Abstract
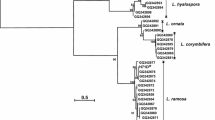
Sixteen yeast isolates identified as belonging to the genus Sugiyamaella were studied in relation to D-xylose fermentation, xylitol production, and xylanase activities. The yeasts were recovered from rotting wood and sugarcane bagasse samples in different Brazilian regions. Sequence analyses of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region and the D1/D2 domains of large subunit rRNA gene showed that these isolates belong to seven new species. The species are described here as Sugiyamaella ayubii f.a., sp. nov. (UFMG-CM-Y607T = CBS 14108T), Sugiyamaella bahiana f.a., sp. nov. (UFMG-CM-Y304T = CBS 13474T), Sugiyamaella bonitensis f.a., sp. nov. (UFMG-CM-Y608T = CBS 14270T), Sugiyamaella carassensis f.a., sp. nov. (UFMG-CM-Y606T = CBS 14107T), Sugiyamaella ligni f.a., sp. nov. (UFMG-CM-Y295T = CBS 13482T), Sugiyamaella valenteae f.a., sp. nov. (UFMG-CM-Y609T = CBS 14109T) and Sugiyamaella xylolytica f.a., sp. nov. (UFMG-CM-Y348T = CBS 13493T). Strains of the described species S. boreocaroliniensis, S. lignohabitans, S. novakii and S. xylanicola, isolated from rotting wood of Brazilian ecosystems, were also compared for traits relevant to xylose metabolism. S. valenteae sp. nov., S. xylolytica sp. nov., S. bahiana sp. nov., S. bonitensis sp. nov., S. boreocarolinensis, S. lignohabitans and S. xylanicola were able to ferment d-xylose to ethanol. Xylitol production was observed for all Sugiyamaella species studied, except for S. ayubii sp. nov. All species studied showed xylanolytic activity, with S. xylanicola, S. lignohabitans and S. valenteae sp. nov. having the highest values. Our results suggest these Sugiyamaella species have good potential for biotechnological applications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 21:403–410
Biely P, Vrsanská M, Krátký Z (1980) Xylan-degrading enzymes of the yeast Cryptococcus albidus. Eur J Biochem 108:313–321
Cadete RM, Santos RO, Melo MA, Mouro A, Gonçalves DL, Stambuk BU, Gomes FCO, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2009) Spathaspora arborariae sp. nov., a D-xylose-fermenting yeast species isolated from rotting wood in Brazil. FEMS Yeast Res 9:1338–1342
Cadete RM, Melo MA, Dussán KJ, Rodrigues RCLB, da Silva SS, Zilli JE, Vital MJS, Gomes FCO, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2012) Diversity and physiological characterization of d-xylose-fermenting yeasts isolated from the Brazilian Amazonian Forest. PLoS One 7:e43135
Cadete RM, Melo MA, Zilli JE, Vital MJ, Mouro A, Prompt AH, Gomes FC, Stambuk BU, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2013) Spathaspora brasiliensis sp. nov., Spathaspora suhii sp. nov., Spathaspora roraimanensis sp. nov. and Spathaspora xylofermentans sp. nov., four novel d-xylose-fermenting yeast species from Brazilian Amazonian forest. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:421–431
Cadete RM, Cheab MAM, Santos RO, Safar SVB, Zilli JE, Vital MJS, Basso LC, Lee CF, Kurtzman CP, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2015) Cyberlindnera xylosilytica sp. nov., a xylitol-producing yeast species isolated from lignocellulosic materials. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:2968–2974
da Silva SS, Afschar AS (1994) Microbial production of xylitol from d-xylose using Candida tropicalis. Bioprocess Eng 11:129–134
Gírio FM, Fonseca C, Carvalheiro F, Duarte LC, Marques S, Bogel-Łukasik R (2010) Hemicelluloses for fuel ethanol: a review. Bioresource Technol 101:4775–4800
Guamán-Burneo MC, Dussán KJ, Cadete RM, Cheab MA, Portero P, Carvajal-Barriga EJ, Silva SS, Rosa CA (2015) Xylitol production by yeasts isolated from rotting wood in the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador, and description of Cyberlindnera galapagoensis f.a., sp. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 108:919–931
Hernández-Pérez AF, de Arruda PV, de Almeida Felipe MDG (2016) Sugarcane straw as a feedstock for xylitol production by Candida guilliermondii FTI 20037. Braz J Microbiol 47:489–496
Houseknecht JL, Hart EL, Suh SO, Zhou JJ (2011) Yeasts in the Sugiyamaella clade associated with wood-ingesting beetles and the proposal of Candida bullrunensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1751–1756
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol. doi:10.1093/molbev/msw054
Kurtzman CP (2011) Sugiyamaella Kurtzman & Robnett 2007. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 817–822
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1998) Identification and phylogeny of ascomycetous yeasts from analysis of nuclear large subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA partial sequences. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73:331–371
