Abstract
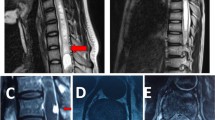
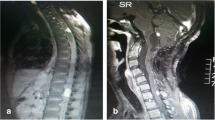
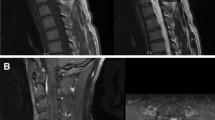
The prognostic factors for surgically removed spinal hemangioblastomas, the impact of VHL disease on outcome, and the role of intraoperative neuromonitoring are still not completely clear. The aim of this study was to review our experience with spinal hemangioblastomas in order to assess potential predictors of neurological outcome after surgery. All cases of spinal hemangioblastomas removed at two Italian academic institutions from 1985 to 2020 were reviewed. Data about clinical presentation and symptom duration, diagnosis of VHL, surgical approach, use of IONM, duration of hospital stay, follow-up, and modified McCormick grade before and after surgery were extracted. Sixty-one patients (31 F, 30 M) underwent 69 surgeries to remove 74 spinal hemangioblastomas (37 cervical, 32 thoracic, 5 lumbar). Improvement was found in 32.3% of cases, neurological condition remained stable in 51.6% of cases, and deteriorated in 16.1% of patients. A worsening trend in VHL patients and an improvement trend in non-VHL patients were detected, despite the lack of statistical significance. Laminotomy and use of IONM were found to be associated with better outcome, although no association was found between surgery without IONM and worse outcome. In most cases, patients affected by spinal hemangioblastomas can expect a good long-term outcome. In our experience, laminotomy seems to be associated with better outcome compared to laminectomy. While its absence is not associated with worse outcome, IONM seems to be associated with a better neurological outcome. Our study suggests that the more impaired the preoperative neurological condition, the worse the outcome.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The corresponding author has full access to all data and material.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
BalDIN ZOTERO_BIBL {"uncited":[],"omitted":[],"custom":[]} CSL_BIBLIOGRAPHY of the studya
Biondi A, Ricciardi GK, Faillot T, Capelle L, Van Effenterre R, Chiras J (2005) Hemangioblastomas of the lower spinal region: report of four cases with preoperative embolization and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:936on.
Bostrower spinal region: report of four cases with preoperative JM, Reinges MHT, (2008) Intramedullary hemangioblastomas: timing of surgery, microsurgical technique and follow-up in 23 patients. Eur Spine J 17:882–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0658-1
Bostrower spinal region: report of four cases with preoperative JM, Reie in adult intramedullary spinal cord tumours: a 20-year single institution experience. BMC Res Notes 7:908. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-7-908
Chang H, Li J, Wang P, Lu X, Li B (2020) Microsurgical treatment of cervical spinal hemangioblastoma. Neurochirurgie 66:56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuchi.2019.11.005
Choi I, Hyun SJ, Kang JK, Rhim SC (2014) Combined muscle motor and somatosensory evoked potentials for intramedullary spinal cord tumour surgery. Yonsei Med J 55(4):1063–1071. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.4.1063
Clark AJ, Lu DC, Richardson RM, Tihan T, Parsa AT, Chou D, Barbaro NM, Kunwar S, Weinstein PR, Lawton MT, Berger MS, McDermott MW (2010) Surgical technique of temporary arterial occlusion in the operative management of spinal hemangioblastomas. World Neurosurg 74:200–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2010.03.016
Conway JE, Chou D, Clatterbuck RE, Brem H, Long DM, Rigamonti D (2001) Hemangioblastomas of the central nervous system in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome and sporadic disease. Neurosurgery 48:55n the operative ma-63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200101000-00009
Das JM, Kesavapisharady K, Sadasivam S, Nair SN (2017) Microsurgical treatment of sporadic and von Hippel-Lindau disease associated spinal hemangioblastomas: a single-institution experience. Asian Spine J 11:548na55. doi: https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.4.548
Deng X, Wang K, Wu L, Yang C, Yang T, Zhao L, Yang J, Wang G, Fang J, Xu Y (2014) Intraspinal hemangioblastomas: analysis of 92 cases in a single institution: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine 21:260ive ma-63. doi: 10.1014.1.SPINE13866
Dwarakanath S, Sharma BS, Mahapatra AK (2008) Intraspinal hemangioblastoma: analysis of 22 cases. J Clin Neurosci 15:1366 of 92 cases in a single institution:
Escott EJ, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Brega K, Lillehei KO (2004) Proximal nerve root spinal hemangioblastomas: presentation of three cases, MR appearance, and literature review. Surg Neurol 61:262DeMasters BK, Brega K, Lillehei KO (2004) Proximal nerve
