Abstract
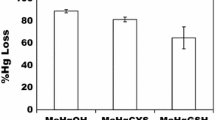
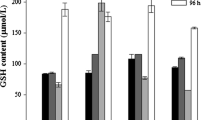
While the toxicological effects of mercury (Hg) are well studied in mammals, little is known about the mechanisms of toxicity to bacterial cells lacking an Hg resistance (mer) operon. We determined that Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 is more sensitive to ionic mercury [Hg(II)] under aerobic conditions than in fumarate reducing conditions, with minimum inhibitory concentrations of 0.25 and 2 μM respectively. This increased sensitivity in aerobic conditions is not due to increased import, as more Hg is associated with cellular material in fumarate reducing conditions than in aerobic conditions. In fumarate reducing conditions, glutathione may provide protection, as glutathione levels decrease in a dose-dependent manner, but this does not occur in aerobic conditions. Hg(II) does not change the redox state of thioredoxin in MR1 in either fumarate reducing conditions or aerobic conditions, although thioredoxin is oxidized in Geobacter sulfurreducens PCA in response to Hg(II) treatment. However, treatment with 0.5 μM Hg(II) increases lipid peroxidation in aerobic conditions but not in fumarate reducing conditions in MR-1. We conclude that the enhanced sensitivity of MR-1 to Hg(II) in aerobic conditions is not due to differences in intracellular responses, but due to damage at the cell envelope.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnér ESJ, Holmgren A (2000) Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem 267(20):6102–6109
Barkay T, Miller SM, Summers AO (2003) Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:355–384
Barkay T, Kritee K, Boyd E, Geesey G (2010) A thermophilic bacterial origin and subsequent constraints by redox, light and salinity on the evolution of the microbial mercuric reductase. Environ Microbiol 12(11):2904–2917
Bersani NA, Merwin JR, Lopez NI, Pearson GD, Merrill GF (2002) Protein electrophoretic mobility shift assay to monitor redox state of thioredoxin in cells. Methods Enzymol 347:317–326
Blindauer C (2011) Bacterial metallothioneins: past, present, and questions for the future. J Biol Inorg Chem 16(7):1011–1024
Botsoglou NA, Fletouris DJ, Papageorgiou GE, Vassilopoulos VN, Mantis AJ, Trakatellis AG (1994) Rapid, sensitive, and specific thiobarbituric acid method for measuring lipid peroxidation in animal tissue, food, and feedstuff samples. J Agric Food Chem 42(9):1931–1937
Branco V, Canário J, Holmgren A, Carvalho C (2011) Inhibition of the thioredoxin system in the brain and liver of zebra-seabreams exposed to waterborne methylmercury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251(2):95–103
Carvalho CLM, Chew E, Hashemy SI, Lu J, Holmgren A (2008) Inhibition of the human thioredoxin system: a molecular mechanism of mercury toxicity. J Biol Chem 283:11913–11923
Coppi MV, Leang C, Sandler SJ, Lovley DR (2001) Development of a genetic system for Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3180–3187
El-Demerdash F (2001) Effects of selenium and mercury on the enzymatic activities and lipid peroxidation in brain, liver, and blood of rats. J Environ Sci Health B 36(4):489–499
Fahey RC, Brown WC, Adams WB, Worsham MB (1978) Occurrence of glutathione in bacteria. J Bacteriol 133(3):1126–1129
Feldman E (2004) Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) assay. Animal models of diabetic complications consortium (AMDCC protocols). Version 1:1–3
Fleming EJ, Mack EE, Green PG, Nelson DC (2006) Mercury methylation from unexpected sources: molybdate-inhibited freshwater sediments and an iron-reducing bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(1):457–464
Gabriel MC, Williamson DG (2004) Principal biogeochemical factors affecting the speciation and transport of mercury through the terrestrial environment. Environ Geochem Health 26(4):421–434
