Abstract
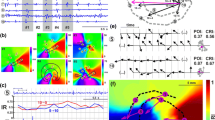
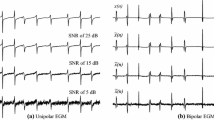
The purpose of this study is to investigate propagation patterns in intracardiac signals recorded during atrial fibrillation (AF) using an approach based on partial directed coherence (PDC), which evaluates directional coupling between multiple signals in the frequency domain. The PDC is evaluated at the dominant frequency of AF signals and tested for significance using a surrogate data procedure specifically designed to assess causality. For significantly coupled sites, the approach allows also to estimate the delay in propagation. The methods potential is illustrated with two simulation scenarios based on a detailed ionic model of the human atrial myocyte as well as with real data recordings, selected to present typical propagation mechanisms and recording situations in atrial tachyarrhythmias. In both simulation scenarios the significant PDCs correctly reflect the direction of coupling and thus the propagation between all recording sites. In the real data recordings, clear propagation patterns are identified which agree with previous clinical observations. Thus, the results illustrate the ability of the novel approach to identify propagation patterns from intracardiac signals during AF, which can provide important information about the underlying AF mechanisms, potentially improving the planning and outcome of arrhythmia ablation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arentz, T., L. Haegeli, P. Sanders, R. Weber, F. J. Neumann, D. Kalusche, and M. Haïssaguerre. High-density mapping of spontaneous pulmonary vein activity initiating atrial fibrillation in humans. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 18:31–38, 2007.
Atienza, F., J. Almendral, J. Moreno, R. Vaidyanathan, A. Talkachou, J. Kalifa, A. Arenal, J. P. Villacastín, E. G. Torrecilla, A. Sánchez, R. Ploutz-Snyder, J. Jalife, and O. Berenfeld. Activation of inward rectifier potassium channels accelerates atrial fibrillation in humans: evidence for a reentrant mechanism. Circulation 114:2434–2442, 2006.
Baccalá, L. A., and K. Sameshima. Partial directed coherence: a new concept in neural structure determination. Biol. Cybern. 84:463–474, 2001.
Baccalá, L. A., K. Sameshima, G. Ballester, A. C. D. Valle, and C. Timo-Iaria. Studying the interaction between brain structures via directed coherence and granger causality. Appl. Signal Process. 5:40–48, 1998.
Baccalá, L. A., K. Sameshima, and D. Y. Takahashi. Generalized partial directed coherence. In: Proc. 15th IEEE Int. Conf. Dig. Sig. Proc., 2007, pp. 162–166.
Barbaro, V., P. Bartolini, G. Calcagnini, F. Censi, and A. Michelucci. Measure of synchronisation of right atrial depolarisation wavefronts during atrial fibrillation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 40:56–62, 2002.
Berenfeld, O., and J. Jalife. Letter by Berenfeld and Jalife regarding article “Dominant frequency of atrial fibrillation correlates poorly with atrial fibrillation cycle length”. Circ. Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 3:e1, 2010.
Botteron, D., and J. Smith. A technique for measurement of the extent of spatial organization of atrial activation during atrial fibrillation in the intact human heart. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42:579–586, 1995.
Censi, F., V. Barbaro, P. Bartolini, G. Calcagnini, A. Michelucci, and S. Cerutti. Non-linear coupling of atrial activation processes during atrial fibrillation in humans. Biol. Cybern. 85:195–201, 2001.
Chavez, M., J. Martinerie, and M. Le Van Quyen. Statistical assessment of nonlinear causality: application to epileptic EEG signals. J. Neurosci. Methods 124:113–128, 2003.
Courtemanche, M., R. J. Ramirez, and S. Nattel. Ionic mechanisms underlying human atrial action potential properties: insights from a mathematical model. Am. J. Physiol. 275:H301–H321, 1998.
Deisenhofer, I., H. Estner, T. Reents, S. Fichtner, A. Bauer, J. Wu, C. Kolb, B. Zrenner, C. Schmitt, and G. Hessling. Does electrogram guided substrate ablation add to the success of pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation? A prospective, randomized study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 20:514–521, 2009.
Elvan, A., A. C. Linnenbank, M. W. van Bemmel, A. R. R. Misier, P. P. H. M. Delnoy, W. P. Beukema, and J. M. T. de Bakker. Dominant frequency of atrial fibrillation correlates poorly with atrial fibrillation cycle length. Circ. Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2:634–644, 2009.
Faes, L., A. Porta, and G. Nollo. Testing frequency domain causality in multivariate time series. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57:1897–1906, 2010.
Franaszczuk, P. J., G. K. Bergey, and M. J. Kaminski. Analysis of mesial temporal seizure onset and propagation using the directed transfer function method. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 91:413–427, 1994.
Freiwald, W., P. Valdes, J. Bosch, R. Biscay, J. Jimenez, L. Rodriguez, V. Rodriguez, A. Kreiter, and W. Singer. Testing non-linearity and directedness of interactions between neural groups in the macaque inferotemporal cortex. J. Neurosci. Methods 94:105–119, 1999.
Granger, C. W. J. Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 37:424–443, 1969.
Grzeda, K. R., S. F. Noujaim, O. Berenfeld, and J. Jalife. Complex fractionated atrial electrograms: properties of time-domain versus frequency-domain methods. Heart Rhythm 6:1475–1482, 2009.
