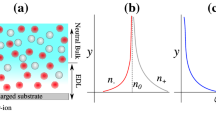
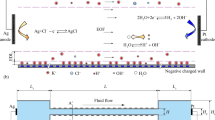
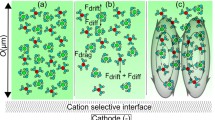
Abstract
The induced-charge electrokinetic (ICEK) phenomena are relatively new area of research in microfluidics and nanofluidics. Different from the traditional electrokinetic phenomena which are based on the interactions between applied electric field and the electrostatic charge, the ICEK phenomena result from the interaction of the applied electric field and the induced charge on polarisable surfaces. Because of the different underline physics, ICEK phenomena have many unique characteristics that may lead to new applications in microfluidics and nanofluidics. In this paper, we review the major advancement of research in the field of ICEK phenomena, discuss the applications and the limitations, and suggest some future research directions.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajdari A (2000) AC pumping of liquids. Phys Rev E 61:R45–R48
Anderson JL (1989) Colloid transport by interfacial forces. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 21:61–99
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods. Wiley, New York
Bazant MZ (2008) Nonlinear electrokinetic phenomena. In: Li D (ed) Encyclopedia of microfluidics and nanofluidics, part 14, vol 14. Springer, New York, pp 1461–1470
Bazant MZ, Ben Y (2006) Theoretical prediction of fast 3d AC electro-osmotic pumps. Lab Chip 6:1455–1461
Bazant MZ, Squires TM (2004) Induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena: theory and microfluidic applications. Phys Rev Lett 92:066101
Bazant MZ, Squires TM (2010) Induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci (in press)
Bazant MZ, Kilic MS, Storey B, Ajdari A (2009) Towards an understanding of nonlinear electrokinetics at large voltages in concentrated solutions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 152:48–88
Ben Y, Chang HC (2002) Nonlinear Smoluchowski slip velocity and micro-vortex generation. J Fluid Mech 461:229–238
Bikerman JJ (1940) Electrokinetic equations and surface conductance. A survey of the diffuse double layer theory of colloidal solutions. Trans Faraday Soc 36:154–160
Brown ABD, Smith CG, Rennie AR (2001) Pumping of water with AC electric fields applied to asymmetric pairs of microelectrodes. Phys Rev E 63:016305
Burch DN, Bazant MZ (2008) Design principle for improved three-dimensional AC electro-osmotic pumps. Phys Rev E 77:055303(R)
Chu KT, Bazant MZ (2005) Electrochemical thin films at and above the classical limiting current. SIAM J Appl Math 65:1485–1505
Chu KT, Bazant MZ (2007) Surface conservation laws at microscopically diffuse interfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 315:319–329
Dukhin AS (1986) Pair interaction of disperse particles in electric-field. 3. Hydrodynamic interaction of ideally polarizable metal particles and dead biological cells. Colloid J USSR 48:376–381
Dukhin AS (1993) Biospecific mechanism of double layer formation and peculiarities of cell electrophoresis. Colloids Surf A 73:29–48
Dukhin SS, Derjaguin BV (1974) Surface and colloid science, Chapter 2, vol 7. Academic Press, New York
Dukhin AS, Murtsovkin VA (1986) Pair interaction of particles in electric field. 2. Influence of polarization of double layer of dielectric particles on their hydrodynamic interaction in stationary electric field. Colloid J USSR 48(2):203–209
Gamayunov NI, Murtsovkin VA, Dukhin AS (1986) Pair interaction of particles in electric field. Part 1: features of hydrodynamic interaction of polarized particles. Colloid J USSR 48(2):197–203
Gamayunov NI, Mantrov GI, Murtsovkin VA (1992) Investigation of the flows induced by an external electric field in the vicinity of conducting particles. J of Colloid 54(1):26–30
Gangwal S, Cayre OJ, Bazant MZ, Velev OD (2008) Induced-charge electrophoresis of metallo-dielectric particles. Phys Rev Lett 100(5) Art No. 058302
Gonzalez A, Ramos A, Green NG, Castellanos A, Morgan H (2000) Fluid flow induced by non-uniform AC electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. II. A linear double-layer analysis. Phys Rev E 61:4019
Gonzalez A, Ramos A, Garcia-Sanchez P (2008) A castellanos effect of the difference in ion mobilities on traveling wave electro-osmosis. IEEE Int Conf Dielectric Liquids 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICDL.2008.4622452
Green NG, Ramos A, Gonzalez A, Morgan H, Castellanos A (2000) Fluid flow induced by non-uniform AC electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. I. Experimental measurements. Phys Rev E 61:4011–4018