Forster MT, Marquardt G, Seifert V, Szelényi A (2012) Spinal cord tumor surgery - importance of continuous intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring after tumor resection. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 15;37(16):E1001–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31824c76a8
Gl;37(16):E1001–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0bougioukas VI, Van Velthoven V (2005) Characterization of hemangioblastomas of spinal nerves. Neurosurgery 56:503–509; discussion 503–509. doi: https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000153909.70381.c8
Gl;37(16):E1001–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0bougioukas VI, Van Velthoven V (2005) Chahe central nervous system. Neurosurgery 57:71nerv discussion 71–76. doi: https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000163250.71951.18
Hao S, Li D, Ma G, Yang J, Wang G (2013) Application of intraoperative indocyanine green videoangiography for resection of spinal cord hemangioblastoma: advantages and limitations. J Clin Neurosci 20:1269–1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2012.12.008
Harati A, Satop G, Yang J, Wang G (2013) Application of intraoperative indocyanine green videoangiography for resection of spinal cord hemangioblastoma: advantagoutcome in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. Surg Neurol Int 3:6. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.92170
Hojo M, Arakawa Y, Funaki T, Yoshida K, Kikuchi T, Takagi Y, Araki Y, Ishii A, Kunieda T, Takahashi JC, Miyamoto S (2014) Usefulness of tumor blood flow imaging by intraoperative indocyanine green videoangiography in hemangioblastoma surgery. World Neurosurg 82:e495-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2013.02.009
Huang J-S, Chang C-J, Jeng C-M (2003) Surgical management of hemangioblastomas of the spinal cord. J Formos Med Assoc 102:868fuln
Hyun SJ, Rhim SC (2009) Combined motor and somatosensory evoked potential monitoring for intramedullary spinal cord tumor surgery: correlation of clinical and neurophysiological data in 17 consecutive procedures. Br J Neurosurg 23(4):393–400. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688690902964744
Imagama S, Ito Z, Ando K, Kobayashi K, Hida T, Ito K, Ishikawa Y, Tsushima M, Matsumoto A, Nakashima H, Wakao N, Sakai Y, Matsuyama Y, Ishiguro N (2017) Rapid worsening of symptoms and high cell proliferative activity in intra- and extramedullary spinal hemangioblastoma: a need for earlier surgery. Global Spine J 7:6s and high cell proliferative ac
Joaquim AF, Ghizoni E, dos Santos MJ, Valadares MGC, da Silva FS, Tedeschi H (2015) Intramedullary hemangioblastomas: surgical results in 16 patients. FOC 39:E18. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.5.FOCUS15171
Juthani RG, Bilsky MH, Vogelbaum MA (2015) Current management and treatment modalities for intramedullary spinal cord tumors. Curr Treat Options Oncol 16(8):39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-015-0358-0
Kanno H, Yamamoto I, Nishikawa R, Matsutani M, Wakabayashi T, Yoshida J, Shitara N, Yamasaki I, Shuin T, Clinical VHL Research Group in Japan (2009) Spinal cord hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Spinal Cord 47:447astoma surgery.038/sc.2008.151
Kim D-G, Son Y-R, Park Y-S, Hyun S-J, Kim K-J, Jahng T-A, Kim H-J, Park KS (2016) Differences in multimodality intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring changes between spinal intramedullary ependymoma and hemangioblastoma. J Clin Neurophysiol 33(120):126. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNP.0000000000000247
Kim TY, Yoon DH, Shin HC, Kim KN, Yi S, Oh JK, Ha Y (2012) Spinal cord hemangioblastomas in von hippel-lindau disease: management of asymptomatic and symptomatic tumors. Yonsei Med J 53:1073Shin HC, Kim10.3349/ymj.2012.53.6.1073
Kimchi G, Knoller N, Korn A, Eyal-Mazuz Y, Sapir Y, Peled A, Harel R (2021) Delayed variations in the diagnostic accuracy of intraoperative neuromonitoring in the resection of intramedullary spinal cord tumors. Neurosurg Focus 50(5):E21. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.2.FOCUS201084
Kothbauer KF, Deletis V, Epstein FJ (1998) Motor-evoked potential monitoring for intramedullary spinal cord tumor surgery: correlation of clinical and neurophysiological data in a series of 100 consecutive procedures. Neurosurg Focus 4:e1. https://doi.org/10.3171/foc.1998.4.5.4
Krammer MJ, Wolf S, Schul DB, Gerstner W, Lumenta CB (2009) Significance of intraoperative motor function monitoring using transcranial electrical motor evoked potentials (MEP) in patients with spinal and cranial lesions near the motor pathways. Br J Neurosurg 23(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688690802563349
