Abstract
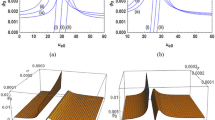
In the new investigation of dust-ion acoustic (DIA) waves with negative dust charges and weakly relativistic ions and electrons in the plasma, compressive and rarefactive DIA solitons of interesting characters are established through the Korteweg-de Vries (KdV) equation. Eventually, the amplitudes of the compressive DIA solitons are found to be constant at some critical temperature ratio αc (electron to ion temperature ratio) identifying some critical dust charge Zdc. It is predicted, that the reception of dust charges by the plasma particles at the variation of temperature starts functioning to the growth of compressive soliton’s constant stage of amplitude after the state of critical αc. The identification of critical dust charge (Zdc) which is found to be very great for solitons of constant amplitudes becomes feasible for very small dust to ion density ratio (σ). But it can be achieved, we observe, due to the relativistic increase in ion-density as in mass, which is also a salient feature of this investigation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Angelis, U., Formisano, V., Giordano, M.: J. Plasma Phys. 40, 399 (1988)
Angelo, N.D.: Planet. Space Sci. 42, 507 (1994)
Barkan, A., D’Angelo, N., Merlino, R.L.: Planet. Space Sci. 44, 239 (1996)
Bliokh, P.V., Yaroshenko, V.V.: Sov. Astron. 29, 330 (1985)
Cairns, R.A., Mamun, A.A., Bingham, R., Dendy, R., Boström, R., Nairns, C.M.C., Shukla, P.K.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 2709 (1995)
Choi, C.R., Lee, D.-Y., Kim, Y.-H., Lee, C.: Phys. Plasmas 16, 043701 (2009)
Ghosh, S., Sarkar, S., Khan, M., Gupta, M.R.: Phys. Lett. A 274, 162 (2000)
Kundu, N.R., Masud, M.M., Ashraf, K.S., Mamun, A.A.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 343, 279 (2013)
Liu, H.F., Wang, S.Q., Li, C.Z., Xiang, Q., Yang, F.Z., Liu, Y.: Phys. Scr. 82, 065402 (2010)
Liu, H.F., Wang, S.Q., Wang, Z., Yang, F.Z., Liu, Y., Li, S.: Adv. Space Res. 51, 2368 (2013)
Mamun, A.A., Cairns, R.A., Shukla, P.K.: Phys. Plasmas 3, 2610 (1996)
Masud, M.M., Mamun, A.A.: Pis’ma V ZhETF 96, 855 (2012)
Nakamura, Y., Sama, A.: Phys. Plasmas 8(9), 3921 (2001)
Nakamura, Y., Bailung, H., Shukla, P.K.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1602 (1999)
Pakzad, H.R.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 324, 41 (2009)
Qi, X., Xu, Y.-x., Duan, W.-s., Yang, L.: Phys. Plasmas 21, 013702 (2014)
Rao, N.N., Shukla, P.K., Yu, M.Y.: Planet. Space Sci. 38, 543 (1990)
Sahu, B., Roychoudhury, R.: Phys. Plasmas 11, 1947 (2004)
Shukla, P.K., Mamun, A.A.: Introduction to Dusty Plasma Physics. IOP, London (2002)
Shukla, P.K., Silin, V.P.: Phys. Scr. 45, 508 (1992)
Verheest, F.: Waves in Dusty Space Plasmas. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht (2000)
Verheest, F., Hellberg, M.: Phys. Plasmas 16(6), 064701 (2009)
Verheest, F., Pillay, S.R.: Phys. Plasmas 15, 013703 (2008)
Whipple, E.C., Northrop, T.G., Mendis, D.A.: J. Geophys. Res. 90, 7405 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalita, B.C., Das, S. Dust ion acoustic (DIA) solitary waves in plasmas with weak relativistic effects in electrons and ions. Astrophys Space Sci 352, 585–592 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-014-1954-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-014-1954-3