Abstract
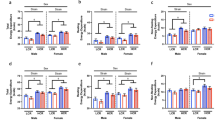
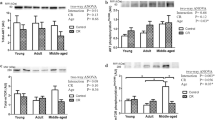
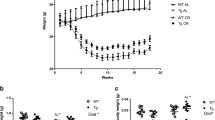
Aging affects the energy metabolism differently in the cardiac and skeletal muscles. The study aim was to assess the effects of short-term calorie restriction (SCR) and refeeding on the expression of genes involved in the control of cardiac and skeletal muscle energy metabolism in old vs. young male rats. Young (4 mo) and old (24 mo) rats were subjected to 60% SCR for 30 days, and refed ad libitum for 2 or 4 days. In the cardiac (CM) and skeletal muscles (SM) we compared the gene expression (qPCR) of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-I (Cpt-I), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (Ppar-β/δ), glucose transporter 4 (Glut4), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (Pgc-1α), and sirtuin 3 (Sirt3). In CM, aging increased Cpt-I expression but did not affect the other genes. In SM, Cpt-I, Glut4, Pgc-1α, and Sirt3 mRNA levels were lower in old than young rats. In CM of only young rats SCR increased Cpt-I expression which remained elevated after refeeding. Upon SCR, the expression of Ppar-β/δ, Glut4, Pgc-1α, and Sirt3 in CM increased in young but not old rats, and refeeding re-established control levels. In SM of young rats SCR increased Ppar-β/δ and Pgc-1α, and decreased Sirt3 expression, whereas refeeding generally decreased these mRNA levels. In SM of old rats SCR decreased only Pgc-1α expression. The adaptive response to SCR and subsequent refeeding is muscle tissue-specific and differs in young and old male rats. SCR appears to increase the efficiency of glucose and fatty acid utilization in the cardiac muscle of young, but not old male rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aerni-Flessner L, Abi-Jaoude M, Koenig A, Payne M, Hruz PW (2012) GLUT4, GLUT1, and GLUT8 are the dominant GLUT transcripts expressed in the murine left ventricle. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-11-63
Arany Z, He H, Lin J, Hoyer K, Handschin C, Toka O, Ahmad F, Matsui T, Chin S, Wu PH, Rybkin II, Shelton JM, Manieri M, Cinti S, Schoen FJ, Bassel-Duby R, Rosenzweig A, Ingwall JS, Spiegelman BM (2005) Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1 alpha controls the energy state and contractile function of cardiac muscle. Cell Metab 1:259–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2005.03.002
Argentino DP, Muñoz MC, Rocha JS, Bartke A, Turyn D, Dominici FP (2005) Short-term caloric restriction does not modify the in vivo insulin signaling pathway leading to Akt activation in skeletal muscle of Ames dwarf (Prop1(df)/Prop1(df)) mice. Horm Metab Res 37:672–679. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-870577
Bartke A, Evans TR, Musters CJM (2019) Anti-aging interventions affect lifespan variability in sex, strain, diet and drug dependent fashion. Aging 11:4066–4074. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102037
Bilski J, Pierzchalski P, Szczepanik M, Bonior J, Zoladz JA (2022) Multifactorial mechanism of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity. Role of physical exercise, microbiota and myokines. Cells 11:160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010160
Bogan JS, Kandror KV (2010) Biogenesis and regulation of insulin-responsive vesicles containing GLUT4. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:506–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2010.03.012
Boldrin L, Ross JA, Whitmore C, Doreste B, Beaver C, Eddaoudi A, Pearce DJ, Morgan JE (2017) The effect of calorie restriction on mouse skeletal muscle is sex, strain and time-dependent. Sci Rep 7:5160. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04896-y
Brandt JM, Djouadi F, Kelly DP (1998) Fatty acids activate transcription of the muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase I gene in cardiac myocytes via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. J Biol Chem 273:23786–23792. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.37.23786
Cao M, Zhao Q, Sun X, Qian H, Lyu S, Chen R, Xia H, Yuan W (2022) Sirtuin 3: Emerging therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 180:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.01.005
Cettour-Rose P, Samec S, Russell AP, Summermatter S, Mainieri D, Carrillo-Theander C, Montani JP, Seydoux J, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Dulloo AG (2005) Redistribution of glucose from skeletal muscle to adipose tissue during catch-up fat: a link between catch-up growth and later metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 54:751–756. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.54.3.751
