Abstract
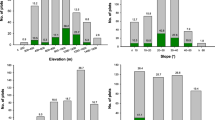
Population dynamics of forest insect pests are a key determinant of forest health globally, but there is often insufficient information on tree susceptibility and environmental drivers of attack to construct pest population models that inform management. We investigated susceptibility of Corymbia citriodora subsp. variegata (spotted gum) plantations to two stem borer families (Cerambycidae, Cossidae) for which the drivers of attack are largely unknown. We surveyed 20 plantations for borer incidence (proportion of trees attacked), severity (number of attacks/attacked tree) and height and collected environmental variables in six categories (site characteristics, physical soil characteristics, foliar nutrition, landscape structure, climate and management). Most attacks on tree stems were associated with the cerambycid beetle Phoracantha solida, which were positively related to secondary attack from the cossid moth Culama australis. Mean incidence of borer attack was 3.5% and highly variable across plantations (0–22%). Phoracantha solida incidence was highly correlated with severity at a plantation scale. Relative tree diameter was the most important associate of P. solida attack incidence; proportionately larger diameter trees were more likely to be attacked where no thinning had occurred. Foliar nutrients, specifically lower concentrations of potassium, iron and nitrogen, were associated with higher P. solida attack incidence. We suggest that measuring incidence can be used as a proxy for severity of P. solida-associated damage at a plantation scale in operational pest surveillance. The results indicate that thinning may reduce the occurrence of proportionately larger diameter trees being attacked. We also recommend further research to determine the effectiveness of adding fertiliser to remediate sites that are deficient in potassium, nitrogen and iron.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott I, Smith R, Williams M, Voutier R (1991) Infestation of regenerated stands of karri (Eucalyptus diversicolor) by bullseye borer (Tryphocaria acanthocera, Cerambycidae) in Western Australia. Aust For 54:66–74
Aukema BH, Carroll AL, Zhu J, Raffa KF, Sickley TA, Taylor SW (2006) Landscape level analysis of mountain pine beetle in British Columbia, Canada: spatiotemporal development and spatial synchrony within the present outbreak. Ecography 29:427–441
Aukema BH, Carroll AL, Zheng Y, Zhu J, Raffa KF, Moore RD, Stahl K, Taylor SW (2008) Movement of outbreak populations of mountain pine beetle: influences of spatiotemporal patterns and climate. Ecography 31:348–358
Carnegie AJ, Cant RG, Eldridge RH (2008a) Forest health surveillance in New South Wales, Australia. Aust For 71:164–176
Carnegie AJ, Lawson SA, Smith TE, Pegg GS, Stone C, McDonald JM (2008) Healthy hardwoods: a field guide to pests, diseases and nutritional disorders in subtropical hardwoods. Forest and Wood Products Australia, Victoria. http://era.daf.qld.gov.au/id/eprint/2039/. Last accessed 31 Jan 2018
Daniel WW (1999) Biostatistics: a foundation for analysis in the health sciences, 7th edn. Wiley, New York
De Schepper V, Steppe K, Van Labeke M-C, Lemeur R (2010) Detailed analysis of double girdling effects on stem diameter variations and sap flow in young oak trees. Environ Exp Bot 68:149–156
Dell B, Robinson J (1993) Symptoms of mineral nutrient deficiencies and the nutrient concentration ranges in seedlings of Eucalyptus maculata Hook. In: Barrow NJ (ed) Plant nutrition—from genetic engineering to field practice. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 285–291
Di Vaio C, Petito A, Buccheri M (2001) Effect of girdling on gas exchanges and leaf mineral content in the “Independence” nectarine. J Plant Nutr 24:1047–1060
Dormann CF, Elith J, Bacher S, Buchmann C, Carl G, Carré G, Marquéz JRG, Gruber B, Lafourcade B, Leitão PJ, Münkemüller T (2013) Collinearity: a review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 36:27–46
Driscoll DA, Kirkpatrick JB, McQuillan PB, Bonham KJ (2010) Classic metapopulations are rare among common beetle species from a naturally fragmented landscape. J Anim Ecol 79:294–303