Gao H, Barua S, Liang Y, Wu L, Dong Y, Reed S, Chen J, Culley D, Kennedy D, Yang Y (2010) Impacts of Shewanella oneidensis c-type cytochromes on aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Microb Biotechnol 3(4):455–466
Gstraunthaler G, Pfaller W, Kotanko P (1983) Glutathione depletion and in vitro lipid peroxidation in mercury or maleate induced acute renal failure. Biochem Pharmacol 32(19):2969–2972
Hansen JM, Zhang H, Jones DP (2006) Differential oxidation of thioredoxin-1, thioredoxin-2, and glutathione by metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 40(1):138–145
Holmgren A (1989) Thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. J Biol Chem 264:13963–13966
Hungate R (1969) A roll tube method for cultivation of strict anaerobes. Methods Microbiol 3B:117–132
Jiang D, Heald SM, Sham T, Stillman MJ (1994) Structures of the cadmium, mercury, and zinc thiolate clusters in metallothionein: XAFS study of Zn7-MT, Cd7-MT, Hg7-MT, and Hg18-MT formed from rabbit liver metallothionein 2. J Am Chem Soc 116(24):11004–11013
Kerin EJ, Gilmour CC, Roden E, Suzuki M, Coates J, Mason R (2006) Mercury methylation by dissimilatory iron-reducing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(12):7919–7921
Kobal AB, Horvat M, Prezelj M, Briški AS, Krsnik M, Dizdarevič T, Mazej D, Falnoga I, Stibilj V, Arnerič N (2004) The impact of long-term past exposure to elemental mercury on antioxidative capacity and lipid peroxidation in mercury miners. J Trace Elem Med Biol 17(4):261–274
Lu TH, Chen CH, Lee MJ, Ho TJ, Leung YM, Hung DZ, Yen CC, He TY, Chen YW (2010) Methylmercury chloride induces alveolar type II epithelial cell damage through an oxidative stress-related mitochondrial cell death pathway. Toxicol Lett 194(3):70–78
Lund B-O, Miller DM, Woods JS (1991) Mercury-induced H2O2 production and lipid peroxidation in vitro in rat kidney mitochondria. Biochem Pharmacol 42 Suppl:S181–S186
Lund B-O, Miller DM, Woods JS (1993) Studies on Hg(II)-induced H2O2 formation and oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro in rat kidney mitochondria. Biochem Pharmacol 45(10):2017–2024
Masip L, Veeravalli K, Georgiou G (2006) The many faces of glutathione in bacteria. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(5–6):753–762. doi:10.1089/ars.2006.8.753
Mergler D, Anderson HA, Chan LHM, Mahaffey KR, Murray M, Sakamoto M, Stern AH (2007) Methylmercury exposure and health effects in humans: a worldwide concern. Ambio 36(1):3–11
Mousavi A, Chavez RD, Ali A-MS, Cabaniss SE (2011) Mercury in natural waters: a mini-review. Environ Forensics 12(1):14–18. doi:10.1080/15275922.2010.547549
Myers CR, Nealson KH (1988) Bacterial manganese reduction and growth with manganese oxide as the sole electron acceptor. Science 240(4857):1319–1321
Nascimento AM, Chartone-Souza E (2003) Operon mer: bacterial resistance to mercury and potential for bioremediation of contaminated environments. Genet Mol Res 2(1):92–101
Qin J, Clore GM, Gronenborn AM (1994) The high-resolution three-dimensional solution structures of the oxidized and reduced states of human thioredoxin. Structure 2(6):503–522
Ranchou-Peyruse M, Monperrus M, Bridou R, Duran R, Amouroux D, Salvado J, Guyoneaud R (2009) Overview of mercury methylation capacities among anaerobic bacteria including representatives of the sulphate-reducers: implications for environmental studies. Geomicrobiol J 26(1):1–8
Sasse J, Gallagher SR (2001) Detection of proteins on blot transfer membranes. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley Interscience, New York
Schaefer JK, Morel FM (2009) High methylation rates of mercury bound to cysteine by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Nat Geosci 2(2):123–126
Schaefer JK, Letowski J, Barkay T (2002) mer-Mediated resistance and volatilization of Hg(II) under anaerobic conditions. Geomicrobiol J 19(1):87–102
