Abstract
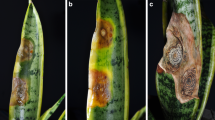
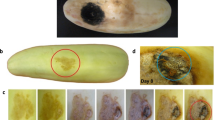
Severe spotting and blight of leaves caused by Colletotrichum destructivum were found on snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus L.), a scrophulariaceous ornamental, in open fields in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan, from June through September 2004. The fungus is added to the group of the pathogens causing anthracnose of snapdragon.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asayama E (1991) Antirrhinum L. In: Hotta M, Ogata K, Nitta A, Hoshikawa K, Yanagi M, Yamazaki K (eds) Useful plants of the world (in Japanese). Heibonsha, Tokyo, Japan, p 97
Baxter AP, van der Westhuizen GCA, Eicker A (1983) Morphology and taxonomy of South African isolates of Colletotrichum. S Afr J Bot 2:259–289
Farr DF, Bills GF, Chamuris GP, Rossman AY (eds) (1989) Fungi on plants and plant products in the United States. APS Press, St. Paul
Kawai I (ed) (1954) Horticultural diseases (in Japanese). Yokendo, Tokyo, p 532
Kawaradani M, Nishimura A, Moriwaki J, Tomioka K, Sato T, Okada K, Nakasone W (2008) Anthracnose of perilla caused by Colletotrichum destructivum (in Japanese with English summary). Jpn J Phytopathol 74:335–339
Kobayashi T (1992) Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Penzig) Penzig et Saccardo. In: Kobayashi T, Katsumoto K, Abiko K, Abe Y, Kakishima M (eds) Illustrated genera of plant pathogenic fungi in Japan (in Japanese). Zenkoku Noson Kyoiku Kyokai, Tokyo, Japan, pp 590–591
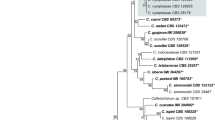
Moriwaki J, Tsukiboshi T, Sato T (2002) Grouping of Colletotrichum species in Japan based on rDNA sequences. J Gen Plant Pathol 68:307–320
Nambu N (1916) Anthracnose of snapdragon (in Japanese). Byochugai Zasshi 3:419
Phytopathological Society of Japan (ed) (2000) Common names of plant diseases in Japan (in Japanese). Japan Plant Protection Association, Tokyo, p 357
Shen S, Goodwin P, Hsiang T (2001) Hemibiotrophic infection and identity of the fungus, Colletotrichum destructivum, causing anthracnose of tobacco. Mycol Res 105:1340–1347
Stewart FC (1900) An anthracnose and a stem rot of Antirrhinum majus. Science 12:581
Sutton BC (1992) The genus Glomerella and its anamorph Colletotrichum. In: Bailey JA, Jeger MJ (eds) Colletotrichum biology, pathology and control. CABI, Wallingford, pp 1–26
Tomioka K (2005a) A trend and importance of studies on new crop-diseases caused by fungi. In: Hashiba T (ed) Developments in plant protection—bridging bioscience (in Japanese). Softscience, Tokyo, pp 15–17
Tomioka K (2005b) Demonstration and diagnosis of new fungal diseases on flowers and vegetables (in Japanese with English summary). Bull Natl Agric Res Cent West Region 5:91–187
Tomioka K, Nakamura H, Sato T (2000) Pathogenicity of Colletotrichum coccodes and C. fuscum to snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus) (Abstract). In: Proceedings of 7th international symposium of the mycological society of Japan, Tsukuba, Japan, p 63
Tomioka K, Moriwaki J, Sato T (2004a) Pathogenicity of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, C. acutatum and C. destructivum to several scrophulariaceous plants, such as Antirrhinum majus (Abstract in Japanese). In: Abstracts of papers presented at the 48th annual meeting of the Mycological Society of Japan, Nagasaki, Japan, p 83
Tomioka K, Moriwaki J, Sato T (2004b) Pathogenicity of some Colletotrichum species to petals of Antirrhinum majus. In: National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences (ed) Genetic and functional diversity of agricultural microorganisms (12th NIAS international workshop on genetic resources), Tsukuba, Japan, pp 117–118
Tomioka K, Moriwaki J, Sato T (2004c) Virulence of some Colletotrichum species to snapdragon. In: Watanabe MM, Suzuki K, Seki T (eds) Innovative roles of biological resource centers. Japan Society for Culture Collections & World Federation for Culture Collections, Tsukuba, Japan, pp 640–641
Tomioka K, Nishikawa J, Moriwaki J, Sato T (2006) Anthracnose of snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus L.) caused by Colletotrichum destructivum O’Gara (Abstract in Japanese). Jpn J Phytopathol 72:51
Tomioka K, Nishikawa J, Moriwaki J, Sato T (2007) Pathogenicity of some Colletotrichum species to scrophulariaceous, floricultural plants (Abstract in Japanese). In: Abstracts of papers presented at the 51st annual meeting of the mycological society of Japan, Tsukuba, Japan, p 61
Tomioka K, Nishikawa J, Moriwaki J, Hirooka Y, Endo M, Nagai T, Sawada H, Aoki T, Sato T (2008) Study on host range of some Colletotrichum species on scrophulariaceous ornamentals (Abstract). J Plant Pathol 90(Suppl 2):191
Tomioka K, Nishikawa J, Moriwaki J, Uzuhashi S, Nagai T, Sawada H, Aoki T, Sato T (2009) New anthracnose of snapdragon by Colletotrichum destructivum O’Gara (Abstract). In: Abstract book of Asian mycological congress 2009 and 11th international marine and freshwater mycology symposium, Taichung, Taiwan, p 116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Tomioka, J. Nishikawa, J. Moriwaki and T. Sato contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomioka, K., Nishikawa, J., Moriwaki, J. et al. Anthracnose of snapdragon caused by Colletotrichum destructivum . J Gen Plant Pathol 77, 60–63 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-010-0278-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-010-0278-6