Elith J, Leathwick JR, Hastie T (2008) A working guide to boosted regression trees. J Anim Ecol 77:802–813
Elliott HJ, Ohmart CP, Wylie FR (1998) Insect pests of Australian forests: ecology and management. Inkata Press, Melbourne
Etxebeste I, Sanchez-Husillos E, Álvarez G, Mass i Gisbert H, Pajares J (2015) Dispersal of Monochamus galloprovincialis (Col.:Cerambycidae) as recorded by mark–release–recapture using pheromone traps. J Appl Ent 140:485–499
Evans JR (1989) Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia 78:9–19
Farr JD, Dick SG, Williams MR, Wheeler IB (2000) Incidence of bullseye borer (Phoracantha acanthocera, (Macleay) Cerambycidae) in 20–35 year old regrowth karri in the south west of Western Australia. Aust For 63:107–123
Feldman RM, Curry GL, Coulson RN (1981) A mathematical model of field population dynamics of the southern pine beetle, Dendroctonus frontalis. Ecol Model 13:261–281
Fischer RA (1968) Stomatal opening: role of potassium uptake by guard cells. Science 160:784–785
Flower CE, Gonzalez-Meler MA (2015) Responses of temperate forest productivity to insect and pathogen disturbances. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66:547–569
Friedman JH (2001) Greedy function approximation: the gradient boosting machine. Ann Stat 29:1189–1232
Friedman JH (2002) Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput Stat Data Anal 38:367–378
Grove SJ (2002) Saproxylic insect ecology and the sustainable management of forests. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 33:1–23
Hanks LM, Paine TD, Millar JG (1991) Mechanisms of resistance in Eucalyptus against larvae of the eucalyptus longhorned borer (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Environ Entomol 20:1583–1588
Hanks LM, Paine TD, Millar JG, Hom JL (1995) Variation among Eucalyptus species in resistance to eucalyptus longhorned borer in Southern California. Entomol Exp Appl 74:185–194
Hanks LM, Paine TD, Millar JG, Campbell CD, Schuch UK (1999) Water relations of host trees and resistance to the phloem-boring beetle Phoracantha semipunctata F. (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Oecologia 119:400–407
Holland JD, Bert DG, Fahrig L (2004) Determining the spatial scale of species’ response to habitat. Bioscience 54:227–233
Isbell R (2002) The Australian soil classification. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood
Jenkins MJ, Hebertson E, Page W, Jorgensen CA (2008) Bark beetles, fuels, fires and implications for forest management in the Intermountain West. For Ecol Manag 254:16–34
Kareiva P, Wennergren U (1995) Connecting landscape patterns to ecosystem and population processes. Nature 373:299–302
Lawson SA, Debuse VJ (2016) Native phloem and wood borers in Australian Mediterranean forest trees. In: Paine TD, Lieutier F (eds) Insects and diseases of Mediterranean forest systems. Springer International Publishing, Bern, pp 455–473
Lawson SA, Wylie FR, Wylie RL, Ryan P (2002). Longicorn beetles (Phoracantha spp.) and giant wood moths (Endoxyla spp.): emerging threats in tropical and subtropical eucalypt plantations in Queensland, Australia. FORSPA Publication (FAO), pp 33–45
Lindsay WL (1974) Role of chelation in micronutrient availability. In: Carson EW (ed) The plant root and its environment. University Press of Virginia, Charlottesville, pp 507–524
Maathuis FJM, Amtmann A (1999) K+ nutrition and Na+ toxicity: the basis of cellular K+/Na+ ratios. Ann Bot 84:123–133
Marschner P (2012) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Martinez-Egea JM (1982) Phoracantha semipunctata Fab.en el suroeste Espanol: resumen de la campana de colocacion de arboles cebo. Boletin de la Estacion Central de Ecologia 11:57–69
Mattson WJ, Addy ND (1975) Phytophagous insects as regulators of forest primary production. Science 190:515–522
Mattson WJ, Haack RA (1987) The role of drought in outbreaks of plant-eating insects. Bioscience 37:110–118
Morin RS, Liebhold AM, Pugh SA, Crocker SJ (2016) Regional assessment of emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis, impacts in forests of the Eastern United States. Biol Invasions. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-016-1296-x
