Abstract
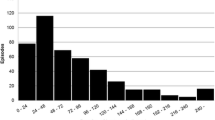
This study reviews the outcome of patients with uncomplicated catheter-related Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia diagnosed in our hospital from January 1997 to December 1999 and treated with short-course antibiotic therapy. Our aim was to assess the effectiveness of this regimen for minimizing complications (relapses, endocarditis and metastatic foci). A total of 213 episodes of bacteremia were registered and 167 (78.4%) were nosocomial. Among these, 87 (52.1%) were catheter-related Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and 20 were primary nosocomial bacteremia. Endocarditis was diagnosed during the acute episode in 7/107 of these patients (2 by persistent fever after catheter removal and 5 by metastatic foci; 3 of them also had cardiac risk factors) and confirmed with transesophageal echocardiography. Among the 84/87 catheter-related Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and 16/20 primary nosocomial bacteremia patients who did not develop endocarditis, 31 patients died during the acute episode (16 due to sepsis despite initiation of antibiotic treatment and 15 due to the underlying disease) and five had osteoarticular foci. The remaining 64 episodes were considered to be uncomplicated bacteremia (no cardiac risk factors, persistent fever, metastatic foci, or clinical signs of endocarditis) and were treated with 10–14 days of high-dose antistaphylococcal antibiotics. Echocardiography was not mandatory in these patients. Of the 64 uncomplicated episodes, 62 were followed for at least 3 months and none relapsed or developed endocarditis. Even though some of the patients might have had subclinical endocarditis, short-course therapy with high doses of antistaphylococcal antibiotics was effective for treating uncomplicated catheter-related Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Transesophageal echocardiography may not be necessary in these cases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mermel LA, Farr BM, Sherertz RJ, et al (2001) Guidelines for the management of intravascular catheter-related infections. Clin Infect Dis 32:1249–1272
Malanoski GJ, Samore MH, Pefanis A, Karchmer AW (1995) Staphylococcus aureus catheter-associated bacteremia: minimal effective therapy and unusual infectious complications associated with arterial sheath catheters. Arch Intern Med 155:1161–1166
Capdevila JA, Segarra A, Planes AM, et al (1993) Successful treatment of hemodialysis catheter-related sepsis without catheter removal. Nephrol Dial Transplant 8:231–234
Lowy FD (1998) Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Eng J Med 339:520–532
Waldvogel FA (2000) Staphylococcus aureus. In: Mandell GL (ed) Douglas and Bennett’s. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. Churchill Livingstone, pp 2069–2092
Mylotte JM, Tayara A (2000) Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: predictors of 30-day mortality in a large cohort. Clin Infect Dis 31:1170–1174
Pahissa A, Capdevila JA, Almirante B, et al (1988) Bacteriemia por Staphylococcus aureus en un hospital universitario. Enf Infec Microbiol Clin 6:32–42
Lautenschlager S, Herzog C, Zimmerli W (1993) Course and outcome of bacteremia due to Staphylococcus aureus: evaluation of different clinical case definitions. Clin Infect Dis 16:567–573
Rubio M, Romero J, Corral O, Roca V, Picazo JJ (1999) Bacteriemia por Staphylococcus aureus; análisis de 311 episodios. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 17:56–64
Jensen AG, Wachmann CH, Poulsen KB, et al (1999) Risk factors for hospital-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Arch Intern Med 159:1437–1444
Raad II, Sabbagh MF (1992) Optimal duration of therapy for catheter-related Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a study of 55 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis 14:75–82
Bayer AS (1982) Staphylococcal bacteremia and endocarditis. State of the art. Arch Intern Med 142:1169–1177
Fowler Jr. VG, Sanders LL, Kong LK, et al (1999) Infective endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus. 59 prospectively identified cases with follow-up. Clin Infect Dis 28:106–114
Steinberg JP, Clark CC, Hackman BO (1996) Nosocomial and community acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremias from 1980 to 1993. Impact of intravenous devices and methicillin resistance. Clin Infect Dis 23:255–259
Darouiche RO, Musher MM (1996) Editorial response: increasing rates of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia- a medical device is a merit in disguise and methicillin resistance is merely vice. Clin Infect Dis 23:260–261
Nielsen J, Ladefoged SD, Kolmos HJ (1998) Dialysis catheter-related septicemia focus on Staphylococcus aureus septicemia. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:2847–2852
Jernigan JA, Farr BM (1993) Short-course of catheter-related Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 119:304–311
Fowler VG Jr, Li J, Corey R, et al (1997) Role of echocardiography in evaluation of patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: experience in 103 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:1072–1078
Capdevila JA, Planes AM, Palomar M, et al (1992) Value of differential quantitative blood cultures in the diagnosis of catheter-related sepsis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 11:403–407
Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK, et al (1994) New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med 96:200–209
Habib G, Derumeaux G, Avierinos JF, et al (1999) Value and limitations of the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol 33:2023–2029
Li JS, Sexton DJ, Mick N, et al (2000) Proposed modifications to the duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 30:633–638
Fowler VG (2001) Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Up to date 2001. http://id.medscape.com/UpToDate/2001/03.01/utd0301.09.fowl/utd0301.09.folw-1.html
Rosen AB, Fowler VG, Corey GR, et al (1999) Cost-effectiveness of transesophageal echocardiography to determine the duration of therapy for intravascular catheter-associated Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Ann Intern Med 130:810–820
Nolan CN, Beaty HN (1976) Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Am J Med 60:495–500
Bayer AS, Lam K, Ginzton L, Norman DC, Chiu CY, Ward JI (1987) Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clinical, serologic, and echocardiographic findings in patients with and without endocarditis. Arch Intern Med 147:457–462
Libman H, Arbeit RD (1984) Complications associated with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Arch Intern Med 144:541–545
Watanakunakorn C (1999) Editorial response: increasing importance of intravascular device-associated Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 28:115–116
Mylonakis E, Calderwood S (2001) Infective endocarditis in adults. N Engl J Med 345:1318–1330
Ribera E, Gomez-Jimenez J, Cortes E, et al (1996) Effectiveness of cloxacillin with and without gentamicin in short-term therapy for right-side S. aureus endocarditis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 125:969–974
Dugdale DC, Ramsey PG (1990) Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in patients with Hickman catheter. Am J Med 89:137–141
Fowler VG Jr, Sanders LL, Sexton DJ, et al (1998) Outcome of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia according with recommendations of infectious diseases specialists: experience with 244 patients. Clin Infect Dis 27:478–486
Berrington A, Gould FK (2001) Use of antibiotic locks to treat colonized central venous catheters. JAC 48:597–603
Sexton DJ (2001) Vascular access infections in patients undergoing dialysis with specific emphasis on the role and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Dis Clin North Amer 15:731–742
Jensen AG, Wachmann CH, Espersen F, Scheibel J, Skinhof P, Frimodt-Moller N (2002) Treatment and outcome of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. A prospective study of 278 cases. Arch Intern Med 162:25–32
Acknowledgements
We thank Celine L. Cavallo for her assistance with English corrections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pigrau, C., Rodríguez, D., Planes, A.M. et al. Management of Catheter-Related Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: When May Sonographic Study Be Unnecessary?. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22, 713–719 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-1041-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-1041-0