Haissaguerre, M., P. Jais, D. Shah, A. Takahashi, M. Hocini, G. Quiniou, S. Garrigue, A. L. Mouroux, P. L. Métayer, and J. Clémenty. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 339:659–666, 1998.
Hoekstra, B. P. T., C. G. H. Diks, M. A. Allessie, and J. DeGoede. Non-linear time series analysis: methods and applications to atrial fibrillation. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanità. 37:325–333, 2001.
Jacquemet, V., N. Virag, Z. Ihara, L. Dang, O. Blanc, S. Zozor, J. M. Vesin, L. Kappenberger, and C. Henriquez. Study of unipolar electrogram morphology in a computer model of atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 14:S172–S179, 2003.
Moe, G. On the multiple wavelet hypothesis of atrial fibrillation. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 140:183–188, 1962.
Müller, T., M. Lauk, M. Reinhard, A. Hetzel, C. H. Lücking, and J. Timmer. Estimation of delay times in biological systems. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31:1423–1439, 2003.
Nademanee, K., J. McKenzie, E. Kosar, M. Schwab, B. Sunsaneewitayakul, T. Vasavakul, C. Khunnawat, and T. Ngarmukos. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 43:2044–2053, 2004.
Ng, J., A. H. Kadish, and J. J. Goldberger. Effect of electrogram characteristics on the relationship of dominant frequency to atrial activation rate in atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 3:1295–1305, 2006.
O’Donnell, D., S. S. Furniss, and J. P. Bourke. Dynamic alterations in right atrial activation during atrial fibrillation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 8:37–40, 2003.
Oral, H., A. Chugh, E. Good, A. Wimmer, S. Dey, N. Gadeela, S. Sankaran, T. Crawford, J. F. Sarrazin, M. Kuhne, N. Chalfoun, D. Wells, M. Frederick, J. Fortino, S. Benloucif-Moore, K. Jongnarangsin, F. Pelosi, F. Bogun, and F. Morady. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation guided by complex electrograms. Circulation 115:2606–2612, 2007.
Platonov, P., M. Stridh, and L. Sörnmo. Letter by Platonov et al regarding article “Dominant frequency of atrial fibrillation correlates poorly with atrial fibrillation cycle length”. Circ. Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 3:e4, 2010.
Ravelli, F., L. Faes, L. Sandrini, F. Gaita, R. Antolini, M. Scaglione, and G. Nollo. Wave similarity mapping shows the spatiotemporal distribution of fibrillatory wave complexity in the human right atrium during paroxysmal and chronic atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 16:1071–1076, 2005.
Richter, U., A. Bollmann, D. Husser, and M. Stridh. Right atrial organization and wavefront analysis in atrial fibrillation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 47:1237–1246, 2009.
Rush, S., and H. Larsen. A practical algorithm for solving dynamic membrane equations. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 25:389–392, 1978.
Saksena, S., N. D. Skadsberg, H. B. Rao, and A. Filipecki. Biatrial and three-dimensional mapping of spontaneous atrial arrhythmias in patients with refractory atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 16:494–504, 2005.
Sanders, P., O. Berenfeld, M. Hocini, P. Jais, R. Vaidyanathan, L. F. Hsu, S. Garrigue, Y. Takahashi, M. Rotter, F. Sacher, C. Scavée, R. Ploutz-Snyder, J. Jalife, and M. Haissaguerre. Spectral analysis identifies sites of high-frequency activity maintaining atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation 112:789–797, 2005.
Schelter, B., J. Timmer, and M. Eichler. Assessing the strength of directed influences among neural signals using renormalized partial directed coherence. J. Neurosci. Methods 179(1):121–130, 2009.
Schwarz, G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 6:461–464, 1978.
Sih, H. J., A. V. Sahakian, C. E. Arentzen, and S. Swiryn. A frequency domain analysis of spatial organization of epicardial maps. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42:718–727, 1995.
Valdés-Sosa, P. A., J. M. Sánchez-Bornot, A. Lage-Castellanos, M. Vega-Hernández, J. Bosch-Bayard, L. Melie-García, and E. Canales-Rodríguez. Estimating brain functional connectivity with sparse multivariate autoregression. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 360:969–981, 2005.
Wilke, C., L. Ding, and B. He. Estimation of time-varying connectivity patterns through the use of an adaptive directed transfer function. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 55:2557–2564, 2008.
Zozor, S., O. Blanc, V. Jacquemet, N. Virag, J. M. Vesin, E. Pruvot, L. Kappenberger, and C. Henriquez. A numerical scheme for modeling wavefront propagation on a monolayer of arbitrary geometry. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 50:412–420, 2003.
Zrenner, B., G. Ndrepepa, M. R. Karch, M. A. Schneider, J. Schreieck, A. Schömig, and C. Schmitt. Electrophysiologic characteristics of paroxysmal and chronic atrial fibrillation in human right atrium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 38:1143–1149, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Nathalie Virag oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, U., Faes, L., Cristoforetti, A. et al. A Novel Approach to Propagation Pattern Analysis in Intracardiac Atrial Fibrillation Signals. Ann Biomed Eng 39, 310–323 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-010-0146-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-010-0146-8