Kr(1):48–55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/02688690802563349 cranial lesions near the motor pathways. Br J Neurosurgnal cord tumeasibility and clinical results in a series of 18 patients. J Neurosurg Spine 1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.5.SPINE1975
Lee DK, Choe WJ, Chung CK, Kim HJ (2003) Spinal cord hemangioblastoma: surgical strategy and clinical outcome. J Neurooncol 61:27nical results1023/a:1021297622944
Li X, Wang J, Niu J, Hong J, Feng Y (2016) Diagnosis and microsurgical treatment of spinal hemangioblastoma. Neurol Sci 37:899:27nical results1023/a:1021297622944
Liu A, Jain A, Sankey EW, Jallo GI, Bettegowda C (2016) Sporadic intramedullary hemangioblastoma of the spine: a single institutional review of 21 cases. Neurol Res 38:205–209. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743132815Y.0000000097
Lonser RR, Glenn GM, Walther M, Chew EY, Libutti SK, Linehan WM, Oldfield EH (2003) von Hippel-Lindau disease. The Lancet 361:2059nal review of 21 c6/S0140–6736(03)13643–4
Lonser RR, Oldfield EH (2005) Microsurgical resection of spinal cord hemangioblastomas. Neurosurgery 57:372se. The Lancet 361:2059nal review of 21 c6/S0140–6736(03)13643–4–
Lonser RR, Weil RJ, Wanebo JE, DeVroom HL, Oldfield EH (2003) Surgical management of spinal cord hemangioblastomas in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg 98:106–116. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.98.1.0106
MacDonald DB (2002) Safety of intraoperative transcranial electrical stimulation motor evoked potential monitoring. J Clin Neurophysiol 19:416–429. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004691-200210000-00005
Malis LI (2002) Atraumatic bloodless removal of intramedullary hemangioblastomas of the spinal cord. J Neurosurg 97:1 Clin Neurophysiol 1.2002.97.1.0001
Mandigo CE, Ogden AT, Angevine PD, McCormick PC (2009) Operative management of spinal hemangioblastoma. Neurosurgery 65:1166europhysiol 1.2002.97.1.0001 https://doi.org/10.1097/00004691-
Matsumoto Y, Harimaya K, Doi T, Maeda T, Iwamoto Y (2009) Outcome of osteoplastic laminotomy for excision of spinal cord tumours. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 17(3):275–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/230949900901700305
McCormick PC, Torres R, Post KD, Stein BM (1990) Intramedullary ependymoma of the spinal cord. J Neurosurg 72:523275–523279. https://doi.org/10.1177/23094990090170030
McGirt MJ, Chaichana KL, Atiba A, Bydon A, Witham TF, Yao KC et al (2008) Incidence of spinal deformity after resection of intramedullary spinal cord tumors in children who underwent laminectomy compared with laminoplasty. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1:57–62
McGirt MJ, Garcsurg Pediatr 1:57–6ity after resection of intramedullary spinal cord tumors in children who underwent laminectomy compared with lamino351 https://doi.org/10.1097/00004691-200210000-00005i: https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.98.1.0106.SPINEdural spinal tumors: analysis of 238 patients. Neurosurgery 66:1005–1012. doi: https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000367721.73220.C9
Mehta GU, Asthagiri AR, Bakhtian KD, Auh S, Oldfield EH, Lonser RR (2010) Functional outcome after resection of spinal cord hemangioblastomas associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease: Clinical article. SPI 12:233–242. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.10.SPINE09592
Messerer M, Cossu G, Pralong E, Daniel RT (2017) Intramedullary hemangioblastoma: Microsurgical resection technique. Neurochirurgie 63:376mas assoc: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuchi.2015.11.002
Miller DJ, McCutcheon IE (2000) Hemangioblastomas and other uncommon intramedullary tumors. J Neurooncol 47:253ique. Neurochirurgie 63:376mas ass
Morota N, Deletis V, Constantini S, Kofler M, Cohen H, Epstein FJ (1997) The role of motor evoked potentials during surgery for intramedullary spinal cord tumors. Neurosurgery 41:1327–1336. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199712000-00017
Na JH, Kim HS, Eoh W, Kim JH, Kim JS, Kim E-S (2007) Spinal cord hemangioblastoma of motor evoked potentialoutcome after surgical treatment. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 42:436–440. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2007.42.6.436
Nemeiko I, Borgstedt-Bakke JH, Wichmann TO, Gudmundsdottir G, Rasmussen MM (2019) Characteristics and outcomes in patients with primary intraspinal tumours. Dan Med J 66
Neumann HP, Eggert HR, Scheremet R, Schumacher M, Mohadjer M, Wakhloo AK, Volk B, Hettmannsperger U, Riegler P, Schollmeyer P (1992) Central nervous system lesions in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:898/2009.10.S https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.55.10.898