Chen JH, Ouyang C, Ding Q, Song J, Cao W, Mao L (2015) A moderate low-carbohydrate low-calorie diet improves lipid profile, insulin sensitivity and adiponectin expression in rats. Nutrients 7:4724–4738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7064724
Cheng CF, Ku HC, Lin H (2018) PGC-1alpha as a pivotal factor in lipid and metabolic regulation. Int J Mol Sci 19:3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113447
Colleluori G, Villareal DT (2021) Aging, obesity, sarcopenia and the effect of diet and exercise intervention. Exp Gerontol 155:111561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2021.111561
Colom B, Oliver J, Garcia-Palmer FJ (2015) Sexual dimorphism in the alterations of cardiac muscle mitochondrial bioenergetics associated to the ageing process. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 70:1360–1369. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glu014
de Castro JM, Assumpção JAF, Stein DJ, Toledo RS, da Silva LS, Caumo W, Carraro CC, da Rosa Araujo AS, Torres ILS (2020) Nicotinamide riboside reduces cardiometabolic risk factors and modulates cardiac oxidative stress in obese Wistar rats under caloric restriction. Life Sci 263:118596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118596
Dean DJ, Brozinick JT Jr, Cushman SW, Cartee GD (1998) Calorie restriction increases cell surface GLUT-4 in insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 275:E957–964. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.1998.275.6.E957
Dressel U, Allen TL, Pippal JB, Rohde PR, Lau P, Muscat GE (2003) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta agonist, GW501516, regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid catabolism and energy uncoupling in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Endocrinol 17:2477–2493. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2003-0151
Hallows WC, Yu W, Smith BC, Devries MK, Ellinger JJ, Someya S, Shortreed MR, Prolla T, Markley JL, Smith LM, Zhao S, Guan KL, Denu J (2011) Sirt3 promotes the urea cycle and fatty acid oxidation during dietary restriction. Mol Cell 41:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.01.002
Hanjani NA, Zamaninour N, Najibi N, Hosseini AF, Nasirinezhad F, Vafa MR (2021) The effects of calorie restriction and time-restricted feeding on IGF1 serum level and lipid profile in male Wister rats with previous obesity. Int J Prev Med 12:157. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_38_20
Hebert AS, Dittenhafer-Reed KE, Yu W, Bailey DJ, Selen ES, Boersma MD, Carson JJ, Tonelli M, Balloon AJ, Higbee AJ, Westphall MS, Pagliarini DJ, Prolla TA, Assadi-Porter F, Roy S, Denu JM, Coon JJ (2013) Calorie restriction and SIRT3 trigger global reprogramming of the mitochondrial protein acetylome. Mol Cell 49:186–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.024
Hirschey MD, Shimazu T, Goetzman E, Jing E, Schwer B, Lombard DB, Grueter CA, Harris C, Biddinger S, Ilkayeva OR, Stevens RD, Li Y, Saha AK, Ruderman NB, Bain JR, Newgard CB, Farese RV Jr, Alt FW, Kahn CR, Verdin E (2010) SIRT3 regulates mitochondrial fatty-acid oxidation by reversible enzyme deacetylation. Nature 464(7285):121–125. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08778
Huang H, Iida KT, Sone H, Yokoo T, Yamada N, Ajisaka R (2006) The effect of exercise training on adiponectin receptor expression in KKAy obese/diabetic mice. J Endocrinol 189:643–653. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.1.06630
Jing E, Emanuelli B, Hirschey MD, Boucher J, Lee KY, Lombard D, Verdin EM, Kahn CR (2011) Sirtuin-3 (Sirt3) regulates skeletal muscle metabolism and insulin signaling via altered mitochondrial oxidation and reactive oxygen species production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:14608–14613. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1111308108
Kaczor JJ, Ziółkowski W, Antosiewicz J, Hac S, Tarnopolsky MA, Popinigis J (2006) The effect of aging on anaerobic and aerobic enzyme activities in human skeletal muscle. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/61.4.339
Kanikowska D, Kanikowska A, Swora-Cwynar E, Grzymisławski M, Sato M, Bręborowicz A, Witowski J, Korybalska K (2021) Moderate caloric restriction partially improved oxidative stress markers in obese humans. Antioxid (Basel) 10:1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10071018
