Abstract
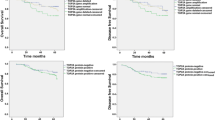
Introduction Overexpression of Topoisomerase II alpha (TOP2A) has been implicated with gene amplification of the 17q21 amplicon and consecutively with ErbB2 overexpression and amplification. However, gene amplification does not necessarily correlate with RNA and protein expression. There is growing evidence that TOP2A protein expression is a strong prognostic and TOP2A gene amplification might be a predictive marker (particularly for the use of anthracyclines). Methods Large scale analysis was performed using Affymetrix microarray data from n = 1,681 breast cancer patients to evaluate TOP2A expression. Results TOP2A expression showed a strong correlation with tumor size (χ2-test, P < 0.001), grading (P < 0.001), ErbB2 (P < 0.001) and Ki67 expression (P < 0.001) as well as nodal status (P = 0.042). Survival analysis revealed a significant prognostic value in ER positive (n = 994; log rank P < 0.001), but not in ER negative breast cancer patients (n = 369, P = 0.35). The prognostic impact of TOP2A expression was independent of Ki67 expression in ER positive tumors (P = 0.002 and P = 0.007 for high and low Ki67, respectively). Moreover a worse prognosis of high TOP2A expressing tumors was found in the subgroup of ErbB2 negative tumors (P < 0.001) and a trend among ErbB2 positive tumors (P = 0.11). The prognostic value of TOP2A was independent of whether the patients were untreated or had received adjuvant therapy. In multivariate Cox regression analysis including standard parameters TOP2A emerged to be the top prognostic marker (HR 2.40, 95% CI 1.68–3.43, P < 0.001). Conclusion TOP2A expression is an independent prognostic factor in ER positive breast cancer and could be helpful for risk assessment in ER positive breast cancer patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang JC (2002) Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(6):430–440
Pritchard KI, Messersmith H, Elavathil L, Trudeau M, O’Malley F, Dhesy-Thind B (2008) HER-2 and topoisomerase II as predictors of response to chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 26(5):736–744
Gennari A, Sormani MP, Pronzato P, Puntoni M, Colozza M, Pfeffer U, Bruzzi P (2008) HER2 status and efficacy of adjuvant anthracyclines in early breast cancer: a pooled analysis of randomized trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(1):14–20
Di Leo A, Gancberg D, Larsimont D, Tanner M, Jarvinen T, Rouas G, Dolci S, Leroy JY, Paesmans M, Isola J, Piccart MJ (2002) HER-2 amplification and topoisomerase IIalpha gene aberrations as predictive markers in node-positive breast cancer patients randomly treated either with an anthracycline-based therapy or with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil. Clin Cancer Res 8(5):1107–1116
Coon JS, Marcus E, Gupta-Burt S, Seelig S, Jacobson K, Chen S, Renta V, Fronda G, Preisler HD (2002) Amplification and overexpression of topoisomerase IIalpha predict response to anthracycline-based therapy in locally advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8(4):1061–1067
Cardoso F, Durbecq V, Larsimont D, Paesmans M, Leroy JY, Rouas G, Sotiriou C, Renard N, Richard V, Piccart MJ, Di Leo A (2004) Correlation between complete response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy and topoisomerase II-alpha gene amplification and protein overexpression in locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer. Int J Oncol 24(1):201–209
Tanner M, Isola J, Wiklund T, Erikstein B, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P, Malmström P, Wilking N, Nilsson J, Bergh J (2006) Topoisomerase IIalpha gene amplification predicts favorable treatment response to tailored and dose-escalated anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy in HER-2/neu-amplified breast cancer: Scandinavian Breast Group Trial 9401. J Clin Oncol 24(16):2428–2436
Arriola E, Moreno A, Varela M, Serra JM, Falo C, Benito E, Escobedo AP (2006) Predictive value of HER-2 and Topoisomerase IIalpha in response to primary doxorubicin in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 42(17):2954–2960
Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, Norton L, Ravdin P, Taube S, Somerfield MR, Hayes DF, Bast RC Jr (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(33):5287–5312
Knoop AS, Knudsen H, Balslev E, Rasmussen BB, Overgaard J, Nielsen KV, Schonau A, Gunnarsdóttir K, Olsen KE, Mouridsen H, Ejlertsen B (2005) Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. Retrospective analysis of topoisomerase IIa amplifications and deletions as predictive markers in primary breast cancer patients randomly assigned to cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil or cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and fluorouracil: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol 23(30):7483–7490
