Abstract
Objectives
Chronic neuropathies are a common cause of neurological disability worldwide. However, few reports have evaluated, in real life, the prevalence of the several conditions which can cause it.
Patients and methods
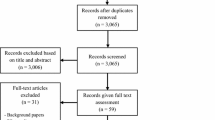
The authors reviewed informatic database for outpatient office to confirm identification of chronic neuropathy in a 3-year interval period.
Results
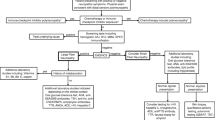
Among the 100 selected patients with chronic neuropathies, almost one fifth (19%) remained idiopathic. The most common etiologies were diabetes (17%), dysimmune neuropathies (38%), and vitamin B12 deficiency (9%). In the “dysimmune neuropathies” group, we distinguished various etiologies, including dysimmune neuropathies associated or not with systemic autoimmune diseases (7 and 3%, respectively), chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy (CIDP) (8%), multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) (3%), paraproteinemic (8%), celiac disease-related (6%), and paraneoplastic (3%) neuropathies.
Conclusions
In this report from a single neurological center, treatable causes of chronic neuropathies, such as dysimmune neuropathies, including CIDP, and celiac disease-associated neuropathy, were common. These findings suggest the utility of routine screening with blood testing for dysimmune neuropathy and celiac disease for all patients presenting with idiopathic chronic polyneuropathy in whom primary diagnostic testings had failed to identify an etiology for the disease.
Significance
Our results indicate that patients with peripheral neuropathy could receive a benefit from being evaluated routinely in a specialized neurological center, as many of the conditions that were discovered represented potentially treatable causes of neuropathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD :
-
celiac disease
- CIDP :
-
chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
- CMAP :
-
compound muscle action potential
- CSF :
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- DML :
-
distal motor latency
- GBS :
-
Guillain-Barrè syndrome
- HR CT :
-
high-resolution computed tomography
- MCV :
-
motor conduction velocity
- MGUS :
-
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
- SCV :
-
sensory conduction velocity
- SNAP :
-
Sensory nerve action potential
References
McLeod JG, Tuck RR, Pollard JD, Cameron J, Walsh JC (1984) Chronic polyneuropathy of undetermined cause. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:530–535
Hanewinckel R, Drenthen J, van Oijen M, Hofman A, van Doorn PA, Ikram MA (2016) Prevalence of polyneuropathy in the general middle-aged and elderly population. Neurology 87:1892–1898
Pasnoor M, Nascimento OJM, Trivedi J, Wolfe GI, Nations S, Herbelin L, de Freitas MG, Quintanilha G, Khan S, Dimachkie M, Barohn R (2013) North America and South America (NA-SA) neuropathy project. Int J Neurosci 123:563–567
Hughes RA (1995) Epidemiology of peripheral neuropathy [editorial]. Curr Opin Neurol 8:335–338
Pasnoor M, Dimachkie MM, Barohn RJ (2013) Cryptogenic sensory polyneuropathy. Neurol Clin 31:463–476
Callaghan BC et al (2014) Role of neurologists and diagnostic tests on the management of distal symmetric polyneuropathy. JAMA Neurol 48104:1–7
Farhad K, Traub R, Ruzhansky KM, Brannagan TH (2016) Causes of neuropathy in patients referred as ‘idiopathic neuropathy’. Muscle Nerve 53:856–861. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.24969
Callaghan B, Kerber K, Longoria R, Feldman E, Lisabeth L (2012) Capturing cases of distal symmetric polyneuropathy in a community. Muscle Nerve 46:943–947
Kimura J (1989) Electrodiagnosis in disease of the nerve and muscle: principles and practice
Luigetti M, Padua L, Mazza S, Rossini PM, Sabatelli M, Lo Monaco M (2013) Clinical-neurophysiological correlations in a series of patients with IgM-related neuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol 124:1899–1903
Luigetti M, Sauchelli D, Primiano G, Cuccagna C, Bernardo D, Lo Monaco M, Servidei S (2016) Peripheral neuropathy is a common manifestation of mitochondrial diseases: a single-centre experience. Eur J Neurol 23:1020–1027
Merolli A, Luigetti M, Modoni A, Masciullo M, Lucia Mereu M, Lo Monaco M (2013) Persistence of abnormal electrophysiological findings after carpal tunnel release. J Reconstr Microsurg 29:511–516
Luigetti M, Quaranta D, Modoni A, Mereu ML, Lo Monaco M (2012) Nerve conduction studies of the sural nerve: normative data from a single-center experience. Clin Neurophysiol 123:1891–1892
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS (2010) European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripher. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:1–9