Kebbe M, Sparks JR, Flanagan EW, Redman LM (2021) Beyond weight loss: current perspectives on the impact of calorie restriction on healthspan and lifespan. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab 16:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/17446651.2021.1922077
Kern M, Wells JA, Stephens JM, Elton CW, Friedman JE, Tapscott EB, Pekala PH, Dohm GL (1990) Insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle is determined by glucose transporter (Glut4) protein level. Biochem J 270:397–400. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2700397
Kim JY, Kim DH, Choi J, Park JK, Jeong KS, Leeuwenburgh C, Yu BP, Chung HY (2009) Changes in lipid distribution during aging and its modulation by calorie restriction. Age (Dordr) 31:127–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-009-9089-0
Kleiner S, Nguyen-Tran V, Baré O, Huang X, Spiegelman B, Wu Z (2009) PPAR{delta} agonism activates fatty acid oxidation via PGC-1{alpha} but does not increase mitochondrial gene expression and function. J Biol Chem 284:18624–18633. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.008797
Krämer AI, Handschin C (2019) How epigenetic modifications drive the expression and mediate the action of PGC-1alpha in the regulation of metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 20:5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215449
Krämer DK, Al-Khalili L, Guigas B, Leng Y, Garcia-Roves PM, Krook A (2007) Role of AMP kinase and PPARdelta in the regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism in human skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 282:19313–19320. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M702329200
Kwon S, Seok S, Yau P, Li X, Kemper B, Kemper JK (2017) Obesity and aging diminish sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-mediated deacetylation of SIRT3, leading to hyperacetylation and decreased activity and stability of SIRT3. J Biol Chem 292:17312–17323. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.778720
Lai YC, Tabima DM, Dube JJ, Hughan KS, Vanderpool RR, Goncharov DA, St Croix CM, Garcia-Ocaña A, Goncharova EA, Tofovic SP, Mora AL, Gladwin MT (2016) SIRT3-AMP-activated protein kinase activation by nitrite and metformin improves hyperglycemia and normalizes pulmonary hypertension associated with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 133:717–731. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018935
Larkin LM, Reynolds TH, Supiano MA, Kahn BB, Halter JB (2001) Effect of aging and obesity on insulin responsiveness and GLUT-4 glucose transporter content in skeletal muscle of Fischer 344 x Brown Norway rats. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 56:B486–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/56.11.b486
Lee CK, Allison DB, Brand J, Weindruch R, Prolla TA (2002) Transcriptional profiles associated with aging and middle age-onset caloric restriction in mouse hearts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:14988–14993. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.232308999
Leick L, Fentz J, Biensø RS, Knudsen JG, Jeppesen J, Kiens B, Wojtaszewski JF, Pilegaard H (2010) PGC-1{alpha} is required for AICAR-induced expression of GLUT4 and mitochondrial proteins in mouse skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E456–465. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00648.2009
Liu HY, Zheng G, Zhu H, Woldegiorgis G (2007) Hormonal and nutritional regulation of muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase I gene expression in vivo. Arch Biochem Biophys 465:437–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2007.06.026
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mathew AV, Li L, Byun J, Guo Y, Michailidis G, Jaiswal M, Chen YE, Pop-Busui R, Pennathur S (2018) Therapeutic lifestyle changes improve HDL function by inhibiting myeloperoxidase-mediated oxidation in patients with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 41:2431–2437. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-0049
Michael LF, Wu Z, Cheatham RB, Puigserver P, Adelmant G, Lehman JJ, Kelly DP, Spiegelman BM (2001) Restoration of insulin-sensitive glucose transporter (GLUT4) gene expression in muscle cells by the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:3820–3825. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.061035098
Miller BF, Robinson MM, Bruss MD, Hellerstein M, Hamilton KL (2012) A comprehensive assessment of mitochondrial protein synthesis and cellular proliferation with age and caloric restriction. Aging Cell 11:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00769.x
