Abstract
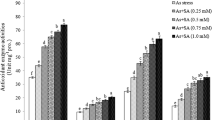
Arsenic is a non-essential and toxic heavy metal, which can cause physiological disorder in plants. The present study was undertaken to examine the possible roles of sodium nitroprusside (SNP, a donor of NO) in protection against oxidative damage due to arsenic (As) toxicity in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants. In this study, we measured physiochemical parameters (photosynthetic pigments, lipid peroxidation, endogenous hormones, minerals and phenolic contents) in faba bean plants exposed to AS (100, 200 and 400 µM) alone or combined with NO (100 µM). The results showed that application of all concentrations of arsenic (100, 200 and 400 µM) induced decrease on growth parameters, seed yield, photosynthetic pigments, phytohormones, minerals contents (N3−, P3−, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+) as compared to control plants but increased lipid peroxidation, Na + and total phenolic compounds fraction. Foliar application of 100 µM NO reversed the inhibition induced by As treatment. In addition, arsenic was undetected in harvested seeds at all applied concentrations of arsenic. Therefore, it could be concluded that NO might account for the alleviating effect of As stress on Vicia faba plants.
Zusammenfassung
Arsen ist ein nicht-essentielles und giftiges Schwermetall, das in Pflanzen zu physiologischen Störungen führen kann. Die vorliegende Studie wurde durchgeführt, um die möglichen Rollen von Natriumnitroprussid (Sodium Nitroprusside = SNP, ein NO-Ableger) als Schutz gegen oxidative Schädigung aufgrund von Arsen-Toxizität (As) in Puffbohnen-Pflanzen (Vicia faba L.) zu untersuchen. In dieser Studie ermittelten wir physiochemische Parameter (photosynthetische Pigmente, Lipidperoxidation, endogene Hormone, Mineralien und Phenolgehalt) in Puffbohnen-Pflanzen, die AS (100, 200 and 400 µM) allein oder kombiniert mit NO (100 µM) ausgesetzt waren. Die Ereignisse zeigten, dass verglichen zu den Kontrollpflanzen, die Anwendung aller Konzentrationen von Arsen (100, 200 and 400 µM) zu einem Abfall der Wachstumsparameter, Samenernte, photosynthetischen Pigmente, Phytohormone und des Mineraliengehalts (N3−, P3−, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+) führte; es gab jedoch erhöhte Werte für Lipidperoxidation, Na+ und den Gesamtanteil an Phenolverbindungen. Die Blattanwendung von 100 µM NO kehrte die durch die As-Behandlung induzierte Inhibierung um. Zusätzlich wurde Arsen bei allen angewendeten Arsenkonzentrationen nicht in geernteten Samen entdeckt. Daher konnte geschlussfolgert werden, dass NO der Grund für den mildernden Effekt bei der As-Belastung von Vicia faba-Pflanzen ist.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Rahman SS, Mazen MM, Mohamed HI, Mahmoud NM (2012) Induction of defence related enzymes and phenolic compounds in lupin (Lupinus albus L.) and their effects on host resistance against Fusarium wilt. Eur J Plant Pathol 134:105–116
Allen S, Grimshay HM, Parkinson JA, Quarmby C (1974) Chemical Analysis of ecological materials. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p 565
AOAC (1995) Association of Official Agricultural Chemists.—Official Methods of Analysis, 16th edn. Washington
AOAC (2005) Association of Official Agricultural Chemists. In: Hortwitz W, Latimer GW (eds) Official Methods of Analysis, 18th edn. Gaithersburg
Arasimowicz M, Floryszak-Wieczorek J (2007) Nitric oxide as a bioactive signaling molecule in plant stress responses. Plant Sci 172:876–887
Azizur Rahman M, Hasegava H (2011) Aquatic arsenic: phytoremediation using floating macrophytes. Chemosphere 83:633–646
Basta NT, Ryan JA, Chaney RL (2005) Trace element chemistry in residual-treated soil: key concepts and metal bioavailability. J Environ Qual 34(1):49–63
Białonska D, Zobel AM, Kura´s M, Tykarska T, Sawicka-Kapusta K (2007) Phenolic compounds and cell structure in bilberry leaves affected by emissions from a Zn-Pb smelter. Water Air Soil Poll 181(1–4):123–133
Blum U, Shafer R, Lehmen ME (1999) Evidence for inhibitory allelopathic interactions including phenolic acids in field soils. Concept vs. an experimental model. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18:673–693
Chohan A, Parmar U, Raina SK (2012) Effect of sodium nitroprusside on morphological characters under chilling stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J Environ Biol 33(4):695–698
Choudhury B, Chowdhury S, Biswas AK (2011) Regulation of growth and metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by arsenic and its possible reversal by phosphate. J Plant Interact 6(1):15–24
Cooper T (1977) The Tools of Biochemistry. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7(7):1085–1097
Dong Y, Xu L, Wang Q, Fan Z, Kong J, Bai X (2014) Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on photosynthesis, antioxidative ability, and mineral element contents of perennial ryegrass under copper stress. J Plant Interact 9(1):402–411
