Abstract
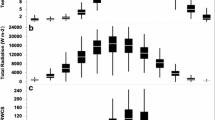
Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton biomass and species composition in the shallow hypertrophic Lake Manyas, Turkey, were studied biweekly from January 2003 to December 2004 to determine steady-state phases in phytoplankton assemblages. Steady-state phases were defined when one, two or three coexisting species contributed to at least 80% of the standing biomass for at least 2 weeks and during that time the total biomass did not change significantly. Ten steady-state phases were identified throughout the study peiod. During those periods, Achnanthes microcephala (Kützing) Cleve twice dominated the phytoplankton biomass alone and contributed to more than 50% of the total biomass in seven phases. Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing, Anabaena spiroides Klebahn, Cyclotella stylorum Brightwell, Pediastrum boryanum (Turpin) Meneghini and Phacus pusillus Lemmermann were also represented once in steady-state phytoplankton assemblages. A. microcephala was dominant usually during cold periods of the year, while M. aeruginosa and A. spiroides were usually dominant in warm seasons. The total number of species showed a clear decrease during steady-state phases at all stations. All stations were significantly different in terms of the measured physical and chemical parameters (P < 0.05) and phytoplankton biomass (F = 117, P < 0.05).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbay N, Anul N, Yerli S, Soyupak S, Yurteri C (1999) Seasonal distribution of large phytoplankton in the Keban Dam Reservoir. J Plankton Res 21:771–787
Albay M, Akcaalan R (2003) Comparative study of periphyton colonization on Common Reed (Phragmites australis) and artificial substrate in a shallow lake, Manyas, Turkey. Hydrobiologia 506–509:531–540
Alvarez-Cobelas M, Jacobsen BA (1992) Hypertrophic phytoplankton: an overview. Freshw Forum 2:184–199
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 13th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Pollution Control Federation, Washington DC
Aykulu G, Obalı O, Gönülol A (1983) Distribution of phytoplankton in lakes around Ankara (in Turkish). Turk J Bot 7:277–288
Borics G, Tothmeresz B, Grigorszky I, Padisak J, Varbyro G, Szabo S (2003) Algal assemblage types of bog-lakes in Hungary and their relation to water chemistry, hydrological conditions and habitat diversity. Hydrobiologia 502:145–155
Bourrelly P (1970) Les Algues D’eau Douce Tome III: Les Algues Bleues et Rouges, Eugleniens, Peridiniens, et Cryptomonadines. Boudee, Paris
Büyükışık B, Parlak H (1989) Investigation on ecology of the Bird lake Bandirma (in Turkish). Ankara Univ J Fish 6:160–175
Çelik K (2006) Spatial and seasonal variations in chlorophyll-nutrient relationships in the shallow hypertrophic Lake Manyas, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 117:261–269
Çelik K, Ongun T (2006) Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages across nutrient gradients in the shallow hypertrophic Lake Manyas, Turkey. Lake Reserv Manage 22(3):250–260
Çelik K, Ongun T (2007) The relationships between certain physical and chemical variables and the seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton assemblagesof two inlets of a shallow hypertrophic lake with different nutrient inputs. Environ Monit Assess 124:321–330
Davidson K, Wood G, John E, Flynn K (1999) An investigation of non-steady-state algal growth I. An experimental model ecosystem. J Plankton Res 21:811–837
Dokulil MT, Teubner K (2003) Eutrophication and restoration of shallow lakes—the concept of stable equilibria revisited. Hydrobiologia 506–509:29–35
Edmondson WT (1971) Productivity in freshwaters. IPB Handbook No 17. Blackwell, Oxford
El-Bestawy EA, El-Salam AZA, Mansy AERH (2007) Potential use of environmental cyanobacterial species in bioremediation of lindane-contaminated effluents. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 59:180–192
Elliott JA, Reynolds CS, Irish TE (2000) The diversity and succession of phytoplankton communities in disturbance-free environments, using the model PROTECH. Archiv Hydrobiol 149:241–258
Feuillade JB, Feuillade M (1987) Modelling steady-state growth and photosynthesis rates of Oscillatoria rubescens continuous cultures in relation to temperature and irradiance. J Plankton Res 9:445–457
Geitler L (1925) Cyanophyceae. In: Pascher A (ed) Die Süsswasser Flora Deutschland. Österreichs und der Schweiz. Gustav Fischer, Jena, pp 1–450
Hardin G (1960) The competitive exclusion principle. Science 131:1292–1297
Hustedt F (1930) Baccillariophyta (Diatome). In: Pascher A (ed) Die Süsswasser Flora Mitteleuropas. Gustav Fischer, Jena, pp 1–466
Huszar V, Kruk C, Caraco N (2003) Steady-state assemblages of phytoplankton in four temperate lakes (NE USA). Hydrobiologia 502:97–109
Jensen NG (1985) The Pennate Diatoms (Hustedt’s Die Kieselalgen, 2. Teil). Koeltz, Koenigstein
Johnson RE, Tuchman NC, Peterson CG (1997) Changes in the vertica microdistribution of diatoms within a developing periphyton mat. J N Am Benthol Soc 16:503–519
