Abstract
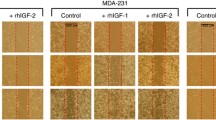
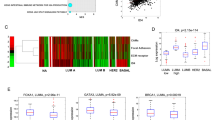
In order to display the full metastatic phenotype, the cancer cell must acquire the ability to migrate. In breast cancer, we have previously shown that insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) enhances cell motility in the highly metastatic MDA-231BO cell line by activating the type I IGF receptor (IGF1R). This motility response requires activation of IRS-2 and integrin ligation. In order to identify the key molecules downstream of IRS-2, we examined several signaling pathways known to be involved in cell motility. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) was not activated by IGF-I, but IGF-I caused redistribution of FAK away from focal adhesion plaques. IGF-I treatment of MDA-231BO cells activated RhoA and inhibition of Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibited the IGF-mediated motility response. The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), p38, was also activated by IGF-I and inhibition of p38 by SB203580 blocked IGF-I induced cell motility. ROCK inhibition with Y-27632 also inhibited p38 phosphorylation suggesting that p38 lies downstream of ROCK. Both Erk1,2 and phosphatidyl-3 kinase (PI3K) were required for IGF-I stimulated cell motility, but only PI3K appeared to be directly downstream of IGF-I. Thus, IGF-I activation of its receptor coordinates multiple signaling pathways required for cell motility. Defining the key molecules downstream of the type I IGF receptor may provide a basis for optimizing therapies directed at this target.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ME Doerr JI Jones (1996) ArticleTitleThe roles of integrins, extracellular matrix proteins in the insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells J Biol Chem 271 2443–2447 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.271.5.2443 Occurrence Handle8576205
JG Jackson X Zhang T Yoneda D Yee (2001) ArticleTitleRegulation of breast cancer cell motility by insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) in metastatic variants of human breast cancer cell lines Oncogene 20 7318–7325 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.onc.1204920 Occurrence Handle11704861
E Sahai CJ Marshall (2002) ArticleTitleRHO-GTPases and cancer Nat Rev Cancer 2 133–142 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nrc725 Occurrence Handle12635176
ZM Jaffer J Chernoff (2004) ArticleTitleThe cross-Rho’ds of cell–cell adhesion J Biol Chem 279 35123–35126 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.R400010200 Occurrence Handle15133033
G Fritz C Brachetti F Bahlmann M Schmidt B Kaina (2002) ArticleTitleRho GTPases in human breast tumours: expression and mutation analyses and correlation with clinical parameters Br J Cancer 87 635–644 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.bjc.6600510 Occurrence Handle12237774
SJ Ahn KW Chung RA Lee IA Park SH Lee DE Park DY Noh (2003) ArticleTitleOverexpression of betaPix-a in human breast cancer tissues Cancer Lett 193 99–107 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3835(03)00004-1 Occurrence Handle12691829
A Schnelzer D Prechtel U Knaus K Dehne M Gerhard H Graeff N Harbeck M Schmitt E. Lengyel (2000) ArticleTitleRac1 in human breast cancer: overexpression, mutation analysis, and characterization of a new isoform, Rac1b Oncogene 19 3013–3020 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.onc.1203621 Occurrence Handle10871853
KL Golen Particlevan ZF Wu XT Qiao LW Bao SD Merajver (2000) ArticleTitleRhoC GTPase, a novel transforming oncogene for human mammary epithelial cells that partially recapitulates the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype Cancer Res 60 5832–5838 Occurrence Handle11059780
CG Kleer KL Golen Particlevan Y Zhang ZF Wu MA Rubin SD Merajver (2002) ArticleTitleCharacterization of RhoC expression in benign and malignant breast disease: a potential new marker for small breast carcinomas with metastatic ability Am J Pathol 160 579–584 Occurrence Handle11839578
B Bouzahzah C Albanese F Ahmed F Pixley MP Lisanti JD Segall J Condeelis D Joyce A Minden CJ Der A Chan M Symons RG. Pestell (2001) ArticleTitleRho family GTPases regulate mammary epithelium cell growth and metastasis through distinguishable pathways Mol Med 7 816–830 Occurrence Handle11844870
K Kimura M Ito M Amano K Chihara Y Fukata M Nakafuku B Yamamori J Feng T Nakano K Okawa A Iwamatsu K Kaibuchi (1996) ArticleTitleRegulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) Science 273 245–248 Occurrence Handle8662509