Duc G (1997) Faba bean (Vicia faba L). Field Crops Res 53:99–109
Durner J, Klessig DF (1999) Nitric oxide as a signal in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:369–374
Farnese FS, Alves JO, Gusman GS, Leao GA, Silveira NM, Silva PEM, Ribeiro C, Cambraia J (2014) Effects of adding nitroprusside on arsenic stressed response of Pistia stratiotes L. under hydroponic conditions. Int J Phytoremediat 16:123–137
Farrag HF, Al-Sodany YM, Otiby FG (2014) Effect of heavy metal pollution on protein expression, enzyme activity, pigments and phytohormones in some plants growing in Wadi Alargy wetlands, Taif, Saudi Arabia. Life Sci J 11(1):148–155
Finnegan PM, Chen W (2012) Arsenic toxicity: the effects on plant metabolism. Front Physiol 3:182
Garcia BM, Recamales MAF, Cordoba F (2012) Effects of cadmium on phenolic composition and antioxidant activities of Erica andevalensis. J Bot 2012:1–6
Garcia-Mata C, Lamattina L (2002) Nitric and abscisic and cross talk in guard cells. Plant Physiol 128:790–792
Gilberti L, Menezes A, Rodrigues AC, Fernandes GW, Berbara RLL, Marota HB (2014) Effects of arsenic on the growth, uptake and distribution of nutrients in the tropical species Baccharis dracunculifolia DC (Asteraceae). Euro. J Toxicol Sci 2014:1–18
Goupy P, Hugues M, Biovin P, Amiot MJ (1999) Antioxidant composition and activity of barley (Hordeum vulgare) and malt extracts and of isolated phenolic compounds. J Sci Food Agric 79(12):1625–1634
Gulz PA (2002) Arsenic uptake of common crop plants from contaminated soil sand interaction with phosphate. Swiss Fed Inst Technol Zurich (108p)
Haider S, Azmat R (2012) Failure of survival strategies in adaption of heavy metal environment in Lens culinaris and Phaseolus mungo. Pak J Bot 44(6):1959–1964
Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain MA, Fujita M (2010) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of nitric oxide induced abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Am. J Plant Physiol 5:295–324
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hogg N, Kalyanaraman B (1999) Nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation. Biochem Biophys Acta 1411:378–384
Ismail GSM (2012) Protective role of nitric oxide against arsenic-induced damages in germinating mung bean seeds. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1303–1311
Jiang MY, Yang WY, Xu J, Chen QY (1994) Active oxygen damage effect of chlorophyll degradation in rice seedlings under osmotic stress. Acta Bot Sin 36:289–295
Jin JW, Xu YF, Huang YF (2010) Protective effect of nitric oxide against arsenic-induced oxidative damage in tall fescue leaves. Afr J Biotechnol 9:1619–1627
Kazemi N (2012) Effect of exogenous nitric oxide on alleviating nickel-induced oxidative stress in leaves of tomato plants. Int J Agri Sci 2(9):799–809
Kazemi N, Khavari-Nejad RA, Fahimi H, Saadatmand S, Nejad-Sattari T (2010) Effect of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on lipid peroxidation andantioxidant enzyme activities in leaves of Brassica napus L. under nickel stress. Sci Hortic 126:402–407
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Bačkor M (2009) Phenolic metabolism of Matricaria chamomilla plants exposed to nickel. Plant Physiol 166:1460–1464
Kumari A, Sheokand S, Swaraj K (2010) Nitric oxide induced alleviation of toxic effects of short term and long term Cd stress on growth, oxidative metabolism and Cd accumulation in Chickpea. Braz J Plant Physiol 22(4):271–284
Laspina NV, Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2005) Nitric oxide protects sunflower leaves against Cd-induced oxidative stress. Plant Sci 169:323–330
Leterrier M, Valderrama R, Chaki M, Airaki M, Palma JM, Barroso JB, Corpas FJ (2012) Function of nitric oxide under environmental stress conditions. In: Khan NA, Nazer R, Iqbal N, Anjum NA (eds) Phytohormones and abiotic stress tolerance plants, Springer, Berlin, pp 99–113
Liu CP, Luo CL, Gao Y, Li FB, Lin LW, Wu CA, Li XD (2010) Arsenic contamination and potential health risk implications at an abandoned tungsten mine, southern China. Environ Poll 158:820–826
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Meharg AA, Hartley-Whitaker J (2002) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and non-resistant plant species. New Phytol 154:29–43
Metzener H, Rau H, Senger H (1965) Untersuchungen zur Synchronisierbarteit einzelner Pigmentan Angel Mutanten von Chlorela. Planta 65:186
Michalak A (2006) Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Pol J Environ Stud 15:523–530
Miller CO, Skoog F, von Saltza HM, Okumura FS, Strong FM (1955) Kinetin: structure and synthesis of kinetin. J Am Chem Soc 77:2662–2663
Mohamed HI (2011) Molecular and biochemical studies on the effect of gamma rays on lead toxicity in cowpea (Vigna sinensis) plants. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:1205–1218
Monni S, Uhling C, Hansen E, Magel E (2001) Ecophysiological responses of Empetrum nigrum to heavy metal pollution. Environ Poll 112:121–129
