Abstract
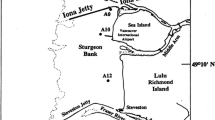
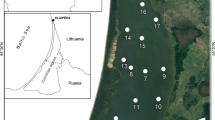
Mesophotic (low light) sands were studied in Hawaiian coastal waters (39–204 m water depth) from O‘ahu to Kaho‘olawe by sampling inside and outside of extensive macroalgal meadows of chlorophytes Halimeda kanaloana and Udotea sp. during September 2004, December 2004, and November 2006. Porewater nutrient concentrations in these permeable sediments were comparable to those in nearshore sands and were highly elevated at sediment depths available to holdfasts of some algae (5–10 cm); maximum levels were 3.0 µM reactive phosphorus, 33 µM nitrate, 0.70 µM nitrite, 38 µM ammonium, and 130 µM silicic acid. Benthic material is calculated to be the major source of organic matter driving diagenesis in these sediments. Vegetated sediments appeared more oxidizing than unvegetated sediments, and the presence of macroalgae, particularly Halimeda, was generally associated with higher sediment dissolved inorganic carbon levels. Halimeda-vegetated sediments generally had low dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) levels compared to the Udotea-vegetated and non-vegetated sediments, consistent with the net N loss indicated by sediment stoichiometric relationships. In contrast, Udotea-vegetated sediments showed minimal apparent algal DIN uptake.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott IA, Huisman JM (2004) Marine green and brown algae of the Hawaiian Islands. Bishop Museum Press, Hawai‘i
Agegian CR, Abbott IA (1985) Deep water macroalgal communities: a comparison between Penguin Bank (Hawaii) and Johnston Atoll. In: Harmelin VM, Salvat B, La Croix C, Gabrie C, Toffart JL (eds) Proceeding of the 5th international coral reef congress, vol 5. Antenne Museum-Ephe, Moorea
Alford MH, Gregg MC, Merrifield MA (2006) Structure, propagation, and mixing of energetic baroclinic tides in Mamala Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. J Phys Oceanogr 36:997–1018
Aponte NE, Ballantine DL (2001) Depth distribution of algal species on the deep insular fore reef at Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas. Deep-Sea Res 48:2185–2194
Ascani F, Richards KJ, Firing E, Grant S, Johnson KS, Jia Y, Lukas R, Karl DM (2013) Physical and biological controls of nitrate concentrations in the upper subtropical North Pacific Ocean. Deep-Sea Res 93:119–134
Atkinson MJ, Smith SV (1983) C:N: P ratios of benthic marine plants. Limnol Oceanogr 28:568–574
Berner RA (1977) Stoichiometric models for nutrient regeneration in anoxic sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 22:781–786
Broecker WS, Peng TH (1982) Tracers in the sea. Eldigio Press, Lamont-Doherty Geol Obs, New York
Burdige DJ (2006) Geochemistry of marine sediments. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Canfield DE, Thamdrup B (2009) Towards a consistent classification scheme for geochemical environments, or, why we wish the term ‘suboxic’ would go away. Geobiology 7:385–392
Colin PL (1986) Benthic community distribution in the Enewetak Atoll lagoon, Marshall Islands. Bull Mar Sci 38:129–143
Davison IR, Stewart WDP (1983) Occurrence and significance of nitrogen transport in the brown alga Laminaria digitate. Mar Biol 77:107–112
Davison IR, Stewart WDP (1984) Studies on nitrate reductase activity in Laminaria digitata (Huds.) Lamour. I. Longitudinal and transverse profiles of nitrate reductase activity within the thallus. J Exp Mar Biol 74:201–210
Dean WE (1974) Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. J Sed Petrol 44:242–248
Dickson AG, Goyet C (eds) (1994) Handbook of methods for the analysis of the various parameters of the carbon dioxide system in sea water, Version 2. ORNL/CDIAC-74 Oak Ridge National Lab, Tennessee
