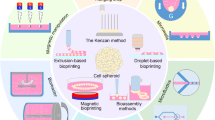
Abstract
Microstructured extracellular matrix (ECM), which contains heterogeneous features of the same size scale (5–100 μm) as tissue organoids, has become an important material for the engineering of functional tissues and for the study of tissue-level biology. This review describes methods to generate this class of ECM, and highlights recent advances in the application of microstructured ECM to problems in basic and applied biology. It also discusses computational techniques to analyze and optimize the microstructural patterns for a desired functional output.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affolter, M., S. Bellusci, N. Itoh, B. Shilo, J.-P. Thiery, and Z. Werb. Tube or not tube: remodeling epithelial tissues by branching morphogenesis. Dev. Cell 4:11–18, 2003.
Barocas, V. H., A. G. Moon, and R. T. Tranquillo. The fibroblast-populated collagen microsphere assay of cell traction force—part 2: measurement of the cell traction parameter. J. Biomech. Eng. 117:161–170, 1995.
Bellamkonda, R. V. Peripheral nerve regeneration: an opinion on channels, scaffolds and anisotropy. Biomaterials 27:3515–3518, 2006.
Bettinger, C. J., K. M. Cyr, A. Matsumoto, R. Langer, J. T. Borenstein, and D. L. Kaplan. Silk fibroin microfluidic devices. Adv. Mater. 19:2847–2850, 2007.
Cabodi, M., N. W. Choi, J. P. Gleghorn, C. S. Lee, L. J. Bonassar, and A. D. Stroock. A microfluidic biomaterial. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127:13788–13789, 2005.
Choi, N. W., M. Cabodi, B. Held, J. P. Gleghorn, L. J. Bonassar, and A. D. Stroock. Microfluidic scaffolds for tissue engineering. Nat. Mater. 6:908–915, 2007.
Chrobak, K. M., D. R. Potter, and J. Tien. Formation of perfused, functional microvascular tubes in vitro. Microvasc. Res. 71:185–196, 2006.
Cui, X., and T. Boland. Human microvasculature fabrication using thermal inkjet printing technology. Biomaterials 30:6221–6227, 2009.
Du, Y., E. Lo, S. Ali, and A. Khademhosseini. Directed assembly of cell-laden microgels for fabrication of 3D tissue constructs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105:9522–9527, 2008.
Engelmayr, Jr., G. C., M. Cheng, C. J. Bettinger, J. T. Borenstein, R. Langer, and L. E. Freed. Accordion-like honeycombs for tissue engineering of cardiac anisotropy. Nat. Mater. 7:1003–1010, 2008.
Gjorevski, N., and C. M. Nelson. Endogenous patterns of mechanical stress are required for branching morphogenesis. Integr. Biol. 2:424–434, 2010.
Gjorevski, N., and C. M. Nelson. Mapping of mechanical strains and stresses around quiescent engineered three-dimensional epithelial tissues. Biophys. J. 103:152–162, 2012.
Golden, A. P., and J. Tien. Fabrication of microfluidic hydrogels using molded gelatin as a sacrificial element. Lab Chip 7:720–725, 2007.
Guo, C.-L., M. Ouyang, J.-Y. Yu, J. Maslov, A. Price, and C.-Y. Shen. Long-range mechanical force enables self-assembly of epithelial tubular patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109:5576–5582, 2012.
Guo, L., and J. J. Pribaz. Clinical flap prefabrication. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 124:340e–350e, 2009.
Hahn, M. S., J. S. Miller, and J. L. West. Three-dimensional biochemical and biomechanical patterning of hydrogels for guiding cell behavior. Adv. Mater. 18:2679–2684, 2006.
Hay, E. D. Collagen and other matrix glycoproteins in embryogenesis. In: Cell Biology of Extracellular Matrix, edited by E. D. Hay. New York: Plenum Press, 1991, pp. 419–462.
Ilina, O., G.-J. Bakker, A. Vasaturo, R. M. Hofmann, and P. Friedl. Two-photon laser-generated microtracks in 3D collagen lattices: principles of MMP-dependent and -independent collective cancer cell invasion. Phys. Biol. 8:015010, 2011.
Khademhosseini, A., R. Langer, J. Borenstein, and J. P. Vacanti. Microscale technologies for tissue engineering and biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103:2480–2487, 2006.
Kloxin, A. M., A. M. Kasko, C. N. Salinas, and K. S. Anseth. Photodegradable hydrogels for dynamic tuning of physical and chemical properties. Science 324:59–63, 2009.