Muller P, Hilgenberg W (1986) Isomers of zeatin and zeatin riboside in club root tissue: evidence for trans-zeatin bio-synthesis by Plasmadiophora brassicae. Physiol Plant 66:245–250
Namdjoyana S, Kermanian H (2013) Exogenous nitric oxide (as sodium nitroprusside) ameliorates arsenic-induced oxidative stress in watercress (Nasturtium officinale R. Br.) plants. Sci Hortic 161:350–356
Ozturk F, Duma F, Leblebici Z, Temizgul R (2010) Arsenic accumulation and bio-logical responses of watercress (Nasturtium officinale R. Br.) exposed to arsenite. Environ Exp Bot 69:167–174
Pal M, Szalai G, Horvath E, Janada T, Paldi E (2002) Effect of salicylic acid during heavy metal stress. Acta Biol Szeged 46:119–120
Sampietro DA, Vattuone MA, Isla MI (2006) Plant growth inhibitors isolated from sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) straw. J Plant Physiol 163:837–846
Seregin IV, Kozhevnikova AD (2008) Roles of root and shoot tissues in transport and accumulation of cadmium, lead, nickel, and strontium. Russ J Plant Physiol 55(1):1–22
Shindy WW, Smith O (1975) Identification of plant hormones from cotton ovules. Plant Physiol 55:550–554
Singh HP, Kaur S, Batish DR, Sharma VP, Sharma N, Kohli RK (2009) Nitric oxide alleviates arsenic toxicity by reducing oxidative damage in the roots of Oryza sativa (rice). Nitric Oxide 20(4):289–297
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical methods, 7th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Stoeva N, Bineva T (2003) Oxidative changes and photosynthesis in oat plants grown in As-contaminated soil. Bulg. J Plant Physiol 29:87–95
Stoeva N, Berova М, Zlatev Z (2003) Physiological response of maize to arsenic contamination. Biol Plant 47:449–452
Talukdar D (2014) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversal by thiourea in mung bean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek.) genotype. Cent Euro. J Exp Biol 3(2):13–18
Tripathi RD, Srivastava S, Mishra S, Singh N (2007) Arsenic hazards: strategies for tolerance and remediation by plants. Trends Biotechnol 25:158–165
Tu C, Ma LQ (2005) Effects of arsenic on concentration and distribution of nutrients in the fronds of the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Environ Poll 135:333–340
Vogel AJ (1975) In a Text-book of Practical Organic Chemistry, 3rd edn. English Language Book Society and Longmans Growth Ltd., London
Wang YS, Yang ZM (2005) Nitric oxide reduces aluminum toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in the roots of Cassia tora L. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1915–1923
Wang QH, Liang X, Dong YJ, Xu LL, Zhang XW, Hou J, Fan ZY (2013) Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on cadmium toxicity, element contents and antioxidative system in perennial ryegrass. Plant Growth Regul 69:11–20
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Effects of heavy metal toxicity on growth, symbiosis, seed yield and metal uptake in pea grown in metal amended soil. Bull Environ Contam Tox 81:152–158
Xiong J, Fu G, Tao L, Zhu C (2010) Roles of nitric oxide in alleviating heavy metal toxicity in plants. Arch Biochem Biophys 497:13–20
Zhang Y, Han X, Chen X, Jin H, Cui X (2009) Exogenous nitric oxide on antioxidative system and ATPase activities from tomato seedlings under copper stress. Sci Hortei 123:217–223
Zhang XW, Dong YJ, Qiu XK, Hu GQ, Wang YH, Wang QH (2012) Exogenous nitric oxide alleviates iron-deficiency chlorosis in peanut growing on calcareous soil. Plant Soil Environ 58(3):111–120
Zheng C, Jiang D, Liu F, Dai T, Liu W, Jing Q, Cao W (2009) Exogenous nitric oxide improves seed germination in wheat against mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by high salinity. Environ Exp Bot 67(1):222–227
Zhou B, Guo Z, Xing J, Huang B (2005) Nitric oxide is involved in abscisic acid induced antioxidant activities in Stylosanthes guianensis. J Exp Bot 56:3223–3228
Zhou ZS, Guo K, Elbaz AA, Yang ZM (2009) Salicylic acid alleviates mercury toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa. Environ Exp Bot 65:27–34
Zhu JK, Liu JP, Xiong LM (1998) Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in Arabidopsis: evidence for a critical role of potassium nutrition. Plant Cell 10:1181–1191
Acknowledgment
We wish to express my deep thanks and gratitude to Prof. Dr. Awatif Aly Mohsen, Professor of Plant Physiology, Plant Department, Faculty of Sciences, Tanta University, for critical review of this manuscript and continuous encouragement throughout this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, H.I., Latif, H.H. & Hanafy, R.S. Influence of Nitric Oxide Application on Some Biochemical Aspects, Endogenous Hormones, Minerals and Phenolic Compounds of Vicia faba Plant Grown under Arsenic Stress. Gesunde Pflanzen 68, 99–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-016-0363-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-016-0363-7