Nahrung HF, Smith TE, Wiegand AN, Lawson SA, Debuse VJ (2014) Host tree influences on longicorn beetle (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) attack in subtropical Corymbia (Myrtales: Myrtaceae). Environ Entomol 43:37–46
Naing L, Winn T, Rusli BN (2006) Practical issues in calculating the sample size for prevalence studies. Arch Orofac Sci 1:9–14
New South Wales Office of Environment and Heritage (2015) A vegetation map for the Northern Rivers Catchment Management Authority to support application of the Biodiversity Forecasting Toolkit VIS_ID 524 + Mid North Coast Vegetation (EcoLogical Version) VIS_ID 3886. www.environment.nsw.gov.au/resources/research/VegMapList.xls. Last accessed Apr 2014
Paine TD, Malinoski MK, Scriven GT (1990) Rating Eucalyptus vigor and the risk of insect infestation: leaf surface area and sapwood: heartwood ratio. Can J For Res 20:1485–1489
R Development Core Team (2004) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-pro-ject.org. Last accessed 11 Aug 2016
Ridgeway G (2004) GBM Generalized boosted regression models. R package, version 1.3-5. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/gbm/gbm.pdf. Last Accessed 17 Dec 2018
Safranik L, Wilson B (2006) The mountain pine beetle: a synthesis of biology, management and impacts on lodgepole pine. Can For Serv, Victoria, p 299
Sattler PS, Williams RD (1999) The conservation status of Queensland’s bioregional ecosystems. Environmental Protection Agency, Brisbane
Schachtman D, Liu W (1999) Molecular pieces to the puzzle of the interaction between potassium and sodium uptake in plants. Trends Plant Sci 4:281–287
Seaton S, Matusick G, Ruthrof KX, Hardy GESJ (2015) Outbreak of Phoracantha semipunctata in response to severe drought in a Mediterranean Eucalyptus forest. Forests 6:3868–3881
Shore TL, Safranyik L, Hawkes BC, Taylor SW (2006) Effects of the mountain pine beetle on lodgepole pine stand structure and dynamics. In: Safranik L, Wilson B (eds) The mountain pine beetle: a synthesis of biology, management and impacts on lodgepole pine. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria
Sousa E, Rodrigues JM, Bonifáco LF, Naves PM, Rodrigues A (2011) Management and control of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, in Portugal. In: Boeri F, Chung JA (eds) Nematodes: morphology, functions and management strategies. Hauppauge, New York
Stone C (1993) Insect pest problems of eucalypt plantations in Australia. 2. New South Wales. Aust For 56:363–369
Tscharntke T, Steffan-Dewenter I, Kruess A, Theis C (2002) Characteristics of insect populations on habitat fragments: a mini review. Ecol Res 17:229–239
Wang Q (1995) A Taxonomic revision of the Australian genus Phoracantha Newman (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Invertebr Taxon 9:865–958
White TCR (1969) An index to measure weather-induced stress of trees associated with outbreaks of psyllids in Australia. Ecology 50:905–909
Wylie FR, Peters BC (1993) Insect pest problems of eucalypt plantations in Australia. 1. Queensland. Aust For 56:358–362
Acknowledgements
We thank everyone who helped with the fieldwork including Scott Swift, John Huth, Tony Burridge, Janet McDonald, Manon Griffiths, Bruce Hogg and Chris Fitzgerald. Special thanks go to Bruce Hogg for his work on data management and programming to create the climate variables used in the study. We are very grateful to Matt Nagel for GIS analysis and to Angus Carnegie for his expertise in borer biology and his help in identifying potential sites in New South Wales. We are very grateful to Neil Gourley, formerly of HQPlantations for providing the plantation management data, and for the cooperation of HQPlantations staff more widely. We thank the land owners for allowing access to the land and the Queensland Government’s Plantation Hardwood Research Fund, HQ Plantations and the former forestry company Elders Forestry for funding the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by J.J. Duan.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debuse, V.J., Smith, T.E., Holloway, C.T. et al. Environmental influences on stem borer incidence in Australian subtropical Corymbia plantations. J Pest Sci 92, 579–593 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-01069-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-018-01069-2