Abstract
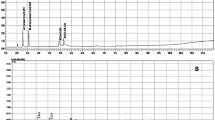
A method was developed using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC), a versatile mode of liquid chromatography, to determine cocaine, its main degradation products, benzoylecgonine and ecgonine, main pyrolytic products, anhydroecgonine and anhydroecgonine methyl ester, to be used as standards, and a frequent contaminant, levamisole. Detection of all compounds was achieved using two detectors connected in series: charged aerosol detector (CAD) and ultraviolet detector (UV). No method was found in the literature using HILIC coupled to CAD and UV to determine these compounds. The method was carried out with a Phenomenex Kinetex HILIC (150 mm × 4.6 mm ID; 2,6 µm) column with mobile-phase acetonitrile: 10 mM ammonium acetate pH 6.3 (75:25 v/v) with flow rate 0.8 mL min−1 and oven temperature set at 30 °C. CAD detection was performed using a nitrogen pressure of 35 psi, range of 100 pA and the UV detection at 200 nm. Validation parameters such as selectivity, linearity, precision and accuracy were evaluated. Methods were successfully validated to detect and quantify all related substances.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maldaner AO, Schmidt LL, Locatelli MAF, Jardim WF, Almeida FV, Pereira CEB, Silva CM (2012) Estimating Cocaine Consumption in the Brazilian Federal District (FD) by Sewage Analysis. Journal of Brazilian Chemical Society 23(5):861–867
Casa Civil—Presidência da República (2011). In: Institui o Plano Integrado de Enfrentamento ao Crack e outras Drogas, cria o seu Comitê Gestor, e dá outras providências. DECRETO No 7.179, DE 20 DE MAIO DE 2010
Casa Civil—Presidência da República (2006). In: Institui o Sistema Nacional de Políticas Públicas sobre Drogas—Sisnad; prescreve medidas para prevenção do uso indevido, atenção e reinserção social de usuários e dependentes de drogas; estabelece normas para repressão à produção não autorizada
Lociciro S, Hayoz P, Esseiva P, Dujourdy L, Besacier F, Margot P (2007) Cocaine profiling for strategic intelligence purposes, a cross-border project between France and Switzerland. Part I. Optimisation and harmonisation of the profiling method. Forensic Sci Int 167(2–3):220–228. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.06.052
Ehleringer JR, Casale JF, Barnette JE, Xu X, Lott MJ, Hurley J (2012) 14C analyses quantify time lag between coca leaf harvest and street-level seizure of cocaine. Forensic Sci Int 214(1–3):7–12. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2011.05.003
Evrard I, Legleye S, Cadet-Taïrou A (2010) Composition, purity and perceived quality of street cocaine in France. The International journal on drug policy 21(5):399–406. doi:10.1016/j.drugpo.2010.03.004
Ehleringer JR, Casale JF, Lott MJ, Ford VL, Craig O, Mulville J, Pearson MP, Sokol R, Gelsthorpe K, Stacey R, Collins M (2000) Tracing the geographical origin of cocaine. Nature 408(November):311–312
Brunt TM, Rigter S, Hoek J, Vogels N, Van Dijk P, Niesink RJM (2009) An analysis of cocaine powder in the Netherlands: content and health hazards due to adulterants. Addiction 104(5):7
Valente MJ, Carvalho F, Bastos ML, Carvalho M, Pinho PG (2012) Gas chromatography—biochemicals narcotics and essential oils. InTech. doi:10.5772/1964
Montagna M, Stramesi C, Vignali C (2000) Simultaneous hair testing for opiates, cocaine, and metabolites by GC–MS: a survey of applicants for driving licenses with a history of drug use. Forensic Sci Int 107:157–167
Lapachinske SF, Okai GG, dos Santos A, de Bairros AV, Yonamine M (2015) Analysis of cocaine and its adulterants in drugs for international trafficking seized by the Brazilian Federal Police. Forensic Sci Int 247:48–53. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2014.11.028
Buszewski B, Noga S (2012) Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)–a powerful separation technique. Anal Bioanal Chem 402(1):231–247. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5308-5
Brunetto MR, Delgado Cayama Y, Gutiérrez García L, Gallignani M, Obando M (2005) Determination of cocaine and benzoylecgonine by direct injection of human urine into a column-switching liquid chromatography system with diode-array detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 37(1):115–120. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.09.048
Pereira AG, D’Avila FB, Ferreira PCL, Holler MG, Limberger RP, Fröehlich PE (2014) Determination of cocaine, its metabolites and pyrolytic products by LC-MS using a chemometric approach. Analytical Methods 6(2):456. doi:10.1039/c3ay41548a
Bisceglia KJ, Roberts AL, Schantz MM, Lippa KA (2010) Quantification of drugs of abuse in municipal wastewater via SPE and direct injection liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 398(6):2701–2712. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-4191-9
