Abstract
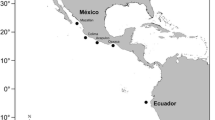
The invasive red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) provides a valuable opportunity for studying the population genetics of invasive species that disperse rapidly. We analyzed the population genetic structure among 12 populations of the crayfish in China based on the internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) region. The ITS1 of 815 bp aligned across 34 haplotypes; the average GC content was 53.9%. AMOVA showed that intrapopulation variation (95.26%) was much higher than interpopulation variation (4.74%). Genetic differentiation between the Taiwan and mainland populations (F st = 0.160) was moderate, but the Chinese population (Taiwan and the mainland combined) and an American population were highly differentiated (0.682 and 0.977, respectively). Gene flow between the Chinese and American populations (N m = 0.006 and 0.117, respectively) was lower than that between Taiwan and the mainland (1.536). Phylogenetic trees showed that three major genealogical clusters matched the sample locations well, suggesting that genetic differentiation is created largely by geographic isolation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbaresi S, Fani R, Gherardi F, Mengoni A, Souty-Grosset C (2003) Genetic variability in European populations of an invasive American crayfish: preliminary results. Biol Invasions 5:269–274
Bazin E, Glémin S, Galtier N (2006) Population size does not influence mitochondrial genetic diversity in animals. Science 312:570–572
Campbell CS, Wright WA, Cox M, Vining TF, Major CS, Arsenault MP (2005) Nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) in Picea (Pinaceae): sequence divergence and structure. Mol Phylogenet Evol 35:165–185
Cao LL, Zhou LZ, Zhang BW (2010) Genetic patterns of an invasive Procambarus clarkii population in the three river basins of Anhui Province. Biodivers Sci 18:398–407
Coleman AW (2003) ITS2 is a double-edged tool for eukaryote evolutionary comparisons. Trends Genet 19:370–375
Coleman AW, Vacquier VD (2002) Exploring the phylogenetic utility of ITS sequences for animals (Haliotis). J Mol Evol 54:246–257
Ellstrand NC, Elam DR (1993) Population genetic consequences of small population size: implications for plant conservation. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 24:217–243
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online 1:47–50
Fabry S, Köhler A, Coleman AW (1999) Intraspecies analysis: comparison on ITS sequence data and gene intron sequence data with breeding data for a worldwide collection of Gonium pectorale. J Mol Evol 48:94–101
Fullerton SM, Carvalho BA, Clark AG (2001) Local rates of recombination are positively correlated with GC content in the human genome. Mol Biol Evol 18:1139–1142
Galtier N, Piganeau G, Mouchiroud D, Duret L (2001) GC-content evolution in mammalian genomes: the biased gene conversion hypothesis. Genetics 159:907–911
Hardesty BD, Dick CW, Hamrick JL, Degen B, Hubbell SP, Bermingham E (2010) Geographic influence on genetic structure in the widespread neotropical tree Simarouba amara (Simaroubaceae). Trop Plant Biol 3:28–39
Harris DJ, Crandall KA (2000) Intragenomic variation within ITS1 and ITS2 of freshwater crayfishes (Decapoda: Cambaridae): implications for phylogenetic and microsatellite studies. Mol Biol Evol 17(2):284–291
Hedgecock D, Stelmach DJ, Nelson K, Lindenfelser ME, Malecha SR (1979) Genetic divergence and biogeography of natural populations of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Proc World Maric Soc 10:873–879
Huner JV (1988) Procambarus in North America and elsewhere. In: Holdich DM, Lowery RS (eds) Freshwater crayfish: biology, management and exploitation. Timber Press, Portland, OR, pp 239–261
Ibrahim KM, Nichols RA, Hewitt GM (1996) Spatial patterns of genetic variation generated by different forms of dispersal during range expansion. Heredity 77:282–291
Ji YJ, Zhang DX, He LJ (2003) Evolutionary conservation and versatility of a new set of primers for amplifying the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer regions in insects and other invertebrates. Mol Ecol Notes 3:581–585
Kan XZ, Wang SS, Ding X, Wang XQ (2007) Structural evolution of nrDNA ITS in Pinaceae and its phylogenetic implications. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:765–777
Keller LF, Waller DM (2002) Inbreeding effects in wild populations. Trends Ecol Evol 17:230–241
Li SC, Xu YX, Du LQ, Yi XL, Men XD, Xie JY (2005) Investigation and analysis of alien invasions in Chinese farming industry. Chin Agric Sci Bull 21:156–159
Miller BR, Crabtree MB, Savage HM (1996) Phylogeny of fourteen Culex mosquito species, including the Culex pipiens complex, inferred from the internal transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA. Insect Mol Biol 5:93–107
