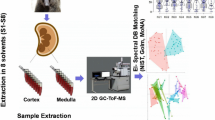
Abstract
Kidneys are an important organ since they make a significant contribution to the metabolism and excretion of drugs in vivo. The aim of this study was to identity and tentatively elucidate honokiol metabolites in the rat kidney, after healthy rats were exposed to a 1:1 mixture of labeled 13C-honokiol and unlabeled honokiol, by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer platform. This platform is well known for its fast acquisition speed, superior sensitivity, high resolution, and excellent mass accuracy. Finally, a total of 19 metabolites belonging to phase II metabolites were identified tentatively by exact mass, and the fragmentation spectra of four metabolites are reported for the first reported time. Our results indicated that honokiol was metabolized via phase II biotransformation including sulfation, acetylation, glucuronidation and amino acid conjugation in rat kidney tissues. This is the first study focused on the honokiol biotransformation in the tissue of kidney, providing important details for a comprehensive standing of the metabolites of honokiol.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaid M, Sharma SD, Katiyar SK (2010) Honokiol, a phytochemical from the Magnolia plant, inhibits photocarcinogenesis by targeting UVB-induced inflammatory mediators and cell cycle regulators: development of topical formulation. Carcinogenesis 31(11):2004–2011
Chen L, Zhang Q, Yang G, Fan L, Tang J, Garrard I, Ignatova S, Fisher D, Sutherland IA (2007) Rapid purification and scale-up of honokiol and magnolol using high-capacity high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1142(2):115–122
Chang KH, Yan MD, Yao CJ, Lin PC, Lai GM (2013) Honokiol-induced apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncol Lett 6(5):1435–1438
Guillermo RF, Santha S, Stevens J, Coughlin E, Patel P, Kaushik RS, Dwivedi C (2013) Honokiol inhibits tumor growth in a xenograft melanoma mice model and activates the apoptotic signaling pathway in vivo. Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1538-7445
Steinmann P, Walters DK, Arlt MJ, Banke IJ, Ziegler U, Langsam B, Arbiser J, Muff R, Born W, Fuchs B (2012) Antimetastatic activity of honokiol in osteosarcoma. Cancer 118(8):2117–2127
Nagalingam A, Arbiser J, Bonner MY, Saxena N, Sharma D (2012) Honokiol, a promising small molecular weight natural agent, activates AMP-activated protein kinase in breast cancer cells via LKB1-dependent pathway and inhibits breast carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1538-7445
Chilampalli S, Averineni R, Xie JS, Perumal O, Dwivedi C (2011) Development of honokiol for the prevention of UVB-induced skin tumor development. Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1538-7445
Li W, Wang Q, Su Q, Ma D, An C, Ma L, Liang H (2014) Honokiol suppresses renal cancer cells’ metastasis via dual-blocking epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell properties through modulating miR-141/ZEB2 signaling. Mol Cells 37(5):383–388
Scheepstra M, Nieto L, Hirsch AK, Fuchs S, Leysen S, Lam CV, in hetPanhuis L, van Boeckel CA, Wienk H, Boelens R, Ottmann C, Milroy LG, Brunsveld L (2014) A natural-product switch for a dynamic protein interface. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(25):6443–6448
Wu JP, Zhang W, Wu F, Zhao Y, Cheng LF, Xie JJ, Yao HP (2010) Honokiol: an effective inhibitor of high-glucose-induced up regulation of inflammatory cytokine production in human renal mesangial cells. Inflamm Res 59(12):1073–1079
Li D, Xue R, Li Z, Chen M, Jiang W, Huang C (2014) In vivo metabolism study of Timosapon in BIII in rat using HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Chromatographia 77(11–12):853–858
Huang M, Choo LW, Ho PC (2008) Characterization of metabolites of meisoindigo in male and female rat kidney microsomes by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with positive electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22(23):3835–3845
Lohr JW, Willsky GR, Acara MA (1998) Renal drug metabolism. Pharmacol rev 50(1):107–142
Imaoka S, Nagashima K, Funae Y (1990) Characterization of three cytochrome P450s purified from renal microsomes of untreated male rats and comparison with human renal cytochrome P450. Arch Biochem Biophys 276(2):473–480
Fraser DR, Kodicek E (1970) Unique biosynthesis by kidney of a biologically active vitamin D metabolite. Nutr Rev 39(5):215–218
Fraser D, Kooh SW, Kind HP, Holick MF, Tanaka Y, DeLuca HF (1973) Pathogenesis of hereditary vitamin-D-dependent rickets: an inborn error of vitamin D metabolism involving defective conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. New Engl J Med 289(16):817–822
Anders MW (1980) Metabolism of drugs by the kidney. Kidney Int 18(5):636–647
Redegeld FA, Hofman GA, Noordhoek J (1988) Conjugative clearance of 1-naphthol and disposition of its glucuronide and sulfate conjugates in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244(1):263–267
Quebbemann AJ, Anders MW (1973) Renal tubular conjugation and excretion of phenol and p-nitropiienol in the chicken: differing mechanisms of renal transfer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 184(3):695–708
Diamond GL, Quebbemann AJ (1981) In vivo quantification of renal sulfate and glucuronide conjugation in the chicken. Drug Metab Dispos 9(5):402–409
Böhmdorfer M, Maier-Salamon A, Taferner B, Reznicek G, Thalhammer T, Hering S, Hüfner A, Schühly W, Jäger W (2011) In vitro metabolism and disposition of honokiol in rat and human livers. J Pharm Sci 100(8):3506–3516
Liu J, Tang M, Lai H, Dong Y, Xie C, Ye H, Ma L, Qiu N, Li Y, Cai L, Chen L (2013) Identification of metabolites of honokiol in rat urine using 13C stable isotope labeling and liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1295:48–56
Lai H, Tang M, Liu J, Dong Y, Qiu N, Li S, Ma L, Yang J, Song H, Zhang Y, Peng A, Chen L (2013) Identification of honokiol metabolites in rats by the method of stable isotope cluster technique and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 931:157–163
Dong Y, Tang M, Song H, Li R, Wang C, Ye H, Qiu N, Zhang Y, Chen L, Wei Y (2014) Characterization of metabolic profile of honokiol in rat feces using liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry and 13C stable isotope labeling. J Chromatogr B 953–954:20–29
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81374017 and 81402493).
Conflict of interest
There authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. Wang and H. Ye contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Ye, H., Tang, M. et al. Honokiol Metabolites Study in Rat Kidney Employing UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS and 13C Stable Isotope Labeling. Chromatographia 78, 507–514 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2859-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2859-1