Dore JE, Karl DM (1996) Nitrification in the euphotic zone as a source for nitrite, nitrate, and nitrous oxide at Station ALOHA. Limnol Oceanogr 41:1619–1628
Drew EA, Abel KM (1988) Studies on Halimeda. I. The distribution and species composition of Halimeda meadows throughout the Great Barrier Reef Province. Coral Reefs 6:195–205
Drupp PS, De Carlo EH, Mackenzie FT (2016) Porewater CO2—carbonic acid system chemistry in permeable carbonate reef sands. Mar Chem 185:48–64. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2016.04.004
Eiseman N, Blair S (1982) New records and range extensions of deepwater algae from East Flower Garden Bank, northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Contrib Mar Sci 25:21–26
Erftemeijer PLA, Middleburg JJ (1993) Sediment-nutrient interactions in tropical seagrass beds: a comparison between a terrigenous and a carbonate sedimentary environment in South Sulawesi (Indonesia). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 102:187–198
Falter JL, Sansone FJ (2000a) Shallow pore water sampling in reef sediments. Coral Reefs 19:93–97
Falter JL, Sansone FJ (2000b) Hydraulic control of pore water geochemistry within the oxic-suboxic zone of a permeable sediment. Limnol Oceanogr 45:550–557
Fogaren KE, Sansone FJ, De Carlo EH (2013) Porewater temporal variability in a wave-impacted permeable sediment. Mar Chem 149:74–84
Froelich PN, Klinkhammer GP, Bender ML, Luedtke NA, Heath GR, Cullen D, Dauphin P, Hammond D, Hartmann B, Maynard V (1979) Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43:1075–1090
Fukunaga A (2008) Invertebrate community associated with the macroalga Halimeda kanaloana meadow in Maui, Hawaii. Int Rev Hydrobiol 93:328–341
Graham JE, Wilcox LW, Graham LE (2008) Algae, 2nd edn. Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco
Gruber N, Sarmiento JL (1997) Global patterns of marine nitrogen fixation and denitrification. Global Biogeochem Cycles 11:235–266
Haberstroh PR, Sansone FJ (1999) Reef framework diagenesis across wave-flushed oxic-suboxic-anoxic transition zones. Coral Reefs 18:229–240
Hanisak MD, Blair SM (1988) The deep-water macroalgal community of the East Florida continental shelf (USA). Helgol Meeresunters 42:133–163
Hecky RE, Mopper K, Kilham P, Degens ET (1973) The amino acid and sugar composition of diatom cell-walls 19:323–331
Heiri O, Lotter AF, Lemcke G (2001) Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. J Paleolimnol 25:101–110
Herbert RA (1999) Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 23:563–590
Hillis-Colinvaux L (1980) Ecology and taxonomy of Halimeda: primary producer of coral reefs. Adv Mar Biol 17:1–327
Jackson GA (1977) Nutrients and production of giant kelp, Macrocystis pyrifera, off southern California. Limnol Oceanogr 22:979–995
Kahng SE, Kelley CD (2007) Vertical zonation of megabenthic taxa on a deep photosynthetic reef (50–140 m) in the Au’au Channel, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 26:679–687
Kahng SE, Garcia-Sais JR, Spalding HL, Brokovich E, Wagner D, Weil E, Hinderstein L, Toonen RJ (2010) Community ecology of mesophotic coral reef ecosystems. Coral Reefs 29:255–275
Karl DM (1999) A sea of change: biogeochemical variability in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Ecosystems 2:181–214
Knowles R (1982) Denitrification. Microbiol Rev 46:43–70
Laws EA, Redalje DG, Haas LW, Bienfang PK, Eppley RW, Harrison WG, Karl DM, Marra J (1984) High phytoplankton growth and production rates in oligotrophic Hawaiian coastal waters. Limnol Oceanogr 29:1161–1169
Leichter JJ, Stokes MD, Genovese SJ (2008) Deep water macroalgal communities adjacent to the Florida Keys reef tract. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 356:123–138
Li YH, Gregory S (1974) Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep-sea sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:703–714