England JD, Gronseth GS, Franklin G, Carter GT, Kinsella LJ, Cohen JA, Asbury AK, Szigeti K, Lupski JR, Latov N, Lewis RA, Low PA, Fisher MA, Herrmann DN, Howard JF Jr, Lauria G, Miller RG, Polydefkis M, Sumner AJ, American Academy of Neurology (2009) Practice parameter: evaluation of distal symmetric polyneuropathy: role of laboratory and genetic testing (an evidence-based review): report of the American Academy of Neurology, American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and Am. Neurology 72:185–192
Karam C, Tramontozzi LA (2016) Rapid screening for inflammatory neuropathies by standardized clinical criteria. Neurol Clin Pract 6:384–388
Rajabally YA, Nicolas G, Piéret F, Bouche P, Van Den Bergh PYK (2009) Validity of diagnostic criteria for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a multicentre European study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:1364–1368
Lewis RA, Sumner AJ, Brown MJ, A A (1982) Multifocal demyelinating neuropathy with persistent conduction block. Neurology 32:958–964
American Diabetes Association (2012) Standards of medical care in diabetes—2012. Diabetes Care 35(suppl 1):S12
Saperstein DS, Katz JS, Amato AA, Barohn RJ (2001) Clinical spectrum of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Muscle Nerve 24:311–324
Willison HJ et al (2001) The clinical and laboratory features of chronic sensory ataxic neuropathy with anti-disialosyl IgM antibodies. Brain 124:1968–1977
Rubio-Tapia A, Hill ID, Kelly CP, Calderwood AH, Murray JA (2013) ACG clinical guidelines: diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 108:656–676
Raffi GB, Violante FS (1981) Is freon 113 neurotoxic? A case report. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 49:125–127
Sharp CW & Rosenberg NL (1992) Volatile Substances Subst Abus A Compr Textb 303–327
Kestenberg SH, Young ER (1988) Potential problems associated with occupational exposure to nitrous oxide. Dent Assoc 54:277–286
Barohn RJ (1998) Approach to peripheral neuropathy and neuronopathy. Semin Neurol 18:7–18
Dyck PJ, Oviatt KF, Lambert EH (1981) Intensive evaluation of feferred unclassdied neuropahes yields improved diagnosis. Ann Neurol 10:222–226
Luigetti M, Conte A, Del A, Giulia G (2013) TTR-related amyloid neuropathy: clinical, electrophysiological and pathological findings in 15 unrelated patients. Neurol Sci 34:1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1105-y
Zilliox L, Russell JW (2011) Treatment of diabetic sensory polyneuropathy. Curr Treat Options Neurol 13:143–159
Latov N (2014) Diagnosis and treatment of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Nat Rev Neurol 10:435–446
Brannagan TH (2011) Current diagnosis of CIDP: the need for biomarkers. J Peripher Nerv Syst 16:3–13
Querol L, Illa I (2015) Paranodal and other autoantibodies in chronic inflammatory neuropathies. Curr Opin Neurol 28:474–479
Luostarinen L, Himanen SL, Luostarinen M, Collin P, Pirttilä T (2003) Neuromuscular and sensory disturbances in patients with well treated coeliac disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:490–494
Hadjivassiliou M, Sanders DS, Grünewald RA, Woodroofe N, Boscolo S, Aeschlimann D (2010) Gluten sensitivity: from gut to brain. Lancet Neurol 9:318–330
Hadjivassiliou M, Sanders DS, Gru RA (2010) Sensory ganglionopathy due to gluten sensitivity. Neurology 75(11):1003–1008
Ramchandren S, Lewis RA (2009) Monoclonal gammopathy and neuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol 22:480–485
Katz JS, Saperstein DS, Gronseth G, Amato AA, Barohn RJ (2000) Distal acquired demyelinating symmetric (DADS) neuropathy. Neurology 54:615–620
Notermans NC, Franssen H, Eurelings M, Van Der Graaf Y, Wokke JHJ (2000) Diagnostic criteria for demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Muscle Nerve 23:73–79
Darnell RB, Posner JB (2003) Mechanisms of disease: paraneoplastic syndromes involving the nervous system. Nejm 349:1543–1554
Gundogdu B, Rosenfeld M. R. & Rudnicki SA (2013) Paraneoplastic neuromuscular disorders. Neuromuscul Disord Clin Pract 1501–1514. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6567-6_75
Graus F, Delattre JY, Antoine JC, Dalmau J, Giometto B, Grisold W, Honnorat J, Smitt PS, Vedeler Ch, Verschuuren JJ, Vincent A, Voltz R (2004) Recommended diagnostic criteria for paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1135–1140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Publication statement
We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ricci, L., Luigetti, M., Florio, L. et al. Causes of chronic neuropathies: a single-center experience. Neurol Sci 40, 1611–1617 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03899-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03899-z