Oh TS, Yun JW (2012) DNA microarray analysis reveals differential gene expression in the soleus muscle between male and female rats exposed to a high fat diet. Mol Biol Rep 396:6569–6580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1486-2
Park JS, Holloszy JO, Kim K, Koh JH (2020) Exercise training-induced PPARbeta increases PGC-1alpha protein stability and improves insulin-induced glucose uptake in rodent muscles. Nutrients 12:652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030652
Pattanakuhar S, Sutham W, Sripetchwandee J, Minta W, Mantor D, Palee S, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2019) Combined exercise and calorie restriction therapies restore contractile and mitochondrial functions in skeletal muscle of obese-insulin resistant rats. Nutrition 62:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.11.031
Pires RC, Souza EE, Vanzela EC, Ribeiro RA, Silva-Santos JC, Carneiro EM, Boschero AC, Amaral ME (2014) Short-term calorie restriction improves glucose homeostasis in old rats: involvement of AMPK. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39:895–901. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2013-0520
Qiang W, Weiqiang K, Qing Z, Pengju Z, Yi L (2007) Aging impairs insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in rat skeletal muscle via suppressing AMPK alpha. Exp Mol Med 39:535–543. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.59
Qiu X, Brown K, Hirschey MD, Verdin E, Chen D (2010) Calorie restriction reduces oxidative stress by SIRT3-mediated SOD2 activation. Cell Metab. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.11.015. 12:662-7
Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM, Puigserver P (2005) Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1α and SIRT1. Nature 434:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03354
Sczelecki S, Besse-Patin A, Abboud A, Kleiner S, Laznik-Bogoslavski D, Wrann CD, Ruas JL, Haibe-Kains B, Estall JL (2014) Loss of Pgc-1α expression in aging mouse muscle potentiates glucose intolerance and systemic inflammation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E157–167. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00578.2013
Sequea DA, Sharma N, Arias EB, Cartee GD (2012) Calorie restriction enhances insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and Akt phosphorylation in both fast-twitch and slow-twitch skeletal muscle of 24-month-old rats. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67:1279–1285. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls085
Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Hua L, Dittenhafer-Reed KE, Schwer B, Lombard DB, Li Y, Bunkenborg J, Alt FW, Denu JM, Jacobson MP, Verdin E (2010) SIRT3 deacetylates mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthase 2 and regulates ketone body production. Cell Metab 12:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.11.003
Sithara T, Drosatos K (2021) Metabolic complications in cardiac aging. Front Physiol 12:669497. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.669497
Song J, Ke SF, Zhou CC, Zhang SL, Guan YF, Xu TY, Sheng CQ, Wang P, Miao CY (2014) Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase is required for the calorie restriction-mediated improvements in oxidative stress, mitochondrial biogenesis, and metabolic adaptation. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 69:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glt122
Tauriainen E, Luostarinen M, Martonen E, Finckenberg P, Kovalainen M, Huotari A, Herzig KH, Lecklin A, Mervaala E (2011) Distinct effects of calorie restriction and resveratrol on diet-induced obesity and Fatty liver formation. J Nutr Metab 2011:525094. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/525094
van de Ven RAH, Santos D, Haigis MC (2017) Mitochondrial sirtuins and molecular mechanisms of aging. Trends Mol Med 23:320–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2017.02.005
Vargas-Ortiz K, Pérez-Vázquez V, Macías-Cervantes MH (2019) Exercise and Sirtuins: A way to mitochondrial health in skeletal muscle. Int J Mol Sci 20:2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112717
Vijay V, Han T, Moland CL, Kwekel JC, Fuscoe JC, Desai VG (2015) Sexual dimorphism in the expression of mitochondria-related genes in rat heart at different ages. PLoS ONE 10:e0117047. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117047
Vion J, Sramkova V, Montastier E, Marquès MA, Caspar-Bauguil S, Duparc T, Martinez LO, Bourlier V, Harant I, Larrouy D, Moussaoui N, Bonnel S, Vindis C, Dray C, Valet P, Saulnier-Blache JS, Schanstra JP, Thalamas C, Viguerie N, Moro C, Langin D (2021) Metabolic and cardiovascular adaptations to an 8-wk lifestyle weight loss intervention in younger and older obese men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 321:E325–E337. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00109.2021