Green NG, Ramos A, Gonzalez A, Castellanos A, Morgan H (2002) Fluid flow induced by non-uniform AC electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. III. Observation of streamlines and numerical simulation. Phys Rev E 66:026305
Gregersen MM, Okkels F, Bazant MZ, Bruus H (2009) Topology and shape optimization of induced-charge electro-osmotic micro-pumps. New J Phys 11:075016
Harnett CK, Templeton J, Dunphy-Guzman K, Senousy YM, Kanouff MP (2008) Model based design of a microfluidic mixer driven by induced charge electroosmosis. Lab Chip 8:565–572
Hoffman BD, Shaqfeh ESG (2009) The effect of Brownian motion on the stability of sedimenting suspensions of polarizable rods in an electric field. J Fluid Mech 624:361–388
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta potential in colloid science: principles and applications. Academic Press, New York
Hunter RJ (2001) Foundations of colloid science. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Khair AS, Squires TM (2008) Fundamental aspects of concentration polarization arising from non-uniform electrokinetic transport. Phys Fluids 20:087102
Kilic MS, Bazant MZ (2007) Induced-charge electrophoresis near an insulating Wall. arXiv:0712.0453
Laser DJ, Santiago JG (2004) A review of micro-pumps. J Micromech Microeng 14:R35–R64
Levich VG (1962) Physicochemical hydrodynamics. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Levitan JA, Devasenathipathy S, Studer V, Ben Y, Thorsen T, Squires TM, Bazant MZ (2005) Experimental observation of induced-charge electro-osmosis around a metal wire in a microchannel. Colloids Surf A 267:122–132
Li D (2004) Electrokinetics in microfluidics. Academic Press, New York
Li D (2008) Encyclopedia of microfluidics and nanofluidics. Springer, New York
Long D, Ajdari A (1998) Symmetry properties of the electrophoretic motion of patterned colloidal particles. Phys Rev Lett 8:1529–1532
Lyklema J (1995) Fundamentals of interface and colloid science. Volume II: solid-liquid interfaces. Academic Press, San Diego
Mansuripur T, Pascall AJ, Squires TM (2009) Asymmetric flows over symmetric surfaces: capacitive coupling in induced charge electro-osmosis. New J Phys 11:075030
Mishchuk NA, Takhistov PV (1995) Electroosmosis of the second kind. Colloids Surf A 95:119–131
Murtsovkin VA (1996) Nonlinear flows near polarized disperse particles. Colloid J 58(3):341–349
Olesen LH (2006) AC electrokinetic micro-pumps, Ph.D. thesis, Danish Technical University. http://www2.mic.dtu.dk/research/MIFTS/publications/PhD/PhDthesisLHO.pdf
Olesen LH, Bruus H, Ajdari A (2006) AC electrokinetic micropumps: the effect of geometrical confinement, faradaic current injection and nonlinear surface capacitance. Phys Rev E 73, Art. no. 056313
Olesen LH, Bazant MZ, Bruus H (2009) Strongly nonlinear dynamics of electrolytes in large ac voltages. Phys Fluid Dyn ArXiv: 0908.3501v1
Pascall AJ, Squires TM (2010) Induced charge electroosmosis over controllably-contaminated electrodes. Phys Rev Lett 104(8) (Art. no. 088301)
Ramos A, Morgan H, Green NG, Castellanos A (1999) AC electric-field-induced fluid flow in microelectrodes. J Colloid Interface Sci 217:420–422
Rose KA, Meier JA, Dougherty GM, Santiago JG (2007) Rotational electrophoresis of striped metallic microrods. Phys Rev E 75:011503
Rubinstein I, Shtilman L (1979) Voltage against current curves of cation exchange membranes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II 75:231–246
Saintillan D (2008) Nonlinear interactions in electrophoresis of ideally polarizable particles. Phys Fluids 20:067104
Saintillan D, Darve E, Shaqfeh ESG (2006a) Hydrodynamic interactions in the induced-charge electrophoresis of colloidal rod dispersions. J Fluid Mech 563:223–259
Saintillan D, Shaqfeh ESG, Darve E (2006b) Stabilization of a suspension of sedimenting rods by induced-charge electrophoresis. Phys Fluids 18(12):121503
Saville DA (1977) Electrokinetics effect with small particles. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 9:321–337
Schoch RB, Han JY, Renaud P (2008) Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev Mod Phys 80(3):839–883
Simonov IN, Dukhin SS (1973) Theory of electrophoresis of solid conducting particles in case of ideal polarization of a thin diffuse double-layer. Colloid J USSR 35(1):191–193
Soni G, Squires TM, Meinhart CD (2007) Nonlinear phenomena in induced-charge electroosmosis: a numerical and experimental investigation. In: Viovy JL, Tabeling P, Descroix S, Malaquin L (eds) Micro total analysis systems, vol 1, Chemical and Biological Microsystems Society, pp 291–293