Ikegami T, Tomomatsu K, Takubo H, Horie K, Tanaka N (2008) Separation efficiencies in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1184(1–2):474–503. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.01.075
Jia S, Park JH, Lee J, Kwon SW (2011) Comparison of two aerosol-based detectors for the analysis of gabapentin in pharmaceutical formulations by hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta 85(5):2301–2306. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2011.04.012
Bisceglia KJ, Roberts L, Lippa K (2012) A hydrolysis procedure for the analysis of total cocaine residues in wastewater. Anal Bioanal Chem 402(3):1277–1287. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5553-7
Giroud C, Michaud K, Sporkert F, Eap C, Augsburger M, Cardinal P, Mangin P (2004) A Fatal Overdose of Cocaine Associated with Coingestion of Marijuana, Buprenorphine, and Fluoxetine. Body Fluid and Tissue Distribution of Cocaine and Its Metabolites Determined by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 28(6):464–474
Gheorghe A, van Nuijs A, Pecceu B, Bervoets L, Jorens PG, Blust R, Neels H, Covaci A (2008) Analysis of cocaine and its principal metabolites in waste and surface water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 391(4):1309–1319. doi:10.1007/s00216-007-1754-5
Janicka M, Kot-Wasik A, Namieśnik J (2010) Analytical procedures for determination of cocaine and its metabolites in biological samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 29(3):209–224. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2009.12.005
Almeling S, Ilko D, Holzgrabe U (2012) Charged aerosol detection in pharmaceutical analysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 69:50–63. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2012.03.019
Dixon RW (2002) Development and testing of a detection method for liquid chromatography based on aerosol charging. Anal Chem 74(13):2930–2937
International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) (2005) Guideline validation of analytical procedures
USP 34. The United States Pharmacopeia. 35th ed. (2011). Rockville: United States Pharmacopoeial Convention
Unodoc—United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (2012) Recommended methods for the Identification and Analysis of Cocaine in Seized Materials. Viena
Joseph A, Rustum A (2010) Development and validation of a RP-HPLC method for the determination of gentamicin sulfate and its related substances in a pharmaceutical cream using a short pentafluorophenyl column and a charged aerosol detector. J Pharm Biomed Anal 51(3):521–531. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2009.09.002
Cohen RD, Liu Y, Gong X (2012) Analysis of volatile bases by high performance liquid chromatography with aerosol-based detection. J Chromatogr A 1229:172–179. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.01.036
Vervoort N, Daemen D, Török G (2008) Performance evaluation of evaporative light scattering detection and charged aerosol detection in reversed phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1189(1–2):92–100. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.10.111
Vehovec T, Obreza A (2010) Review of operating principle and applications of the charged aerosol detector. J Chromatogr A 1217(10):1549–1556. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.01.007
Gamache PH, Ryan S, Freeto SM, Asa DJ, Matthew J, Cole RO (2005) HPLC Analysis of Nonvolatile Analytes. 23(2)
Toffoli F, Avico U (1965) Unodoc coca paste residues. Viena
Passaglia M (2009) Toxicologia Forense, 2nd edn. Millennium, Campinas
Fukushima AR (2010) Perfil da cocaína comercializada como crack na região Metropolitana de São Paulo em período de vinte meses
Nováková L, Lopéz SA, Solichová D, Satínský D, Kulichová B, Horna A, Solich P (2009) Comparison of UV and charged aerosol detection approach in pharmaceutical analysis of statins. Talanta 78(3):834–839. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2008.12.057
Holzgrabe U, Nap C-J, Kunz N, Almeling S (2011) Identification and control of impurities in streptomycin sulfate by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass detection and corona charged-aerosol detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 56(2):271–279. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2011.05.027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, A.G., D’Avila, F.B., Ferreira, P.C.L. et al. Method Development and Validation for Determination of Cocaine, its Main Metabolites and Pyrolytic Products by HPLC–UV–CAD. Chromatographia 79, 179–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-3011-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-3011-y