Wang ZQ, Bell-Farrow AD, Sonntag W, Cefalu WT (1997) Effect of age and caloric restriction on insulin receptor binding and glucose transporter levels in aging rats. Exp Gerontol 32:671–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0531-5565(97)00054-5
Wang P, Liu J, Li Y, Wu S, Luo J, Yang H, Subbiah R, Chatham J, Zhelyabovska O, Yang Q (2010) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta is an essential transcriptional regulator for mitochondrial protection and biogenesis in adult heart. Circ Res 106:911–919. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.206185
Wang H, Arias EB, Cartee GD (2016) Calorie restriction leads to greater Akt2 activity and glucose uptake by insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle from old rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 310:R449–458. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00449.2015
Wende AR, Kim J, Holland WL, Wayment BE, O’Neill BT, Tuinei J, Brahma MK, Pepin ME, McCrory MA, Luptak I, Halade GV, Litwin SE, Abel ED (2017) Glucose transporter 4-deficient hearts develop maladaptive hypertrophy in response to physiological or pathological stresses. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 313:H1098–H1108. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00101.2017
Wronska A, Kmiec Z (2012) Structural and biochemical characteristics of various white adipose tissue depots. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 205:194–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2012.02409.x
Yang M, Rigdon J, Tsai SA (2019) Association of triglyceride to HDL cholesterol ratio with cardiometabolic outcomes. J Investig Med 67:663–668. https://doi.org/10.1136/jim-2018-000869
Yu W, Qin J, Chen C, Fu Y, Wang W (2018) Moderate calorie restriction attenuates age-associated alterations and improves cardiac function by increasing SIRT1 and SIRT3 expression. Mol Med Rep 18:4087–4094. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9390
Zeng H, He X, Chen JX (2020) Endothelial sirtuin 3 dictates glucose transport to cardiomyocyte and sensitizes pressure overload-induced heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc 9:e015895. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.120.015895
Zhao L, Zou X, Feng Z, Luo C, Liu J, Li H, Chang L, Wang H, Li Y, Long J, Gao F, Liu J (2014) Evidence for association of mitochondrial metabolism alteration with lipid accumulation in aging rats. Exp Gerontol 56:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2014.02.001
Zheng J, Chen LL, Zhang HH, Hu X, Kong W, Hu D (2012) Resveratrol improves insulin resistance of catch-up growth by increasing mitochondrial complexes and antioxidant function in skeletal muscle. Metabolism 61:954–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2011.11.005
Zubrzycki A, Cierpka-Kmiec K, Kmiec Z, Wronska A (2018) The role of low-calorie diets and intermittent fasting in the treatment of obesity and type-2 diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.26402/jpp.2018.5.02
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by National Science Centre (Grant No. N401 038038 to Z.K.) and the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education (statutory Grant ST-12 to Z.K., young scientist Grant No. MN 01–0049/08 to A.Ł.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AŁ performed the experiments, analysed the data, and prepared the first draft of the manuscript. AW conducted the experiments and data analysis, prepared the final draft of the manuscript, and the revised version of the manuscript. PW designed the primers for qPCR and evaluated the statistical analysis. ZK designed the study and contributed to data interpretation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethical approval
All animal experimental procedures had been authorized by the Local Ethical Committee in Gdansk (protocol no 11/2011) and were conducted in agreement with the institutional and European guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ławniczak, A., Wrońska, A., Wierzbicki, P. et al. Aging and short-term calorie restriction differently affect the cardiac and skeletal muscle expression of genes regulating energy substrate utilization in male rats. Biogerontology 23, 325–340 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-022-09965-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-022-09965-y