Koh, W.-G., A. Revzin, and M. V. Pishko. Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel microstructures encapsulating living cells. Langmuir 18:2459–2462, 2002.
Lee, K., N. Gjorevski, E. Boghaert, D. C. Radisky, and C. M. Nelson. Snail1, Snail2, and E47 promote mammary epithelial branching morphogenesis. EMBO J. 30:2662–2674, 2011.
Ling, Y., J. Rubin, Y. Deng, C. Huang, U. Demirci, J. M. Karp, and A. Khademhosseini. A cell-laden microfluidic hydrogel. Lab Chip 7:756–762, 2007.
Mak, A. F. Unconfined compression of hydrated viscoelastic tissues: a biphasic poroviscoelastic analysis. Biorheology 23:371–383, 1986.
Miller, J. S., K. R. Stevens, M. T. Yang, B. M. Baker, D.-H. T. Nguyen, D. M. Cohen, E. Toro, A. A. Chen, P. A. Galie, X. Yu, R. Chaturvedi, S. N. Bhatia, and C. S. Chen. Rapid casting of patterned vascular networks for perfusable engineered three-dimensional tissues. Nat. Mater. 11:768–774, 2012.
Mow, V. C., S. C. Kuei, W. M. Lai, and C. G. Armstrong. Biphasic creep and stress relaxation of articular cartilage in compression: theory and experiments. J. Biomech. Eng. 102:73–84, 1980.
Nelson, C. M., and M. J. Bissell. Of extracellular matrix, scaffolds, and signaling: tissue architecture regulates development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 22:287–309, 2006.
Nelson, C. M., J. L. Inman, and M. J. Bissell. Three-dimensional lithographically defined organotypic tissue arrays for quantitative analysis of morphogenesis and neoplastic progression. Nat. Protoc. 3:674–678, 2008.
Nelson, C. M., and J. Tien. Microstructured extracellular matrices in tissue engineering and development. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 17:518–523, 2006.
Nelson, C. M., M. M. VanDuijn, J. L. Inman, D. A. Fletcher, and M. J. Bissell. Tissue geometry determines sites of mammary branching morphogenesis in organotypic cultures. Science 314:298–300, 2006.
Nguyen, D.-H. T., S. C. Stapleton, M. T. Yang, S. S. Cha, C. K. Choi, P. A. Galie, and C. S. Chen. Biomimetic model to reconstitute angiogenic sprouting morphogenesis in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110:6712–6717, 2013.
Nichol, J. W., S. T. Koshy, H. Bae, C. M. Hwang, S. Yamanlar, and A. Khademhosseini. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 31:5536–5544, 2010.
Ott, H. C., B. Clippinger, C. Conrad, C. Schuetz, I. Pomerantseva, L. Ikonomou, D. Kotton, and J. P. Vacanti. Regeneration and orthotopic transplantation of a bioartificial lung. Nat. Med. 16:927–933, 2010.
Ott, H. C., T. S. Matthiesen, S.-K. Goh, L. D. Black, S. M. Kren, T. I. Netoff, and D. A. Taylor. Perfusion-decellularized matrix: using nature’s platform to engineer a bioartificial heart. Nat. Med. 14:213–221, 2008.
Pavlovich, A. L., E. Boghaert, and C. M. Nelson. Mammary branch initiation and extension are inhibited by separate pathways downstream of TGFβ in culture. Exp. Cell Res. 317:1872–1884, 2011.
Petersen, T. H., E. A. Calle, L. Zhao, E. J. Lee, L. Gui, M. B. Raredon, K. Gavrilov, T. Yi, Z. W. Zhuang, C. Breuer, E. Herzog, and L. E. Niklason. Tissue-engineered lungs for in vivo implantation. Science 329:538–541, 2010.
Polacheck, W. J., R. Li, S. G. M. Uzel, and R. D. Kamm. Microfluidic platforms for mechanobiology. Lab Chip 13:2252–2267, 2013.
Price, G. M., K. K. Chu, J. G. Truslow, M. D. Tang-Schomer, A. P. Golden, J. Mertz, and J. Tien. Bonding of macromolecular hydrogels using perturbants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130:6664–6665, 2008.
Price, G. M., K. H. K. Wong, J. G. Truslow, A. D. Leung, C. Acharya, and J. Tien. Effect of mechanical factors on the function of engineered human blood microvessels in microfluidic collagen gels. Biomaterials 31:6182–6189, 2010.