Okawa A, Shinomiya K, Takakuda K, Nakai O (1996) A cadaveric study on the stability of lumbar segment after partial laminotomy and facetectomy with intact posterior ligaments. J Spinal Disord 9:518–526
Ortega-Martc study on the s JM, Fernof lumbar segment after partial lamindríguez-Srtega-Martc study on the s JM, Fernof lumbar segment after partial lamindríguez-d facetectomy with intact posterior ligaments. J Spinal Disord 9:518–26tem lesions in von Hippel
Pai SB, Krishna KN (2003) Secondary holocord syringomyelia with spinal hemangioblastoma: a report of two cases. Neurol India 51:67–68
Park CH, Lee C-H, Hyun SJ, Jahng T-A, Kim H-J, Kim K-J (2012) Surgical outcome of spinal cord hemangioblastomas. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 52:221d 9:. doi: https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.3.221
Park DM, Zhuang Z, Chen L, Szerlip N, Maric I, Li J, Sohn T, Kim SH, Lubensky IA, Vortmeyer AO, Rodgers GP, Oldfield EH, Lonser RR (2007) von Hippel-Lindau disease-associated hemangioblastomas are derived from embryologic multipotent cells. PLoS Med 4:e60. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0040060
Parker F, Aghakhani N, Ducati LG, Yacubian-Fernandes A, Silva MV, David P, Richard S, Tadie M (2009) Results of microsurgical treatment of medulla oblongata and spinal cord hemangioblastomas: a comparison of two distinct clinical patient groups. J Neurooncol 93:133–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9861-0
Pavesi G, Feletti A, Berlucchi S, Opocher G, Martella M, Murgia A, Scienza R (2008) Neurosurgical treatment of von Hippel-Lindau-associated hemangioblastomas: benefits, risks and outcome. J Neurosurg Sci 52:29–36
Pietil G, Feletti A, Berlucchi S, Opocher G, Martella M, Murgia A, Scienza R (2008) Neurosurgical treatment of von Hippel-Lindau-associated hemangioblastomas: benefits, ris
Pluta RM, Iuliano B, DeVroom HL, Nguyen T, Oldfield EH (2003) Comparison of anterior and posterior surgical approaches in the treatment of ventral spinal hemangioblastomas in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg 98:117–124. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.98.1.0117
Prokopienko M, Kunert P, PodgHL, Nguyen T, Oldfield EH (2003) Comparison of anterior and posterior surgical approaches in the treatment of ventral spinal hemangioblastomas in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg
Richards O, Goacher E, Pal D, Tyagi A, Chumas P, Derham C (2020) Intramedullary spinal cord tumours - a single centre, 10-year review of clinical and pathological outcomes. Br J Neurosurg 1dullary spinal cord tumours - a single
Roonprapunt C, Silvera VM, Setton A, Freed D, Epstein FJ, Jallo GI (2001) Surgical management of isolated hemangioblastomas of the spinal cord. Neurosurgery 49:321–327; discussion 327–328. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200108000-00012
Sadashivam S, Abraham M, Kesavapisharady K, Nair SN (2020) Long-term outcome and prognostic factors of intramedullary spinal hemangioblastomas. Neurosurg Rev 43:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-1025-2
Sala F, Bricolo A, Faccioli F, Lanteri P, Gerosa M (2007) Surgery for intramedullary spinal cord tumors: the role of intraoperative (neurophysiological) monitoring. Eur Spine J 16(Suppl 2):130–139
Sala F, Palandri G, Basso E, Lanteri P, Deletis V, Faccioli F, Bricolo A (2006) Motor evoked potential monitoring improves outcome after surgery for intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a historical control study. Neurosurgery 58:112917–13; discussion 1129–1143. doi: https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000215948.97195.58
Samuel N, Tetreault L, Santaguida C, Nater A, Moayeri N, Massicotte EM, Fehlings MG (2016) Clinical and pathological outcomes after resection of intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a single-institution case series. Neurosurg Focus 41:E8. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.5.FOCUS16147
Scibilia A, Terranova C, Rizzo V, Raffa G, Morelli A, Esposito F, Mallamace R, Buda G, Conti A, Quartarone A, Germanò A (2016) Intraoperative neurophysiological mapping and monitoring in spinal tumor surgery: sirens or indispensable tools? Neurosurg Focus 41(2):E18. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.5.FOCUS16141
Serban D, Exergian F (2013) Intramedullary hemangioblastoma - local experience of a tertiary clinic. Chirurgia (Bucur) 108:325afte
Shin DA, Kim SH, Kim KN, Shin HC, Yoon DH (2008) Surgical management of spinal cord haemangioblastoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150:215resection of intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a si