O’Malley FP, Chia S, Tu D et al (2006) Topoisomerase II alpha protein overexpression has predictive utility in a randomized trial comparing CMF to CEF in premenopausal women with node positive breast cancer (NCIC CTG MA. 5). Presented at San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, December 14–15, 2006
Rody A, Karn T, Gätje R, Ahr A, Solbach C, Kourtis K, Munnes M, Loibl S, Kissler S, Ruckhäberle E, Holtrich U, von Minckwitz G, Kaufmann M (2007) Gene expression profiling of breast cancer patients treated with docetaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide within the GEPARTRIO trial: HER-2, but not topoisomerase II alpha and microtubule-associated protein tau, is highly predictive of tumor response. Breast 16(1):86–93
Slamon D, Eiermann W, Robert N, Pienkowski T, Martin M, Pawlicki M, Chan M, Smylie M, Liu M, Falkson C, Pinter T, Fornander T, Shiftan T, Valero V, Mackey J, Tabah-Fisch I, Buyse M, Lindsay MA, Riva A, Bee V, Pegram M, Press M, Crown J. on behalf of the BCIRG 006 Investigators, Phase III randomized trial comparing doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (ACT) with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel and trastuzumab (ACTH) with docetaxel, carboplatin and trastuzumab (TCH) in HER2 positive early breast cancer patients: BCIRG 006 study, SABCS 2005, abstr. 1
Mueller RE, Parkes RK, Andrulis I, O’Malley FP (2004) Amplification of the TOP2A gene does not predict high levels of topoisomerase II alpha protein in human breast tumor samples. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 39(4):288–297
Fritz P, Cabrera CM, Dippon J, Gerteis A, Simon W, Aulitzky WE, van der Kuip H (2005) c-ErbB2 and topoisomerase IIalpha protein expression independently predict poor survival in primary human breast cancer: a retrospective study. Breast Cancer Res 7(3):R374–R384
Arriola E, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Lambros MB, Jones RL, James M, Savage K, Smith IE, Dowsett M, Reis-Filho JS (2007) Topoisomerase II alpha amplification may predict benefit from adjuvant anthracyclines in HER2 positive early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 106(2):181–189
Rody A, Holtrich U, Gaetje R, Gehrmann M, Engels K, von Minckwitz G, Loibl S, Diallo-Danebrock R, Ruckhäberle E, Metzler D, Ahr A, Solbach C, Karn T, Kaufmann M (2007) Poor outcome in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers predicted by loss of plexin B1. Clin Cancer Res 13(4):1115–1122
Ruckhäberle E, Rody A, Engels K, Gaetje R, von Minckwitz G, Schiffmann S, Grösch S, Geisslinger G, Holtrich U, Karn T, Kaufmann M (2007) Microarray analysis of altered sphingolipid metabolism reveals prognostic significance of sphingosine kinase 1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9836-9
Rody A, Holtrich U, Muller V, Gaetje R, Diallo R, Gehrmann M, von Minckwitz G, Engels K, Karn T, Kaufmann M (2006) c-kit: identification of co-regulated genes by gene expression profiling and clinical relevance of two breast cancer subtypes with stem cell like features. 2006 ASCO annual meeting proceedings part I. J Clin Oncol 24:622
Ahr A, Karn T, Solbach C, Seiter T, Strebhardt K, Holtrich U, Kaufmann M (2002) Identification of high risk breast-cancer patients by gene expression profiling. Lancet 359(9301):131–132
Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB, Vergara L, Ploner A, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Klaar S, Liu ET, Bergh J (2005) An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(38):13550–13555
Pawitan Y, Bjohle J, Amler L, Borg AL, Egyhazi S, Hall P, Han X, Holmberg L, Huang F, Klaar S, Liu ET, Miller L, Nordgren H, Ploner A, Sandelin K, Shaw PM, Smeds J, Skoog L, Wedren S, Bergh J (2005) Gene expression profiling spares early breast cancer patients from adjuvant therapy: derived and validated in two population-based cohorts. Breast Cancer Res 7(6):R953–R964
Wang Y, Klijn JG, Zhang Y, Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Yang F, Talantov D, Timmermans M, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Yu J, Jatkoe T, Berns EM, Atkins D, Foekens JA (2005) Gene-expression profiles to predict distant metastasis of lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer. Lancet 365(9460):671–679
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Padua D, Bos P, Nguyen DX, Nuyten D, Kreike B, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Ishwaran H, Foekens JA, van de Vijver M, Massagué J (2007) Lung metastasis genes couple breast tumor size and metastatic spread. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(16):6740–6745
Sotiriou C, Wirapati P, Loi S, Harris A, Fox S, Smeds J, Nordgren H, Farmer P, Praz V, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Larsimont D, Cardoso F, Peterse H, Nuyten D, Buyse M, Van de Vijver MJ, Bergh J, Piccart M, Delorenzi M (2006) Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(4):262–272
Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Lallemand F, Tutt AM, Gillet C, Ellis P, Harris A, Bergh J, Foekens JA, Klijn JG, Larsimont D, Buyse M, Bontempi G, Delorenzi M, Piccart MJ, Sotiriou C (2007) Definition of clinically distinct molecular subtypes in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinomas through genomic grade. J Clin Oncol 25(10):1239–1246
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL, Massagué J (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436(7050):518–524
Desmedt C, Piette F, Loi S, Wang Y, Lallemand F, Haibe-Kains B, Viale G, Delorenzi M, Zhang Y, d’Assignies MS, Bergh J, Lidereau R, Ellis P, Harris AL, Klijn JG, Foekens JA, Cardoso F, Piccart MJ, Buyse M, Sotiriou C (2007) TRANSBIG consortium. Strong time dependence of the 76-gene prognostic signature for node-negative breast cancer patients in the TRANSBIG multicenter independent validation series. Clin Cancer Res 13(11):3207–3214
The International Genomics Consortium (IGC). The expO project (Expression Project For Oncology) http://www.intgen.org/
Li C, Wong WH (2001) Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(1):31–36
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope LM, Hobbs B, Speed TP (2003) Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic Acids Res 31(4):e15
Foekens JA, Atkins D, Zhang Y, Sweep FC, Harbeck N, Paradiso A, Cufer T, Sieuwerts AM, Talantov D, Span PN, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Zito AF, Specht K, Hoefler H, Golouh R, Schittulli F, Schmitt M, Beex LV, Klijn JG, Wang Y (2006) Multicenter validation of a gene expression-based prognostic signature in lymph node-negative primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(11):1665–1671
Gong Y, Yan K, Lin F, Anderson K, Sotiriou C, Andre F, Holmes FA, Valero V, Booser D, Pippen JE Jr, Vukelja S, Gomez H, Mejia J, Barajas LJ, Hess KR, Sneige N, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L, Symmans WF (2007) Determination of oestrogen-receptor status and ERBB2 status of breast carcinoma: a gene-expression profiling study. Lancet Oncol 8(3):203–211
Bonnefoi H, Potti A, Delorenzi M, Mauriac L, Campone M, Tubiana-Hulin M, Petit T, Rouanet P, Jassem J, Blot E, Becette V, Farmer P, André S, Acharya CR, Mukherjee S, Cameron D, Bergh J, Nevins JR, Iggo RD (2007) Validation of gene signatures that predict the response of breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a substudy of the EORTC 10994/BIG 00–01 clinical trial. Lancet Oncol 8(12):1071–1078
Alexe G, Dalgin GS, Scanfeld D, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP, DeLisi C, Harris L, Barnard N, Martel M, Levine AJ, Ganesan S, Bhanot G (2007) High expression of lymphocyte-associated genes in node-negative HER2+ breast cancers correlates with lower recurrence rates. Cancer Res 67(22):10669–10676
de Azambuja E, Cardoso F, de Castro G Jr, Colozza M, Mano MS, Durbecq V, Sotiriou C, Larsimont D, Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Paesmans M (2007) Ki-67 as prognostic marker in early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of published studies involving 12,155 patients. Br J Cancer 96(10):1504–1513
Spyratos F, Ferrero-Poüs M, Trassard M, Hacène K, Phillips E, Tubiana-Hulin M, Le Doussal V (2002) Correlation between MIB-1 and other proliferation markers: clinical implications of the MIB-1 cutoff value. Cancer 94(8):2151–2159
Isaacs RJ, Davies SL, Sandri MI, Redwood C, Wells NJ, Hickson ID (1998) Physiological regulation of eukaryotic topoisomerase II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1400(1–3):121–137
Isaacs RJ, Harris AL, Hickson ID (1996) Regulation of the human topoisomerase IIalpha gene promoter in confluence-arrested cells. J Biol Chem 271(28):16741–16747
Bagwell CB, Clark GM, Spyratos F, Chassevent A, Bendahl PO, Stål O, Killander D, Jourdan ML, Romain S, Hunsberger B, Baldetorp B (2001) Optimizing flow cytometric DNA ploidy and S-phase fraction as independent prognostic markers for node-negative breast cancer specimens. Cytometry 46(3):121–135
Hannemann J, Kristel P, van Tinteren H, Bontenbal M, van Hoesel QG, Smit WM, Nooij MA, Voest EE, van der Wall E, Hupperets P, de Vries EG, Rodenhuis S, van de Vijver MJ (2006) Molecular subtypes of breast cancer and amplification of topoisomerase II alpha: predictive role in dose intensive adjuvant chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 95(10):1334–1341
Acknowledgements
We thank Katherina Kourtis and Samira Adel for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Krebshilfe, the Margarete Bonifer-Stiftung, Bad Soden, the BANSS-Stiftung, Biedenkopf, and the Dr. Robert Pfleger-Stiftung, Bamberg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Rody and T. Karn contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rody, A., Karn, T., Ruckhäberle, E. et al. Gene expression of topoisomerase II alpha (TOP2A) by microarray analysis is highly prognostic in estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 113, 457–466 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-9964-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-9964-x