Schaefer JK, Rocks SS, Zheng W, Liang L, Gu B, Morel FM (2011) Active transport, substrate specificity, and methylation of Hg(II) in anaerobic bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(21):8714–8719
Schulter K (2000) Review: evaporation of mercury from soils. An integration and synthesis of current knowledge. Environ Geol 39:249–271
Selin NE (2009) Global biogeochemical cycling of mercury: a review. Annu Rev Environ Resour 34(1):43–63
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18(2):321–336
Tchounwou PB, Ayensu WK, Ninashvili N, Sutton D (2003) Review: environmental exposure to mercury and its toxicopathologic implications for public health. Environ Toxicol 18(3):149–175
Ullrich SM, Tanton TW, Abdrashitova SA (2001) Mercury in the aquatic environment: a review of factors affecting methylation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 31(3):241–293
Ung C, Lam S, Hlaing M, Winata C, Korzh S, Mathavan S, Gong Z (2010) Mercury-induced hepatotoxicity in zebrafish: in vivo mechanistic insights from transcriptome analysis, phenotype anchoring and targeted gene expression validation. Bmc Genomics 11(1):212
Vandeputte C, Guizon I, Genestie-Denis I, Vannier B, Lorenzon G (1994) A microtiter plate assay for total glutathione and glutathione disulfide contents in cultured/isolated cells: performance study of a new miniaturized protocol. Cell Biol Toxicol 10(5–6):415–421
Virtanen JK, Voutilainen S, Rissanen TH, Mursu J, Tuomainen T-P, Korhonen MJ, Valkonen V-P, Seppänen K, Laukkanen JA, Salonen JT (2005) Mercury, fish oils, and risk of acute coronary events and cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease, and all-cause mortality in men in eastern Finland. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(1):228–233
Virtanen JK, Rissanen TH, Voutilainen S, Tuomainen T-P (2007) Mercury as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. J Nutr Biochem 18(2):75–85
Wataha JC, Lewis JB, McCloud VV, Shaw M, Omata Y, Lockwood PE, Messer RL, Hansen JM (2008) Effect of mercury (II) on Nrf2, thioredoxin reductase-1 and thioredoxin-1 in human monocytes. Dent Mater 24(6):765–772
Wiatrowski HA, Ward PM, Barkay T (2006) Novel reduction of mercury(II) by mercury-sensitive dissimilatory metal reducing bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 40(21):6690–6696
Zalups RK, George Cherian M (1992) Renal metallothionein metabolism after a reduction of renal mass. II. Effect of zinc pretreatment on the renal toxicity and intrarenal accumulation of inorganic mercury. Toxicology 71(1):103–117
Zalups RK, Lash LH (1997) Depletion of glutathione in the kidney and the renal disposition of administered inorganic mercury. Drug Metab Dispos 25(4):516–523
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
Growth of MR-1 under aerobic conditions (a) or fumarate reducing conditions (b) in the presence of Hg(II). Thick line 0 Hg(II); open circles 0.1 μM Hg(II); open triangles 0.25 μM Hg(II); open squares 0.5 μM Hg(II); open diamonds 1 μM Hg(II); filled triangles 2 μM Hg(II); filled circles 5 μM Hg(II). Symbols represent the mean of triplicate cultures. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (PPT 146 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Growth of PCA in the presence of Hg(II). Thick line 0 Hg(II); open circles 0.5 μM Hg(II); open squares 1.0 μM Hg(II); open triangles 5.0 μM Hg(II); closed squares 10 μM Hg(II); closed circles 25 μM Hg(II). Symbols represent the mean of triplicate cultures. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (PPT 89 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Robison, T. & Wiatrowski, H. The impact of ionic mercury on antioxidant defenses in two mercury-sensitive anaerobic bacteria. Biometals 26, 1023–1031 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9679-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9679-2