Abstract
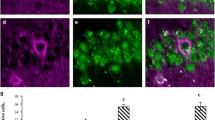
Recent studies on the effects of dietary restriction (DR) in rodents and primates have shown that even late-onset short-term regimens can bring about comparable beneficial changes seen in animals subjected to life-long DR. We studied the effect of aging on the expression of neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), its polysialylated form PSA-NCAM and astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) by immunohistofluorescent staining and immunoblotting in 1, 3, 6, 18 and 24 months old male wistar rats. Maximum expression of NCAM and PSA-NCAM was observed in sub-granular zone (SGZ) or granular cell layer (GCL) of hippocampus, arcuate region and paraventricular area of hypothalamus and piriform cortex layer II from 1 and 3 months old rats, thereafter, gradual downregulation was observed in 6, 18 and 24 months old rats. Progressive increase in astrocytic GFAP expression was noticed in these regions of brain with age. We further addressed whether DR initiated in late adulthood in 24 months old rats confers beneficial effects and can reverse changes in expression of NCAM, PSA-NCAM and GFAP. These results suggest that even late-onset short term DR regimen in old rats can have beneficial effects on neuroplasticity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson AM, Olsen M, Zhernosekov D, Gaardsvoll H, Lisbeth K, Lennemann D et al (1993) Age-related changes in expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule in skeletal muscle: a comparative study of new born, adult and aged rats. Biochem J 290:641–648
Bonfanti L (2006) PSA-NCAM in mammalian structural plasticity and neurogenesis. Prog Neurobiol 80:129–164. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.08.003
Borcel E, Pérez-Alvarez L, Herrero AI, Brionne T, Varea E, Berezin V et al (2008) Chronic stress in adulthood followed by intermittent stress impairs spatial memory and the survival of newborn hippocampal cells in aging animals: prevention by FGL, a peptide mimetic of neural cell adhesion molecule. Behav Pharmacol 19(1):41–49
Bruce-Keller AJ, Umberger G, McFall R et al (1999) Food restriction reduces brain damage and improves behavioral outcome following excitotoxic and metabolic insults. Ann Neurol 45:8–15. doi 10.1002/1531-8249(199901)45:1<8::AID-ART4>3.0.CO;2-V
Cambon K, Hanson SM, Venero C et al (2004) A synthetic neural cell adhesion molecule mimetic peptide promotes synaptogenesis, enhances presynaptic function, and facilitates memory consolidation. J Neurosci 24:4197–4204. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0436-04.2004
Cao SX, Dhahbi JM, Mote PL (2001) Genomic profiling of short- and long-term caloric restriction effects in the liver of aging mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10630–10635. doi:10.1073/pnas.191313598
Crossin KL, Krushel LA (2000) Cellular signalling by neural cell adhesion molecules of immunoglobin superfamily. Dev Dyn 218:260–279. doi 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(200006)218:2<260::AID-DVDY3>3.0.CO;2-9
Dalva MB, McClelland AC, Kayser MS (2007) Cell adhesion molecules: signaling functions at the synapse. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:206–220. doi:10.1038/nrn2075
Duan W, Guo Z, Jiang H et al (2003) Dietary restriction normalizes glucose metabolism and BDNF levels, slows disease progression, and increases survival in huntingtin mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2911–2916. doi:10.1073/pnas.0536856100
Duveau V, Arthaud S, Rougier A, Le Gal La Salle G (2007) Polysialylation of NCAM is upregulated by hyperthermia and participates in heat shock preconditioning-induced neuroprotection. Neurobiol Dis 26(2):385–395. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.01.007
Goto S, Takahashi R, Araki S, Nakamoto H (2002) Dietary restriction initiated in late adulthood can reverse age-related alterations in protein and protein metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci 959:50–56
Hansson E, Muyderman H, Leonova J, Allansson L, Sinclair J, Blomstrand F et al (2000) Astroglia and glutamate in physiology: aspects on glutamate transport, glutamate-induced cell swelling and gap junction communication. Neurochem Int 37:317–329. doi:10.1016/S0197-0186(00)00033-4
Kaur G, Heera PK, Srivastava LK (2002) Neuroendocrine plasticity in GnRH release during rat estrous cycle: correlation with molecular markers of synaptic remodeling. Brain Res 954:421–431. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03301-2
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. doi:10.1038/227680a0
Lee J, Bruce-Keller AJ, Kruman Y, Chan SL, Mattson MP (1999) 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative injury, Evidence for the involvement of stress proteins. J Neurosci Res 57:48–61. doi 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19990701)57:1<48::AID-JNR6>3.0.CO;2-L
Lee J, Bruce-Keller AJ, Kruman Y, Chan SL, Mattson MP (2003) Interactive effects of excitotoxic injury and dietary restriction on microgliosis and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neuromolecular Med 4:179–195. doi:10.1385/NMM:4:3:179
Leuner B, Kozorovitskiy Y, Gross CG, Gould E (2007) Diminished adult neurogenesis in the marmoset brain precedes old age. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(43):17169–17173. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708228104
Maswood N, Young J, Tilmont E et al (2004) Caloric restriction increases neurotrophic factor levels and attenuates neurochemical and behavioral deficits in a primate model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:18171–18176. doi:10.1073/pnas.0405831102