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (2013) Relationships among genera of the Saccharomycotina (Ascomycota) from multigene phylogenetic analysis of type species. FEMS Yeast Res 13:23–33
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (2011a) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T, Robert V (2011b) Methods for isolation, phenotypic characterization and maintenance of yeasts. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (eds) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 87–110
Lachance MA (2012) In defense of yeast sexual life cycles: the forma asexualis-an informal proposal. Yeast Newsl 61:24–25
Lachance MA, Bowles JM, Starmer WT, Barker JSF (1999) Kodamaea kakaduensis and Candida tolerans, two new ascomycetous yeast species from Australian Hibiscus flowers. Can J Microbiol 45:172–177
Lara CA, Santos RO, Cadete RM, Ferreira C, Marques S, Gírio F, Oliveira ES, Rosa CA, Fonseca C (2014) Identification and characterization of xylanolytic yeasts isolated from decaying wood and sugarcane bagasse in Brazil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105:1107–1119
Leathers TD, Gupta SC (1997) Xylitol and riboflavin accumulation in xylose-grown cultures of Pichia guilliermondii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:58–61
Lopes MR, Morais CG, Kominek J, Cadete RM, Soares MA, Uetanabaro APT, Fonseca C, Lachance MA, Hittinger CT, Rosa CA (2016) Genomic analysis and D-xylose fermentation of three novel Spathaspora species: spathaspora girioi sp. nov., Spathaspora hagerdaliae f. a., sp. nov., and Spathaspora gorwiae f. a., sp. nov. FEMS Yeast Res. doi:10.1093/femsyr/fow044
Magioli MD, Scardini VAC, Bastos M, Juliana B, Miguel A, Franck T (2014) A mobilidade brasileira como etanol de segunda geração. Blucher Eng Proc 1:333–350
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Mohamad NL, Kamal SMM, Mokhtar MN (2015) Xylitol biological production: a review of recent studies. Food Rev Int 31:74–89
Morais CG, Lara CA, Marques S, Fonseca C, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2013a) Sugiyamaella xylanicola sp. nov., a xylan-degrading yeast species isolated from rotting-wood in Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2356–2360
Morais CG, Cadete RM, Uetanabaro APT, Rosa LH, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2013b) D-xylose-fermenting and xylanase-producing yeast species from rotting wood of two Atlantic rainforest habitats in Brazil. Fungal Genet Biol 60:19–28
O’Donnell K (1993) Fusarium and its near relatives. In: Reynolds DR, Taylor JW (eds) The fungal holomorph: mitotic, meiotic and pleomorphic speciation in fungal systematic. Proceedings of an international symposium, Oregon, pp 225–233
Prakasham RS, Screenivas R, Hobbs PJ (2009) Current trends in biotechnological production of xylitol and future prospects. Curr Trends Biotechnol Pharm 3:8–36
Ren Y, Chen L, Niu Q, Hui F (2014) Description of Scheffersomyces henanensis sp. nov., a new d-xylose-fermenting yeast species isolated from rotten wood. PLoS One 9:e92315
Sampaio FC, Chaves-Alves VM, Converti A, Passos FML, Coelho JLC (2008) Influence of cultivation conditions on xylose-to-xylitol bioconversion by a new isolate of Debaryomyces hansenii. Bioresour Technol 99:502–508
Schmidell W, Lima UDA, Aquarone E, Borzani W (2001) Modelagem matemática e simulação de processos fermentativos. Biotecnol Ind 2:123–178
Sylvester K, Wang QM, James B, Mendez R, Hulfachor AB, Hittinger CT (2015) Temperature and host preferences drive the diversification of Saccharomyces and other yeasts: a survey and the discovery of eight new yeast species. FEMS Yeast Res 15:002
Urbina H, Schuster J, Blackwell M (2013) The gut of guatemalan passalid beetles: a habitat colonized by cellobiose- and xylose-fermenting yeasts. Fungal Ecol 6:339–355
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee SJWT, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Yano S (2015) Enzymatic saccharification and fermentation technology for ethanol production from woody biomass. J Jpn Pet Inst 58:128–134
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnológico (CNPq—Brazil, Process Number 457499/2014-1), Fundação do Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG, process number APQ-01525-14) and the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (MAL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Letícia M. F. Sena and Camila G. Morais have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sena, L.M.F., Morais, C.G., Lopes, M.R. et al. d-Xylose fermentation, xylitol production and xylanase activities by seven new species of Sugiyamaella . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 53–67 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0775-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0775-5