M Maekawa T Ishizaki S Boku N Watanabe A Fujita A Iwamatsu T Obinata K Ohashi K Mizuno S Narumiya (1999) ArticleTitleSignaling from Rho to the actin cytoskeleton through protein kinases ROCK and LIM-kinase Science 285 895–898 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.285.5429.895 Occurrence Handle10436159
K Yoshioka V Foletta O Bernard K Itoh (2003) ArticleTitleA role for LIM kinase in cancer invasion Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100 7247–7252 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.1232344100 Occurrence Handle12777619
N Ashida H Arai M Yamasaki T Kita (2001) ArticleTitleDistinct signaling pathways for MCP-1-dependent integrin activation and chemotaxis J Biol Chem 276 16555–16560 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M009068200 Occurrence Handle11278464
S Zhang J Han MA Sells J Chernoff UG Knaus RJ Ulevitch GM Bokoch (1995) ArticleTitleRho family GTPases regulate p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase through the downstream mediator Pak1 J Biol Chem 270 23934–23936 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.270.41.23934 Occurrence Handle7592586
S Bagrodia B Derijard RJ Davis RA Cerione (1995) ArticleTitleCdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen- activated protein kinase activation J Biol Chem 270 27995–27998 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.270.47.27995 Occurrence Handle7499279
AA Brahmbhatt RL Klemke (2003) ArticleTitleERK and RhoA differentially regulate pseudopodia growth and retraction during chemotaxis J Biol Chem 278 13016–13025 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M211873200 Occurrence Handle12571246
MJ Brown JA Hallam E Colucci-Guyon S Shaw (2001) ArticleTitleRigidity of circulating lymphocytes is primarily conferred by vimentin intermediate filaments J Immunol 166 6640–6646 Occurrence Handle11359818
WC Sin XQ Chen T Leung L Lim (1998) ArticleTitleRhoA-binding kinase alpha translocation is facilitated by the collapse of the vimentin intermediate filament network Mol Cell Biol 18 6325–6339 Occurrence Handle9774649
P Sachdev YX Jiang W Li T Miki H Maruta EKMS Nur LH Wang (2001) ArticleTitleDifferential requirement for Rho family GTPases in an oncogenic insulin-like growth factor-I receptor-induced cell transformation J Biol Chem 276 26461–26471 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M010995200 Occurrence Handle11346642
HL Cheng ML Steinway JW Russell EL Feldman (2000) ArticleTitleGTPases and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase are critical for insulin-like growth factor-I-mediated Schwann cell motility J Biol Chem 275 27197–27204 Occurrence Handle10829021
X Zhang D Yee (2002) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) inhibits breast cancer cell motility Cancer Res 62 4369–4375 Occurrence Handle12154042
T Yoneda PJ Williams T Hiraga M Niewolna R Nishimura (2001) ArticleTitleA bone-seeking clone exhibits different biological properties from the MDA-MB-231 parental human breast cancer cells and a brain-seeking clone in vivo and in vitro J Bone Miner Res 16 1486–1495 Occurrence Handle11499871
MJ Ratcliffe C Smales JM Staddon (1999) ArticleTitleDephosphorylation of the catenins p120 and p100 in endothelial cells in response to inflammatory stimuli Biochem J 338 471–478 Occurrence Handle10.1042/0264-6021:3380471 Occurrence Handle10024525
EE Sander JP ten Klooster S Delft Particlevan RA Kammen Particlevan der JG Collard (1999) ArticleTitleRac downregulates Rho activity: reciprocal balance between both GTPases determines cellular morphology and migratory behavior J Cell Biol 147 1009–1022 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.147.5.1009 Occurrence Handle10579721
KL Golen Particlevan LW Bao Q Pan FR Miller ZF Wu SD Merajver (2002) ArticleTitleMitogen activated protein kinase pathway is involved in RhoC GTPase induced motility, invasion and angiogenesis in inflammatory breast cancer Clin Exp Metastasis 19 301–311 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1015518114931 Occurrence Handle12090470
G. Albrecht-Buehler (1977) ArticleTitleThe phagokinetic tracks of 3T3 cells Cell 11 395–404 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0092-8674(77)90057-5 Occurrence Handle329998
