Abstract
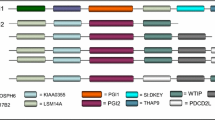
l-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase (GULO) catalyzes the final step in vertebrate vitamin C biosynthesis. Vitamin C-incapable vertebrates lack the GULO gene. Gene structure and phylogenetic analyses showed that vertebrate GULO genes are 64–95% identical at the amino acid level and consist of 11 conserved exons. GULO pseudogenes have multiple indel mutations and premature stop codons in higher primates, guinea pigs, and some bats. No GULO-like sequences were identified in teleost fishes. During animal GULO evolution, exon F was subdivided into F1 and F2. Additional GULO retropseudogenes were identified in dogs, cats, and giant pandas. GULO-flanking genome regions acquired frequent segment translocations and inversions during vertebrate evolution. Purifying selection was detected across vertebrate GULO genes (d N/d S = 0.069), except for some positively selected sites identified in sharks and frogs. These positive sites demonstrated little functional significance when mapped onto the three-dimensional GULO protein structure. Vertebrate GULO genes are conserved except for those that are lost.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbarzadeh A, Farahmand H, Mahjoubi F, Nematollahi MA, Leskinen P, Rytkonen K, Nikinmaa M (2011) The transcription of l-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, a key enzyme for biosynthesis of ascorbate, during development of Persian sturgeon Acipenser persicus. Comp Biochem Physiol B 158:282–288
Birney EC, Jenness R, Ayaz KM (1976) Inability of bats to synthesise l-ascorbic acid. Nature 260:626–628
Biyani N, Madhubala R (2011) Leishmania donovani encodes a functional enzyme involved in vitamin C biosynthesis: arabino-1,4-lactone oxidase. Mol Biochem Parasitol 180:76–85
Chaudhuri CR, Chatterjee IB (1969) l-ascorbic acid synthesis in birds: phylogenetic trend. Science 164:435–436
Cui J, Yuan X, Wang L, Jones G, Zhang S (2011) Recent loss of vitamin C biosynthesis ability in bats. PLoS ONE 6:e27114
Dabrowski K (1990) Gulonolactone oxidase is missing in teleost fish: the direct spectrophotometric assay. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 371:207–214
Deininger PL, Batzer MA (1999) Alu repeats and human disease. Mol Genet Metab 67:183–193
Drouin G, Godin JR, Pagé B (2011) The genetics of vitamin C loss in vertebrates. Curr Genomics 12:371–378
Forneris F, Heuts DP, Delvecchio M, Rovida S, Fraaije MW, Mattevi A (2008) Structural analysis of the catalytic mechanism and stereoselectivity in Streptomyces coelicolor alditol oxidase. Biochemistry 47:978–985
Jaillon O, Aury JM, Brunet F, Petit JL, Stange-Thomann N, Mauceli E, Bouneau L, Fischer C, Ozouf-Costaz C, Bernot A, Nicaud S, Jaffe D, Fisher S, Lutfalla G, Dossat C, Segurens B, Dasilva C, Salanoubat M, Levy M, Boudet N, Castellano S, Anthouard V, Jubin C, Castelli V, Katinka M, Vacherie B, Biémont C, Skalli Z, Cattolico L, Poulain J, De Berardinis V, Cruaud C, Duprat S, Brottier P, Coutanceau JP, Gouzy J, Parra G, Lardier G, Chapple C, McKernan KJ, McEwan P, Bosak S, Kellis M, Volff JN, Guigó R, Zody MC, Mesirov J, Lindblad-Toh K, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Kahn D, Robinson-Rechavi M, Laudet V, Schachter V, Quétier F, Saurin W, Scarpelli C, Wincker P, Lander ES, Weissenbach J, Roest Crollius H (2004) Genome duplication in the teleost fish Tetraodon nigroviridis reveals the early vertebrate proto-karyotype. Nature 431:946–957
Jenness R, Birney EC, Ayaz KL (1978) Ascorbic acid and l-gulonolactone oxidase in lagomorphs. Comp Biochem Physiol B 61:395–399
Jenness R, Birney EC, Ayaz KL, Buzzell DM (1984) Ontogenetic development of l-gulonolactone oxidase activity in several vertebrates. Comp Biochem Physiol B 78:167–173
Lachapelle MY, Drouin G (2011) Inactivation dates of the human and guinea pig vitamin C genes. Genetica 139:199–207
Maeda N, Hagihara H, Nakata Y, Hiller S, Wilder J, Reddick R (2000) Aortic wall damage in mice unable to synthesize ascorbic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:841–846
Martinez del Rio C (1997) Can passerines synthesize vitamin C? Auk 114:513–516
Nakata Y, Maeda N (2002) Vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque morphology in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice unable to make ascorbic acid. Circulation 105:1485–1490
Nandi A, Mukhopadhyay CK, Ghosh MK, Chattopadhyay DJ, Chatterjee IB (1997) Evolutionary significance of vitamin C biosynthesis in terrestrial vertebrates. Free Radic Biol Med 22:1047–1054
Nishikimi M, Kawai T, Yagi K (1992) Guinea pigs possess a highly mutated gene for l-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the key enzyme for l-ascorbic acid biosynthesis missing in this species. J Biol Chem 267:21967–21972
Nishikimi M, Fukuyama R, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Yagi K (1994) Cloning and chromosomal mapping of the human nonfunctional gene for l-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the enzyme for l-ascorbic acid biosynthesis missing in man. J Biol Chem 269:13685–13688
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Pollock JI, Mullin RJ (1987) Vitamin C biosynthesis in prosimians: evidence for the anthropoid affinity of Tarsius. Am J Phys Anthropol 73:65–70
Ravi V, Venkatesh B (2008) Rapidly evolving fish genomes and teleost diversity. Curr Opin Genet Dev 18:544–550
Sauer M, Branduardi P, Valli M, Porro D (2004) Production of l-ascorbic acid by metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Zygosaccharomyces bailii. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6086–6091
Spagnuolo MS, Cigliano L, Balestrieri M, Porta A, Abrescia P (2001) Synthesis of ascorbate and urate in the ovary of water buffalo. Free Radic Res 35:233–243
Togari A, Arai M, Nakagawa S, Banno A, Aoki M, Matsumoto S (1995) Alteration of bone status with ascorbic acid deficiency in ODS (osteogenic disorder Shionogi) rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 68:255–261
Yamashita M, Omura H, Okamoto E, Furuya Y, Yabuuchi M, Fukahi K, Murooka Y (2000) Isolation, characterization, and molecular cloning of a thermostable xylitol oxidase from Streptomyces sp. IKD472. J Biosci Bioeng 89:350–360
Yang Z (2007) PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24:1586–1591
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China (No. 2008F3111) and the Initial Research Fund (No. 2006L20775) from Zhangzhou Normal University to Dr. Hongwen Yang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H. Conserved or Lost: Molecular Evolution of the Key Gene GULO in Vertebrate Vitamin C Biosynthesis. Biochem Genet 51, 413–425 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9574-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9574-0