Abstract
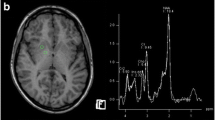
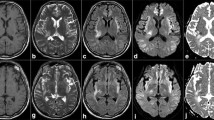
Chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration (CAHD) is a rare neurological disorder of cirrhotic patients, characterized by parkinsonism and cognitive impairment. A T1 hyperintensity on the globus pallidum due to an accumulation of manganese (Mn) is found in these patients. The aim of the study was to investigate CAHD, Mn and the MRI pallidal signal in a series of cirrhotic patients. The association between pallidal T1 hyperintensity, CAHD, and blood levels of Mn, the effect of orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) on the MRI signal and neurological findings, and the role of the pallidal signal as a predictor of CAHD were evaluated. Twenty-six out of 90 patients with cirrhosis had pallidal T1 hyperintensity. Seven patients had CAHD. OLT was followed by the disappearance of CAHD and MRI signal in 2/2 patients. The MRI signal disappeared after OLT in 8/13 patients after a median follow-up time of 24 months. In the patients who did not undergo OLT, CAHD did not present after a median follow-up time of 18 months. The cause of cirrhosis, episodes of acute hepatic encephalopathy and signal intensity were not correlated with CAHD. The blood levels of Mn did not reflect either the MRI signal or CAHD. In conclusion, the pallidal T1 hyperintensity is a prerequisite for the clinical manifestations of CAHD but is not sufficient. The blood levels of Mn as routinely monitored are not a useful marker of Mn burden. The MRI pallidal signal is not a predictor of CAHD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klos KJ, Ahlskog JE, Josephs KA et al (2005) Neurologic spectrum of chronic liver failure and basal ganglia T1 hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging: probable manganese neurotoxicity. Arch Neurol 62:1385–1390
Pinarbasi B, Kaymakoglu S, Matur Z et al (2009) Are acquired hepatocerebral degeneration and hepatic myelopathy reversible? J Clin Gastroenterol 43:176–181
Lee J, Lacomis D, Comu S et al (1998) Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: MR and pathologic findings. Am J Neuroradiol 19:485–487
Ferrara J, Jankovic J (2009) Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. J Neurol 256:320–322
Klos KJ, Ahlskog JE, Kumar N et al (2006) Brain metal concentrations in chronic liver failure patients with pallidal T1 MRI hyperintensity. Neurology 67:1984–1989
Park NH, Park JK, Choi Y et al (2003) Blood manganese correlates with high signal intensities in T1-weighted MRI in patients with liver cirrhosis. NeuroToxicology 24:909–915
Dastur DK, Mangahania DK, Raghavendran KV (1968) Distribution and fate of Mn in the monkey: studies of different parts of the central nervous system and other organs. J Clin Invest 50:9–20
Olanow CW (2004) Manganese-induced Parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 1012:209–223
Long LL, Li XR, Huang ZK et al (2009) Relationship between changes in brain MRI and 1H-MRS, severity of chronic liver damage, and recovery after liver transplantation. Exp Biol Med 234:1075–1085
Stracciari A, Guarino M, Pazzaglia P et al (2001) Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: full recovery after liver transplantation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:136–137
Stracciari A, Baldin E, Cretella L et al (2011) Chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: effects of liver transplantation on neurological manifestations. Neurol Sci 32:411–415
Powell EE, Pender MP, Chalk JB et al (1990) Improvement in chronic hepatocerebral degeneration following liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 98:1079–1082
Servin-Abad L, Tzakis A, Schiff ER, Regev A (2006) Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration in a patient with HCV cirrhosis: complete resolution with subsequent recurrence after liver transplantation Liver Transpl. 7:1161–1165
Shulmann LM, Minagar A, Weiner WJ (2003) Reversal of parkinsonism following liver transplantation. Neurology 60:519
Mattarozzi K, Stracciari A, Vignatelli L et al (2004) Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: longitudinal effects of liver transplantation. Arch Neurol 61:242–247
Krieger D, Krieger S, Theilmann L et al (1995) Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 346:270–274
Francois B, Oliver G, Josiane A, Francis P (1988) Determination of manganese in biological material by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry: a review. Clin Chem 34:227–234
Spahr L, Butterworth RF, Fontaine S et al (1996) Increased blood manganese in cirrhotic patients: relationship to pallidal magnetic resonance signal hyperintensity and neurological symptoms. Hepatology 24:1116–1120
Krieger S, Jauss M, Jansen O et al (1996) Neuropsychiatric profile and hyperintense globus pallidus on T1-weighted magnetic resonance images in liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 111:147–155
Papapetropoulos S, Singer C (2005) Management of the extrapyramidal syndrome in chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration (CAHD). Mov Disord 20:088–1089
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mario Coriasco for his technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maffeo, E., Montuschi, A., Stura, G. et al. Chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration, pallidal T1 MRI hyperintensity and manganese in a series of cirrhotic patients. Neurol Sci 35, 523–530 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1458-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1458-x