GE Meyer E Shelden B Kim EL Feldman (2001) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor I stimulates motility in human neuroblastoma cells Oncogene 20 7542–7550 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.onc.1204927 Occurrence Handle11709726
X Zhang S Kamaraju F Hakuno T Kabuta S Takahashi D Sachdev D Yee (2004) ArticleTitleMotility response to insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in MCF-7 cells is associated with IRS-2 activation and integrin expression Breast Cancer Res Treat 83 161–170 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:BREA.0000010709.31256.c6 Occurrence Handle14997047
M Maekawa T Ishizaki S Boku N Watanabe A Fujita A Iwamatsu T Obinata K Ohashi K Mizuno S Narumiya (1999) ArticleTitleSignaling from Rho to the actin cytoskeleton through protein kinases ROCK and LIM-kinase Science 285 895–898 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.285.5429.895 Occurrence Handle10436159
JG Jackson MF White D. Yee (1998) ArticleTitleInsulin receptor substrate-1 is the predominant signaling molecule activated by insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin, and interleukin-4 in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cells J Biol Chem 273 9994–10003 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.273.16.9994 Occurrence Handle9545345
B Dufourny J Alblas HA Teeffelen Particlevan FM Schaik Particlevan B Burg Particlevan der PH Steenbergh JS Sussenbach (1997) ArticleTitleMitogenic signaling of insulin-like growth factor I in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and is independent of mitogen-activated protein kinase J Biol Chem 272 31163–31171 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.272.49.31163 Occurrence Handle9388270
B Geiger A Bershadsky (2002) ArticleTitleExploring the neighborhood: adhesion-coupled cell mechanosensors Cell 110 139–142 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00831-0 Occurrence Handle12150922
MA Guvakova E Surmacz (1999) ArticleTitleThe activated insulin-like growth factor I receptor induces depolarization in breast epithelial cells characterized by actin filament disassembly and tyrosine dephosphorylation of FAK, Cas, and paxillin Exp Cell Res 251 244–255 Occurrence Handle10.1006/excr.1999.4566 Occurrence Handle10438590
BZ Katz L Romer S Miyamoto T Volberg K Matsumoto E Cukierman B Gieger KM Yamada (2003) ArticleTitleTargeting membrane-localized FAK to focal adhesions: Roles of tyrosine phosphorylation and Src family kinases J Biol Chem 16 16
L Lynch PI Vodyanik D Boettiger MA Guvakova (2005) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor I controls adhesion strength mediated by alpha5beta1 integrins in motile carcinoma cells Mol Biol Cell 16 51–63 Occurrence Handle10.1091/mbc.E04-05-0399 Occurrence Handle15509657
AK Berfield GJ Raugi CK Abrass (1996) ArticleTitleInsulin induces rapid and specific rearrangement of the cytoskeleton of rat mesangial cells in vitro J Histochem Cytochem 44 91–101 Occurrence Handle8609378
H Goto H Kosako K Tanabe M Yanagida M Sakurai M Amano K Kaibuchi M Inagaki (1998) ArticleTitlePhosphorylation of vimentin by Rho-associated kinase at a unique amino-terminal site that is specifically phosphorylated during cytokinesis J Biol Chem 273 11728–11736 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.273.19.11728 Occurrence Handle9565595
S Etienne-Manneville A Hall (2002) ArticleTitleRho GTPases in cell biology Nature 420 629–635
A Stathopoulou I Vlachonikolis D Mavroudis M Perraki C Kouroussis S Apostolaki N Malamos S Kakolyris A Kotsakis N Xenidis D Reppa V Georgoulias (2002) ArticleTitleMolecular detection of cytokeratin-19-positive cells in the peripheral blood of patients with operable breast cancer: evaluation of their prognostic significance J Clin Oncol 20 3404–3412 Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2002.08.135 Occurrence Handle12177100
SH Lee M Eom SJ Lee S Kim HJ Park D Park (2001) ArticleTitleBetaPix-enhanced p38 activation by Cdc42/Rac/PAK/MKK3/6-mediated pathway. Implication in the regulation of membrane ruffling J Biol Chem 276 25066–25072 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M010892200 Occurrence Handle11309380
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Lin, M., van Golen, K.L. et al. Multiple Signaling Pathways are Activated During Insulin-like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) Stimulated Breast Cancer Cell Migration. Breast Cancer Res Treat 93, 159–168 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-4626-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-4626-8