers of lupus renal flare. Lupus 19(11):1272–1280
Doria A, Iaccarino L, Ghirardello A, Zampieri S, Arienti S, Sarzi-Puttini P, Atzeni F, Piccoli A, Todesco S (2006) Long-term prognosis and causes of death in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med 119(8):700–706
Doria A, Rinaldi S, Ermani M, Salaffi F, Iaccarino L, Ghirardello A, Zampieri S, Della Libera S, Perini G, Todesco S (2004) Health-related quality of life in Italian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. II. Role of clinical, immunological and psychological determinants. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(12):1580–1586
Doria A, Arienti S, Rampudda M, Canova M, Tonon M, Sarzi-Puttini P (2008) Preventive strategies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 7(3):192–197
Doria A, Briani C (2008) Lupus: improving long-term prognosis. Lupus 17(3):166–170
Funding
This work is supported by Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology (2014-CXB-44) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2017J01378).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Y-LZ, YX, Y-QL. Performed the experiments: X-LW, YZ, FP, J-JW, C-LJ, S-QL. Analyzed the data: Y-LZ, YX. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: Y-QL, L-CJ. Wrote the paper: YX, Y-LZ. Revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content: Y-LZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, and conforms to the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Lin, Y., Wang, X. et al. Assessment of a high-avidity IgG ANAs for the diagnosis and activity prediction of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 39, 2619–2629 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05040-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05040-4