Abstract
Objective
To characterize a novel xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) from Acinetobacter baumannii by recombinant expression in Escherichia coli and to assess its potential for industrial applications.
Results
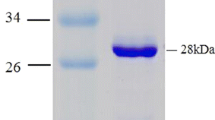
The XDH gene cluster was cloned from A. baumannii CICC 10254, expressed heterologously in E. coli and purified to homogeneity. The purified recombinant XDH consisted of two subunits with the respective molecular weights of 87 kDa and 56 kDa according to SDS-PAGE. XDH catalysis was optimum at pH 8.5 and 40–45 °C, was stable under alkaline conditions (pH 7–11) and the half-inactivation temperature was 60 °C. The K m, turnover number and catalytic efficiency for xanthine were 25 μM, 69 s−1 and 2.7 μM−1 s−1, respectively, which is an improvement over XDHs characterized previously. A. baumannii XDH is less than 50 % identical to previously identified XDH orthologs from other species, and is the first from the Acinetobacter genus to be characterized.
Conclusion
The novel A. baumannii enzyme was found to be among the most active, thermostable and alkaline-tolerant XDH enzymes reported to date and has potential for use in industrial applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD, Goglin K, Molyneaux N, Hujer KM, Lavender H, Jamison JJ, MacDonald IJ, Martin KM, Russo T, Campagnari AA, Hujer AM, Bonomo RA, Gill SR (2008) Comparative genome sequence analysis of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Bacteriol 190:8053–8064
Chen CG, Cheng GY, Hao HH, Dai MH, Wang X, Huang LL, Liu ZL, Yuan ZH (2013) Mechanism of porcine liver xanthine oxidoreductase mediated N-oxide reduction of cyadox as revealed by docking and mutagenesis studies. PLoS ONE 8(9):e73912
Dietzel U, Kuper J, Doebbler JA, Schulte A, Truglio JJ, Leimkuhler S, Kisker C (2009) Mechanism of substrate and inhibitor binding of Rhodobacter capsulatus xanthine dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 284:8768–8776
Enroth C, Eger BT, Okamoto K, Nishino T, Nishino T, Pai EF (2000) Crystal structures of bovine milk xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase: structure-based mechanism of conversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10723–10728
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18(15):2714–2723
Hille R (1996) The mononuclear molybdenum enzymes. Chem Rev 96:2757–2816
Ishikita H, Eger BT, Okamoto K, Nishino T, Pai EF (2012) Protein conformational gating of enzymatic activity in xanthine oxidoreductase. J Am Chem Soc 134(2):999–1009
Kalimuthu P, Leimkuhler S, Bernhardt PV (2012) Low-potential amperometric enzyme biosensor for xanthine and hypoxanthine. Anal Chem 84(23):10359–10365
Leimkuhler S, Hodson R, George GN, Rajagopalan KV (2003) Recombinant Rhodobacter capsulatus xanthine dehydrogenase, a useful model system for the characterization of protein variants leading to xanthinuria I in humans. J Biol Chem 278(23):20802–20811
Smith MG, Gianoulis TA, Pukatzki S, Mekalanos JJ, Ornston LN, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2007) New insights into Acinetobacter baumannii pathogenesis revealed by high-density pyrosequencing and transposon mutagenesis. Genes Dev 21:601–614
Woolfolk CA, Downard JS (1977) Distribution of xanthine-oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase specificity types among bacteria. J Bacteriol 130:1175–1191
Yamaguchi Y, Matsumura T, Ichida K, Okamoto K, Nishino T (2007) Human xanthine oxidase changes its substrate specificity to aldehyde oxidase type upon mutation of amino acid residues in the active site: roles of active site residues in binding and activation of purine substrate. J Biochem 141:513–524
Zarepour M, Kaspari K, Stagge S, Rethmeier R, Mendel RR, Bittner F (2010) Xanthine dehydrogenase AtXDH1 from Arabidopsis thaliana is a potent producer of superoxide anions via its NADH oxidase activity. Plant Mol Biol 72:301–310
Zikakis JP, Treece JM (1971) Xanthine oxidase polymorphism in bovine milk. J Dairy Sci 54:648–654
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 21406132), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Numbers: 2014M550743 and 2015T80094).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1 Comparison between Acinetobacter baumannii xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) identified in this study and previously characterized enzymes.
Supplementary Table 2 Amino acid sequence identity (homology) of A. baumannii XDH identified in this study and other XDHs characterized previously.
Supplementary Table 3 Purification of recombinant A. baumannii XDH following heterologous expression in E. coli.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, CH., Zhao, TX., Li, M. et al. Characterization of a novel Acinetobacter baumannii xanthine dehydrogenase expressed in Escherichia coli . Biotechnol Lett 38, 337–344 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1986-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1986-y