John DM, Whitton BA, Brook AJ (2002) The freshwater algal flora of the British Isles: an identification guide to freshwater and terrestrial algae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Karafistan A, Arık-Çolakoğlu F (2005) Physical, chemical and microbiological water quality of the Manyas Lake, Turkey. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Change 10:127–143
Kelly M (2000) Identification of common benthic diatoms in rivers. Field Stud 9:583–700
Komárek and Fott (1983) Chlorophyceae (Griinalgen) Ordnung Chlorococcales. In: Huber-Pestalozzi G (ed) Das Phytoplankton des Siisswassers 7(1). Schweizerbart, Stuttgart, pp 1–1044
Komarkova J, Tavera R (2003) Steady state of phytoplankton assemblage in the tropical Lake Catemaco (Mexico). Hydrobiologia 502:187–196
Miola A, Bondesan A, Corain L, Favaretto S, Mozzi P, Piovan S, Sostizzo I (2006) Wetlands in the Venetian Po Plain (northeastern Italy) during the Last Glacial Maximum: interplay between vegetation, hydrology and sedimentary environment. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 141:53–81
Moustaka-Gouni M, Vardaka EE, Tryfon E (2007) Phytoplankton species succession in a shallow Mediterranean lake (L. Kastoria, Greece): steady-state dominance of Limnothrix redekei, Microcystis aeruginosa and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Hydrobiologia 575:129–140
Naselli-Flores L, Padisak J, Dokulil MT, Chorus I (2003) Equilibrium/steady-state concept in phytoplankton ecology. Hydrobiologia 502:395–403
Nixdorf B, Mischke U, Rucker J (2003) Phytoplankton assemblages and steady state in deep and shallow eutrophic lakes—an approach to differentiate the habitat properties of Oscillatoriales. Hydrobiologia 502:111–121
Organisation for Economic Co-operation, Development (OECD) (1982) Eutrophication of waters. Monitoring, assessment and control. OECD, Paris
Padisak J, Reynolds CS (2003) Shallow lakes: the absolute, the relative, the functional and the pragmatic. Hydrobiologia 506–509:1–11
Padisak J, Borics G, Feher G, Grigorszky I, Oldal I, Schmidt A, Zambone-Doma Z (2003) Dominant species, functional assemblages and frequency of equilibrium phases in late summer phytoplankton assemblages in Hungarian small shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 502:157–168
Reynolds CS (1993) Scales of disturbance and their role in plankton ecology. Hydrobiologia 249:157–171
Reynolds CS, Thompsom JM, Ferguson AJD, Wiseman SW (1982) Loss processes in the population dynamics of phytoplankton maintained in closed systems. J Plankton Res 4:561–600
Reynolds CS, Huszar V, Kruk C, Naselli-Flores L, Melo S (2002) Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J Plankton Res 24:417–428
SAS Institute (1990) SAS/STAT Users guide, 4th edn. Cary
Shipin OV, Rose PD, Meiring PGJ (1999) Microbial processes underlying the PETRO concept (trickling filter variant). Water Res 33:1645–1651
Sommer U, Padisak J, Reynold CS, Juhasz-Nagy P (1993) Hutchinson’s heritage: the diversity-disturbance relationship in phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 249:1–7
Stoyneva MP (1998) Development of the phytoplankton of the shallow Srebarna Lake (northeastern Bulgaria) across a trophic gradient. Hydrobiologia 369–370:259–267
Stoyneva MP (2003) Steady-state phytoplankton assemblages in shallow Bulgarian wetlands. Hydrobiologia 502:169–176
Sun J, Lıu D (2003) Geometric models for calculating cell biovolume and surface area for phytoplankton. J Plankton Res 25:1331–1346
Turkish Ministry of Environment and Forestry (2005) The environmental report for the city of Balıkesir (in Turkish), Ankara
ter Braak CJF, Verdonschot PMF (1995) Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquat Sci 57:255–289
Utermöhl H (1958) Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton. Methodik Mitt Int Ver Theor Angew Limnol 9:1–38
Via-Ordorika L, Fastner J, Kurmayer R, Hisbergues M, Dittmann E, Komarek J, Erhard M, Chorus I (2004) Distribution of microcystin-producing and non-microcystin-producing Microcystis sp. in European freshwater bodies: detection of microcystins and microcystin genes in individual colonies. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:592–602
Wetzel RG, Likens GE (1991) Limnological analyses. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Zohary T, Pais-Madeira AM, Robarts RD, Hambright KD (1995) Cyanobacteria–phytoplankton dynamics of a hypertrophic African lake. Water Sci Technol 32:103–104
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge our gratitude to Pitsa Johnson, Faculty of Clemson University, USA, for editing the manuscript prior to submission. We would like to thank the staff of Kuşcenneti National Park administration for their courtesy and help during the fieldwork. The support for this research came from Balıkesir University Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çelik, K., Ongun, T. Spatial and temporal dynamics of the steady-state phytoplankton assemblages in a temperate shallow hypertrophic lake (Lake Manyas, Turkey). Limnology 9, 115–123 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-007-0233-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-007-0233-1