Liddell W, Ohlhorst S (1988) Hard substrata community patterns, 1-120 M, North Jamaica. Palaios 3:413–423
Littler MM, Littler DS, Blair SM, Norris JN (1985) Deepest known plant life discovered on an uncharted seamount. Science 227:57–59
Mackin JE, Aller RC (1984) Ammonium adsorption in marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 29:250–257
McRoy CP, McMillan C (1977) Productivity and physiological ecology of seagrasses. In: McRoy CP, Helfferich C (eds) Seagrass ecosystems: a scientific perspective. M. Dekker, New York, pp 53–88
Milchakova NA, Evstigneeva IK, Tankovskaya IN (1999) Flora and bottom vegetation on the deep-water banks of the Mediterranean Sea. In: Malanotte-Rizzoli P, Eremeev VN (eds) The eastern Mediterranean as a laboratory basin for the assessment of contrasting ecosystems. Kluwer Academic Publ, Amsterdam, pp 423–430
Millero F, Huang F, Zhu X, Liu X, Zhang J-Z (2001) Adsorption and desorption of phosphate on calcite and aragonite in seawater. Aquatic Geochem 7:33–56
Müller WE, Wang X, Kropf K, Ushijima H, Geurtsen W, Eckert C, Tahir MN, Tremel W, Boreiko A, Schloßmacher U, Li J (2008) Bioorganic/inorganic hybrid composition of sponge spicules: matrix of the giant spicules and of the comitalia of the deep sea hexactinellid Monorhaphis. J Struct Biol 161:188–203
Norris JN, Olsen JL (1991) Deep-water green algae from the Bahamas, including Cladophora vandenhoekii sp. nov. (Cladophorales). Phycologia 30:315–328
Olson JB, Kellogg CA (2010) Microbial ecology of corals, sponges, and algae in mesophotic coral environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:17–30
Parrish FA, Boland RC (2004) Habitat and reef-fish assemblages of banks in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Mar Biol 144:1065–1073
Perdue EM, Koprivnjak JF (2007) Using the C/N ratio to estimate terrigenous inputs of organic matter to aquatic environments. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73:65–72
Peyton KA (2009) Aquatic invasive species impacts in Hawaiian soft sediment habitats. Dissertation, University of Hawaii at Mānoa
Rebreanu L, Vanderborght J-P, Chou L (2008) The diffusion coefficient of dissolved silica revisited. Mar Chem 112:230–233
Redfield AC, Ketchum BH, Richards FA (1963) The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In: Hill MH (ed) The sea, vol 2. Wiley, New York, pp 26–77
Rooney J, Donham E, Montgomery A, Spalding H, Parrish F, Boland R, Fenner D, Gove J, Vetter O (2010) Mesophotic coral ecosystems in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Coral Reefs 29:361–367
Ruttenberg KC, Berner RA (1993) Authigenic apatite formation and burial in sediments from non-upwelling, continental margin environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:991–1007
Sansone FJ, Smith SV, Price JM, Walsh TW, Daniel TH, Andrews CC (1988) Long-term variation in seawater composition at the base of the thermocline. Nature 332:714–717
Sansone FJ, Spalding HL, Smith CM (2008) Submersible-operated porewater sampler for sandy sediments. Limnol Oceanogr: Methods 6:119–125
Schmitz K, Srivastava LM (1979) Long distance transport in Macrocystis integrifolia I. Translocation of 14C-labeled assimilates. Plant Physiol 63:995–1002
Searles RB, Schneider CW (1980) Biogeographic affinities of the shallow and deep water benthic marine algae of North Carolina. Bull Mar Sci 30:732–736
Sevadjian JC, McManus MA, Benoit-Bird KJ, Selph KE (2012) Shoreward advection of phytoplankton and vertical re-distribution of zooplankton by episodic near-bottom water pulses on an insular shelf: Oahu, Hawaii. Cont Shelf Res 50–51:1–15
Shaw TJ, Emerson S, Windom HL (2016) From deep sea pore water to coastal permeable sediments-contributions that cover the oceans: a tribute to Rick and Debbie Jahnke. Aquat Geochem 22:391–399 (Special issue)