Reiffel, A. J., P. W. Henderson, D. D. Krijgh, D. A. Belkin, Y. Zheng, L. J. Bonassar, A. D. Stroock, and J. A. Spector. Mathematical modeling and frequency gradient analysis of cellular and vascular invasion into Integra and Strattice: toward optimal design of tissue regeneration scaffolds. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 129:89–99, 2012.
Schumacher, K. M., S. C. Phua, A. Schumacher, and J. Y. Ying. Controlled formation of biological tubule systems in extracellular matrix gels in vitro. Kidney Int. 73:1187–1192, 2008.
Simian, M., Y. Hirai, M. Navre, Z. Werb, A. Lochter, and M. J. Bissell. The interplay of matrix metalloproteinases, morphogens and growth factors is necessary for branching of mammary epithelial cells. Development 128:3117–3131, 2001.
Song, J. J., J. P. Guyette, S. E. Gilpin, G. Gonzalez, J. P. Vacanti, and H. C. Ott. Regeneration and experimental orthotopic transplantation of a bioengineered kidney. Nat. Med. 19:646–651, 2013.
Sung, J. H., J. Yu, D. Luo, M. L. Shuler, and J. C. March. Microscale 3-D hydrogel scaffold for biomimetic gastrointestinal (GI) tract model. Lab Chip 11:389–392, 2011.
Tang, M. D., A. P. Golden, and J. Tien. Molding of three-dimensional microstructures of gels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125:12988–12989, 2003.
Tang, M. D., A. P. Golden, and J. Tien. Fabrication of collagen gels that contain patterned, micrometer-scale cavities. Adv. Mater. 16:1345–1348, 2004.
Tien, J., J. G. Truslow, and C. M. Nelson. Modulation of invasive phenotype by interstitial pressure-driven convection in aggregates of human breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 7:e45191, 2012.
Truslow, J. G., G. M. Price, and J. Tien. Computational design of drainage systems for vascularized scaffolds. Biomaterials 30:4435–4443, 2009.
Truslow, J. G., and J. Tien. Perfusion systems that minimize vascular volume fraction in engineered tissues. Biomicrofluidics 5:022201, 2011.
Uygun, B. E., A. Soto-Gutierrez, H. Yagi, M.-L. Izamis, M. A. Guzzardi, C. Shulman, J. Milwid, N. Kobayashi, A. Tilles, F. Berthiaume, M. Hertl, Y. Nahmias, M. L. Yarmush, and K. Uygun. Organ reengineering through development of a transplantable recellularized liver graft using decellularized liver matrix. Nat. Med. 16:814–820, 2010.
Vernon, R. B., M. D. Gooden, S. L. Lara, and T. N. Wight. Native fibrillar collagen membranes of micron-scale and submicron thicknesses for cell support and perfusion. Biomaterials 26:1109–1117, 2005.
Vracko, R., and E. P. Benditt. Basal lamina: the scaffold for orderly cell replacement. Observations on regeneration of injured skeletal muscle fibers and capillaries. J. Cell Biol. 55:406–419, 1972.
Wang, H. F. Theory of Linear Poroelasticity with Applications to Geomechanics and Hydrogeology. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2000, 287 pp.
Wong, K. H. K., J. M. Chan, R. D. Kamm, and J. Tien. Microfluidic models of vascular functions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 14:205–230, 2012.
Wong, K. H. K., J. G. Truslow, A. H. Khankhel, K. L. S. Chan, and J. Tien. Artificial lymphatic drainage systems for vascularized microfluidic scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 101:2181–2190, 2013.
Wong, K. H. K., J. G. Truslow, and J. Tien. The role of cyclic AMP in normalizing the function of engineered human blood microvessels in microfluidic collagen gels. Biomaterials 31:4706–4714, 2010.
Zheng, Y., J. Chen, M. Craven, N. W. Choi, S. Totorica, A. Diaz-Santana, P. Kermani, B. Hempstead, C. Fischbach-Teschl, J. A. López, and A. D. Stroock. In vitro microvessels for the study of angiogenesis and thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109:9342–9347, 2012.
Zheng, Y., P. W. Henderson, N. W. Choi, L. J. Bonassar, J. A. Spector, and A. D. Stroock. Microstructured templates for directed growth and vascularization of soft tissue in vivo. Biomaterials 32:5391–5401, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Tzung Hsiai oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tien, J., Nelson, C.M. Microstructured Extracellular Matrices in Tissue Engineering and Development: An Update. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 1413–1423 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0912-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0912-5