Abstract
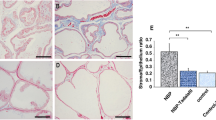
The antibiotic treatment rate of chronic bacterial prostatitis (CBP) is low, and long-term administration can result in adverse events and bacterial resistance. For these reasons, a new preventive modality, which can replace traditional antibiotic therapy, is required. To evaluate the preventive effect of selenium on CBP, the pre-treatments were divided into four groups, administered for 4 weeks, as follows: (1) control, (2) ciprofloxacin, (3) selenium, and (4) ciprofloxacin and selenium. Then, drip infusion of a bacterial suspension (Escherichia coli Z17, O2:K1; H–) into the prostatic urethra of Wistar rats was conducted to induce CBP. In 4 weeks, the results of microbiological culture of prostate and urine samples as well as histological findings of the prostate in each group were analyzed. Selenium decreased bacterial infection significantly; the decrease in infiltration rate of inflammatory cells into prostate tissues in the selenium group was similar to that in the control group. The effect of hindering bacterial infection on prostate tissue was greater in the group administered both selenium and an antibiotic than in other groups given only one of the agents. Although the findings of this study suggest that selenium can have a preventive effect against the occurrence of CBP, methods to prevent CBP are still controversial.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stamey TA, Meares EM Jr, Winningham DG. Chronic bacterial prostatitis and the diffusion of drugs into prostatic fluid. J Urol. 1970;103:187–94.
Nickel JC. Antibiotics for bacterial prostatitis. J Urol. 2000;163:1407.
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG. Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science. 1973;179:588–90.
Maehira F, Luyo GA, Miyagi I, Oshiro M, Yamane N, Kuba M, et al. Alterations of serum selenium concentrations in the acute phase of pathological conditions. Clin Chim Acta. 2002;316:137–46.
Galley HF, Davies MJ, Webster NR. Xanthine oxidase activity and free radical generation in patients with sepsis syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1996;24:1649–53.
Angstwurm MW, Engelmann L, Zimmermann T, Lehmann C, Spes CH, Abel P, et al. Selenium in Intensive Care (SIC): results of a prospective randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple-center study in patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:118–26.
Seo SI, Lee SJ, Kim JC, Choi YJ, Kim SW, Hwang TK, et al. Effects of androgen deprivation on chronic bacterial prostatitis in a rat model. Int J Urol. 2003;10:485–91.
Han CH, Yang CH, Sohn DW, Kim SW, Kang SH, Cho YH. Synergistic effect between lycopene and ciprofloxacin on a chronic bacterial prostatitis rat model. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008;31(suppl 1):S102–7.
Lee YS, Han CH, Kang SH, Lee SJ, Kim SW, Shin OR, et al. Synergistic effect between catechin and ciprofloxacin on chronic bacterial prostatitis rat model. Int J Urol. 2005;12:383–9.
Sohn DW, Han CH, Jung YS, Kim SI, Kim SW, Cho YH. Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects of garlic and synergistic effect between garlic and ciprofloxacin in a chronic bacterial prostatitis rat model. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;34:215–9.
McGuire EJ, Lytton B. Bacterial prostatitis: treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Urology. 1976;7:499–500.
Roberts RO, Lieber MM, Rhodes T, Girman CJ, Bostwick DG, Jacobsen SJ. Prevalence of a physician-assigned diagnosis of prostatitis: the Olmsted County Study of Urinary Symptoms and Health Status Among Men. Urology. 1998;51:578–84.
Cho YH, Lee SJ, Lee JY, Kim SW, Lee CB, Lee WY, et al. Antibacterial effect of intraprostatic zinc injection in a rat model of chronic bacterial prostatitis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002;19:576–82.
Nicolle LE. Uncomplicated urinary tract infection in adults including uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Urol Clin N Am. 2008;35:1–12.
Wagenlehner FM, Weidner W, Naber KG. An update on uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women. Curr Opin Urol. 2009;19:368–74.
Lee BJ, Park SI, Park JM, Chittum HS, Hatfield DL. Molecular biology of selenium and its role in human health. Mol Cells. 1996;6:509–20.
Wintergerst ES, Maggini S, Hornig DH. Contribution of selected vitamins and trace elements to immune function. Ann Nutr Metab. 2007;51:301–23.
Kiremidjian-Schumacher L, Roy M, Wishe HI, Cohen MW, Stotzky G. Supplementation with selenium and human immune cell functions. II. Effect on cytotoxic lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1994;41:115–27.
Spallholz JE, Boylan LM, Larsen HS. Advances in understanding selenium’s role in the immune system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;587:123–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.W., Ha, US., Woo, J.C. et al. Preventive effect of selenium on chronic bacterial prostatitis. J Infect Chemother 18, 30–34 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-011-0276-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10156-011-0276-4