Squires TM (2009) Induced-charge electrokinetics: fundamental challenges and opportunities. Lab Chip 9(17):2477–2483
Squires MT, Bazant MZ (2004) Induced-charge electro-osmosis. J Fluid Mech 509:217–252
Squires TM, Bazant MZ (2006) Breaking symmetries in induced-charge electro-osmosis and electrophoresis. J Fluid Mech 560:65–101
Stone H, Stroock A, Ajdari A (2004) Engineering flows in small devices: microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:381411
Studer A, Pepin A, Chen Y, Ajdari A (2004) An integrated AC electrokinetic pump in a microfluidic loop for fast tunable flow control. Analyst 129:944–949
Suh YK, Kang S (2008) Asymptotic analysis of ion transport in a nonlinear regime around polarized electrodes under AC. Phys Rev E 77:011502
Thamida S, Chang HC (2002) Nonlinear electrokinetic ejection and entrainment due to polarization at nearly insulated wedges. Phys Fluids 14:4315
Urbanski JP, Levitan JA, Bazant MZ, Thorsen T (2006a) Fast AC electro-osmotic pumps with non-planar electrodes. Appl Phys Lett 89:143508
Urbanski JP, Levitan JA, Burch DN, Thorsen T, Bazant MZ (2006b) The effect of step height on the performance of AC electro-osmotic microfluidic pumps. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:332–341
Wang SC, Chena HP, Lee CY, Yu CC, Chang SC (2006) AC electro-osmotic mixing induced by non-contact external electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 22(4):563–567
Wu J (2006) Electrokinetic microfluidics for on-chip bio-particle processing. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 5(2):84–89
Wu J (2008) Interactions of electrical fields with fluids: laboratory-on-a-chip applications. IET Nanobiotechnol 2(1):14–27
Wu Z, Li D (2008a) Micromixing using induced-charge electrokinetic flow. Electrochim Acta 53(19):5827–5835
Wu Z, Li D (2008b) Mixing and flow regulating by induced-charge electrokinetic flow in a microchannel with a pair of conducting triangle hurdles. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:65–76
Wu Z, Li D (2009) Induced-charge electrophoretic motion of ideally polarizable particles. Electrochim Acta 54:3960–3967
Wu Z, Gao Y, Li D (2009) Electrophoretic motion of ideally polarizable particles in a microchannel. Electrophoresis 30:773–781
Yariv E (2005a) Electro-osmotic flow near a surface charge discontinuity. Phys Fluids 17:051702
Yariv E (2005a) Induced-charge electrophoresis of non-spherical particles. Phys Fluids 17, Art. no. 051702
Yariv E (2008) Slender-body approximations for electrophoresis and electro-rotation of polarizable particles. J Fluid Mech 613:85–94
Yariv E (2009) Boundary-induced electrophoresis of uncharged conducting particles: remote-wall approximations. Proc R Soc A 465:709–723
Ye C, Li D (2004) 3-D transient electrophoretic motion of a spherical particle in a T-shaped rectangular microchannel. J Colloid Interface Sci 272:480–488
Yossifon G, Frankel I, Miloh T (2006) On electro-osmotic flows through microchannel junctions. Phys Fluids 18:117108
Yossifon G, Frankel I, Miloh T (2007) Symmetry breaking in induced-charge electro-osmosis over polarizable spheroids. Phys Fluids 19:068105
Zaltzman B, Rubinstein BI (2007) Electro-osmotic slip and electro-convective instability. J Fluid Mech 579:173–226
Zhao H, Bau H (2007a) A microfluidic chaotic stirrer utilizing induced-charge electro-osmosis. Phys Rev E 75:066217
Zhao H, Bau H (2007b) On the effect of induced electro-osmosis on a cylindrical particle next to a surface. Langmuir 23:4053–4063
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank the financial support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada through a research grant to D. Li.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted by request of the authors. Unaltered text was taken from a pre-published version of Bazant MZ, Squires TM (2010) Induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci1 5 (2010) 203–213. Moreover, a few reproduced figures from other published articles lack appropriate references. The authors apologize for their negligence.
An erratum to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-1026-3.
About this article
Cite this article
Daghighi, Y., Li, D. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena. Microfluid Nanofluid 9, 593–611 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0607-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0607-2