Mattson MP (2003) Excitotoxic and excitoprotective mechanisms: abundant targets for the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuromolecular Med 3:65–94. doi:10.1385/NMM:3:2:65
Mattson MP, Duan W, Guo Z (2003) Meal size and frequency affect neuronal plasticity and vulnerability to disease, Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Neurochem 84:417–431. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01586.x
Parkash J, Kaur G (2005) Neuronal-glial plasticity in gonadotropin-releasing hormone release in adult female rats: role of the polysialylated form of the neural cell adhesion molecule. J Endocrinol 186(2):397–409. doi:10.1677/joe.1.06156
Parkash J, Kaur G (2007) Potential of PSA-NCAM in neuron-glial plasticity in the adult hypothalamus: role of noradrenergic and GABAergic neurotransmitters. Brain Res Bull 74(5):317–328. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.07.005
Prolla TA, Mattson MP (2001) Molecular mechanism of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders, lessons from dietary restriction. Trends Neurosci 24:521–531. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(01)00005-4
Ronn LC, Berezin V, Bock E (2000) The neural cell adhesion molecule in synaptic plasticity and ageing. Int J Dev Neurosci 18(2–3):193–199
Rozovsky I, Wei M, Morgan TE et al (2005) Reversible age impairments in neurite outgrowth by manipulations of astrocytic GFAP. Neurobiol Aging 26:705–715. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.06.009
Rutishauser U (2008) Polysialylic acid in the plasticity of developing and adult vertebrate nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:26–35. doi:10.1038/nrn2285
Sandi C (2004) Stress, cognitive impairment and cell adhesion molecules. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:917–932. doi:10.1038/nrn1555
Seki T (2003) Microenvironmental elements supporting adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Anat Sci Int 78(2):69–78. doi:10.1046/j.0022-7722.2003.00043.x
Sharma S, Kaur G (2005) Neuroprotective potential of dietary restriction against kainate-induced excitotoxicity in adult male wistar rats. Brain Res Bull 67(6):482–493. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2005.07.015
Sharma S, Kaur G (2007) Intermittent dietary restriction as a practical anti-ageing intervention. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1114(1):419–427. doi:10.1196/annals.1396.031
Sharma S, Kaur G (2008) Dietary restriction enhances kainate-induced increase in NCAM while blocking the glial activation in adult rat brain. Neurochem Res 33(7):1178–1188. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9503-x
Singh J, Kaur G (2007) Transcriptional regulation of polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule expression by NMDA receptor activation in retinoic acid-differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cultures. Brain Res 1154:8–21. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2007.04.015
Sofroniew MV (2005) Reactive astrocytes in neural repair and protection. Neuroscientist 11(5):400–407. doi:10.1177/1073858405278321
Stranahan AM, Khalil D, Gould E (2007) Running induces widespread structural alterations in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Hippocampus 17(11):1017–1022. doi:10.1002/hipo.20348
Strekalova H, Buhmann C, Kleene R, Eggers C, Saffell J, Hemperly J et al (2006) Elevated levels of neural recognition molecule L1 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer disease and other dementia syndromes. Neurobiol Aging 27(1):1–9. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.11.013
Theodosis DT, Bonhomme R, Vitiello S, Rougon G, Poulain DA (1999) Cell surface expression of polysialylic acid on NCAM is a prerequisite for activity-dependent morphological neuronal and glial plasticity. J Neurosci 19:10228–10236
van Praag H, Shubert T, Zhao C, Gage FH (2005) Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. J Neurosci 25(38):8680–8685. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1731-05.2005
Venero C, Tiling T, Hermans-Borgmeyer I et al (2006) Chronic stress induces opposite changes in the mRNA expression of the cell adhesion molecules NCAM and L1. Neuroscience 115:1211–1219. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00543-2
Weindruch R, Sohal RS (1997) Calorie intake and aging. N Engl J Med 337:986–994. doi:10.1056/NEJM199710023371407
Yu ZF, Mattson MP (1999) Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration reduce focal ischemic brain damage and improve behavioral outcome, evidence for a preconditioning mechanism. J Neurosci Res 57:830–839. doi 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19990915)57:6<830::AID-JNR8>3.0.CO;2-2
Zhu H, Guo Q, Mattson MP (1999) Dietary restriction protects hippocampal neurons against the death-promoting action of a presenilin-1 mutation. Brain Res 842:224–229. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(99)01827-2
Acknowledgements
This grant was funded by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) under National Task Force Project—an initiative on Aging Research. Both Ms. Manpreet Kaur and Mr. Sandeep Sharma are thankful to the ICMR for research fellowship grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, M., Sharma, S. & Kaur, G. Age-related impairments in neuronal plasticity markers and astrocytic GFAP and their reversal by late-onset short term dietary restriction. Biogerontology 9, 441–454 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9168-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9168-0