Moreno IM, Malpica JM, Díaz-Pendón JA, Moriones E, Fraile A, García-Arenal F (2004) Variability and genetic structure of the population of watermelon mosaic virus infecting melon in Spain. Virology 3:451–460
Nei M (1982) Evolution of human races at the gene level. In: Bonne TB, Cohen T, Goodman RM (eds) Human genetics, Part A: the unfolding genome. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 167–181
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Nichols KM, Young WP, Danzmann RG, Robison BD, Rexroad C, Noakes M, Phillips RB, Bentzen P, Spies I, Knudsen K, Allendorf FW, Cunningham BM, Brunelli J, Zhang H, Ristow S, Drew R, Brown KH, Wheeler PA, Thorgaard GH (2003) A consolidated linkage map for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim Genet 34:102–115
Parker IM, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Goodell K, Wonham M, Kareiva PM, Williamson MH, Holle BV, Moyle PB, Byers JE, Goldwasser L (1999) Impact: toward a framework for understanding the ecological effects of invaders. Biol Invasions 1:3–19
Qu YH, Ericson PGP, Lei FM, Li SH (2005) Postglacial colonization of the Tibetan Plateau inferred from the matrilineal genetic structure of the endemic red-necked snow finch, Pyrgilauda ruficollis. Mol Ecol 14:1767–1781
Saccheri I, Kuussaari M, Kankare M, Vikman P, Fortelius W, Hanski I (1998) Inbreeding and extinction in a butterfly metapopulation. Nature 392:491–494
Sassi PL, Chiappero MB, Borghi C, Gardenal CN (2011) High genetic differentiation among populations of the small cavy Microcavia australis occupying different habitats. J Intergr Biol 315:337–348
Schulenburg JH, Englisch U, Wägele JW (1999) Evolution of ITS1 rDNA in the Digenea (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda): 3’ end sequence conservation and its phylogenetic utility. J Mol Evol 48:2–12
Spielman D, Brook BW, Frankham R (2004) Most species are not driven to extinction before genetic factors impact them. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15261–15264
Suarez AV, Holway DA, Case TJ (2001) Patterns of spread in biological invasions dominated by long-distance jump dispersal: insights from Argentine ants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1095–1100
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X Windows interface. Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acid Res 25:4876–4882
Tiunov AV, Cindy H, Andrew H, Tamara VP (2006) Invasion patterns of Lumbricidae into the previously earthworm-free areas of northeastern Europe and the western Great Lakes region of North America. Biol Invasions 8:1223–1234
Vogler AP, Desalle R (1994) Evolution and phylogenetic information content of the ITS-1 region in the tiger beetle, Cicindela dorsalis. Mol Biol Evol 11:393–405
Wang CZ, Li Z, Liang HW, Hu GF, Wu QC, Zou GW, Luo XZ (2009) Genetic diversity in four Procambarus clarkii populations in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Biodivers Sci 17(5):518–523
Xia AJ, Tang JQ, Li JJ (2009) Current status of culture of red swamp crayfish in Jiangsu province. http://www.jsof.gov.cn/art/2009/5/5/art_64_36486.html
Yang SJ, Yin ZH, Ma XM, Lei FM (2006) Phylogeography of ground tit (Pseudopodoces humilis) based on mtDNA: evidence of past fragmentation on the Tibetan Plateau. Mol Phylogenet Evol 41:257–265
Yang SJ, Dong HL, Lei FM (2009) Phylogeography of regional fauna on the Tibetan Plateau: a review. Progress Nat Sci 19:789–799
Yue GH, Wang GL, Zhu BQ, Wang CM, Zhu ZY (2008) Discovery of four natural clones in a crayfish species Procambarus clarkia. Int J Biol Sci 4:279–282
Yue GH, Li JL, Bai ZY, Wang CM, Feng F (2010) Genetic diversity and population structure of the invasive alien red swamp crayfish. Biol Invasions 12:2697–2706
Acknowledgments
We thank Xiang Huang and Lili Zhang for their assistance with the laboratory work. We also thank Jiahao Zhang for supplying his samples, Qianqian Sun (College of Life Sciences, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu, China) for her help in sequence analysis, and Prof. Huabin Zhao (Wuhan University, Wuhan, China) for his helpful suggestions. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31172117) and the Anhui Natural Science Foundation (Grant no. 11040606M76) and the Graduate Student Innovation Research Projects of Anhui University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Zhou, L., Li, X. et al. Population Genetic Structure of the Invasive Red Swamp Crayfish in China Revealed by ITS1 Variation. Biochem Genet 51, 841–852 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9611-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9611-z