Spalding HL (2012) Ecology of mesophotic macroalgae and Halimeda kanaloana meadows in the Main Hawaiian Islands. Dissertation, University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa
Spalding H, Foster MS, Heine JN (2003) Composition, distribution, and abundance of deep-water (> 30 m) macroalgae in Central California. J Phycol 39:273–284
Spalding HL, Conklin KY, Smith CM, O’Kelly CJ, Sherwood AR (2016) New Ulvaceae (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta) from mesophotic ecosystems across the Hawaiian Archipelago. J Phycol 52:40–53
Thamdrup B, Dalsgaard T (2002) Production of N2 through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to nitrate reduction in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1312–1318
Topinka JA (1978) Nitrogen uptake by Fucus spiralis (Phaeophyceae). J Phycol 14:241–247
Treguer P, Nelson DM, Van Bennekom AJ, DeMaster DJ, Leynaert A, Queguiner B (1995) The silica balance in the world ocean: a reestimate. Science 268:375–379
Tribble GW, Sansone FJ, Smith SV (1990) Stoichiometric modeling of carbon diagenesis within a coral reef framework. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:2439–2449
Van Raaphorst W, Malschaert JFP (1996) Ammonium adsorption in superficial North Sea sediments. Cont Shelf Res 16:1415–1435
Verbruggen H, De Clerck O, N’Yeurt ADR, Spalding H, Vroom PS (2006) Phylogeny and taxonomy of Halimeda incrassata, including the description of H. kanaloana and H. heteromorpha spp. nov. (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). European J Phycol 41:337–362
Vroom PS, Smith CM (2001) The challenge of siphonous green algae. Am Sci 89:321–335
Westley MB, Yamagishi H, Popp BN, Yoshida N (2006) Nitrous oxide cycling in the Black Sea inferred from stable isotope and isotopomer distributions. Deep-Sea Res II 53:1802–1816
Williams SL (1984a) Uptake of sediment ammonium and translocation in a marine green macroalga Caulerpa cupressoides. Limnol Oceanogr 29:374–379
Williams SL (1984b) Decomposition of the tropical macroalga Caulerpa cupressoides (West) C. Agardh: field and laboratory studies. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 80:109–124
Williams SL (1988) Disturbance and recovery of a deep-water Caribbean seagrass bed. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 42:63–71
Williams SL, Fisher TR (1985) Kinetics of nitrogen-15 labeled ammonium uptake by Caulerpa cupressoides (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 21:287–296
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Ocean Exploration Program (NA04OAR4300143 to C.M.S.), the NOAA Undersea Research Program, Hawai’i Undersea Research Laboratory (HURL) (to C.M.S.), the NOAA Coral Reef Conservation Program (NA04OAR4600100 to C.M.S.), and the U.S. National Science Foundation (OCE-0327332, OCE-0536607, and OCE-1031947 to F.J.S.). We especially thank Terry Kerby and Max Cremer (HURL) for skillful submersible piloting and for cheerful tolerance of the very uncomfortably warm conditions of these dives, the rest of the HURL submersible and ROV crew, and the crew of the R/V Ka`imikai-o-Kanaloa. We also thank an anonymous reviewer, S.V. Smith, and K.E. Fogaren for suggestions that improved this manuscript; Iuri Herzfeld, Chris Colgrove, and Didier Dumas for laboratory analyses; and Matthew Ross for assistance with graphics. School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology Contrib. No. 9988. Due to an untimely delay in the review process, this paper did not make the publication date for the special issue in tribute to Rick and Debbie Jankhe (Shaw et al. 2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sansone, F.J., Spalding, H.L. & Smith, C.M. Sediment Biogeochemistry of Mesophotic Meadows of Calcifying Macroalgae. Aquat Geochem 23, 141–164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-017-9315-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-017-9315-9