Siller S, SzelH K, KNerlitz L, Tonn JC, Zausinger S, (2017) Spinal cord hemangioblastomas: significance of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring for resection and long-term outcome. J Neurosurg Spine 26:483–493. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.SPINE16595
Sun Hr S, SzelH K, KNerlit, L, Tonn JC, Zausinger S, (2017) Spinal cord hemgioblastomas can be effectively treated by microsurgery alone. World Neurosurg 82:836–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2014.05.024
Takai K, Taniguchi M, Takahashi H, Usui M, Saito N (2010) Comparative analysis of spinal hemangioblastomas in sporadic disease and Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 50:560–567. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.50.560
Van Velthoven V, Reinacher PC, Klisch J, Neumann HPH, Gl) Comparative analysis of spinal hemangioblastomas in sporadic dis special attention to von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neurosurgery 53:1306–1313; discussion 1313–1314. doi: https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000093497.81390.29
Vergauwen E, Steiert C, Kr PC, Klisch J, Neumann HPH, Gl) Comparative analysis of spinal hemangioblastomas in sporadicurgical morbidity in patients with multiple cerebellar and medullary hemangioblastomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 197:106111. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106111
Vougioukas VI, Glert CS, Hubbe U, Berlis A, Omran H, Neumann HPH, Van Velthoven V (2006) Surgical treatment of hemangioblastomas of the central nervous system in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1149–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-0018-y
Wang C (2008) Spinal hemangioblastoma: report on 68 cases. Neurol Res 30:603oven V (2006) Surgical treatment of
Wang Q, Cheng J, Zhang S, Ju Y, Liu W, Hui X (2020) Central nervous system hemangioblastomas in the elderly (over 65 years): Clinical characteristics and outcome analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 189:105622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105622
Westwick HJ, Gigu in the elderly (over 65 years): Clinicaprognosis of spinal hemangioblastoma: a surveillance epidemiology and end results study. Neuroepidemiology 46:14blastoma: a surveillan41147
Xu Q, Bao W, Pang L (2002) Diagnosis and treatment of intramedullary hemangioblastoma of cervical spinal cord. Chin Med J (Engl) 115(10100):101
Yasuda T, Hasegawa T, Yamato Y, Kobayashi S, Togawa D, Banno T, Arima H, Oe S, Matsuyama Y (2016) Relationship between spinal hemangioblastoma location and age. Asian Spine J 10:309 location and aghi S, Togawa D, Bann
Yeh JS, Sgouros S, Walsh AR, Hockley AD (2001) Spinal sagittal malalignment following surgery for primary intramedullary tumours in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 35:318–324
Yousef A, Rutkowski MJ, Yalcin CE, Eren OC, Caliskan I, Tihan T (2019) Sporadic and Von-Hippel Lindau disease-associated spinal hemangioblastomas: institutional experience on their similarities and differences. J Neurooncol 143:547–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03189-w
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Alberto Feletti: conception and design of the work, analysis and interpretation of data, draft of the work, approval of the final version. Alessandro Boaro: analysis and interpretation of data, draft of the work, approval of the final version. Davide Giampiccolo: acquisition and interpretation of data, draft of the work, approval of the final version. Giorgio Casoli: acquisition of data, approval of the final version. Fabio Moscolo: acquisition of data, approval of the final version. Massimiliano Ferrara: acquisition of data, approval of the final version. Francesco Sala: design of the work, interpretation of data, critical revision, approval of the final version. Giacomo Pavesi: design of the work, interpretation of data, critical revision, approval of the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
As this is a retrospective study, no approval was required by the Institutional Ethics Board.
Consent to participate
Consent to participate was not required because of the retrospective nature of the study, and because patients cannot be identified.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was not required because of the retrospective nature of the study, and because patients cannot be identified.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feletti, A., Boaro, A., Giampiccolo, D. et al. Spinal hemangioblastomas: analysis of surgical outcome and prognostic factors. Neurosurg Rev 45, 1645–1661 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01696-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01696-x