Abstract
Purpose
Statins are commonly prescribed medications that potently reduce cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular events. Preclinical studies suggested statins also possess cancer chemopreventive properties. However, the clinical studies provided contradictory results as to whether statins influence the risk of pancreatic cancer. Herein, we present this meta-analysis to assess the association between statin use and risk of pancreatic cancer.
Methods
We conducted a comprehensive search up to August 2011 for the eligible studies. Pooled relative risk (RR) estimates and corresponding 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using the inverse-variance-weighted random-effects model. Subgroup analyses were conducted where data were available. Heterogeneity was assessed by the Cochran’s Q test and the I 2 statistic.
Results
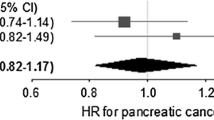
We included 16 studies that involving 1,692,863 participants and 7,807 pancreatic cancer cases. Pooled results only indicated a non-significant decrease of pancreatic cancer risk among all statin users (RR 0.89; 95 % CIs, 0.74–1.07). Similar results were obtained in the subgroup analyses of the long-term (more than 4 years) follow-up (RR 0.94, 0.81–1.08) and statin use (RR 0.97, 0.76–1.23), and a null association was found between lipophilic statin use and pancreatic cancer risk (RR 1.03, 0.92–1.16). No evidence of publication bias was observed in the present meta-analysis. However, significant heterogeneity was detected among all studies (p < 0.00001, I 2 = 81 %).
Conclusions
In conclusion, our results suggest that there is no association between statin use and pancreatic cancer risk, when statins are taken at daily doses for cardiovascular event prevention.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RR:
-
Relative risk
- CIs:
-
Confidence intervals
- RCTs:
-
Randomized controlled trials
- HMG-CoA:
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A
References
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61(4):212–236. doi:10.3322/caac.20121
Hidalgo M (2010) Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 362(17):1605–1617. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0901557
Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, Kirby A, Sourjina T, Peto R, Collins R, Simes R (2005) Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet 366(9493):1267–1278. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67394-1
Newman TB, Hulley SB (1996) Carcinogenicity of lipid-lowering drugs. JAMA 275(1):55–60
Chan KK, Oza AM, Siu LL (2003) The statins as anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res 9(1):10–19
Vaklavas C, Chatzizisis YS, Tsimberidou AM (2011) Common cardiovascular medications in cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther 130(2):177–190. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.01.009
Sumi S, Beauchamp RD, Townsend CM Jr, Uchida T, Murakami M, Rajaraman S, Ishizuka J, Thompson JC (1992) Inhibition of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell growth by lovastatin. Gastroenterology 103(3):982–989
Sumi S, Beauchamp RD, Townsend CM Jr, Pour PM, Ishizuka J, Thompson JC (1994) Lovastatin inhibits pancreatic cancer growth regardless of RAS mutation. Pancreas 9(5):657–661
Kusama T, Mukai M, Iwasaki T, Tatsuta M, Matsumoto Y, Akedo H, Nakamura H (2001) Inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced RhoA translocation and invasion of human pancreatic cancer cells by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. Cancer Res 61(12):4885–4891
Kusama T, Mukai M, Iwasaki T, Tatsuta M, Matsumoto Y, Akedo H, Inoue M, Nakamura H (2002) 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase inhibitors reduce human pancreatic cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Gastroenterology 122(2):308–317
Gbelcova H, Lenicek M, Zelenka J, Knejzlik Z, Dvorakova G, Zadinova M, Pouckova P, Kudla M, Balaz P, Ruml T, Vitek L (2008) Differences in antitumor effects of various statins on human pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 122(6):1214–1221. doi:10.1002/ijc.23242
Khurana V, Sheth A, Caldito G, Barkin JS (2007) Statins reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer in humans—a case-control study of half a million veterans. Pancreas 34(2):260–265. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e318030e963
Kaye JA, Jick H (2004) Statin use and cancer risk in the general practice research database. Br J Cancer 90(3):635–637. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601566
Bradley MC, Hughes CM, Cantwell MM, Murray LJ (2010) Statins and pancreatic cancer risk: a nested case-control study. Cancer Causes Control 21(12):2093–2100. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9628-0
Chiu H-F, Chang C–C, Ho S-C, Wu T-N, Yang C-Y (2011) Statin use and the risk of pancreatic cancer a population-based case-control study. Pancreas 40(5):669–672. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e31821fd5cd
Friedman GD, Flick ED, Udaltsova N, Chan J, Quesenberry CP Jr, Habel LA (2008) Screening statins for possible carcinogenic risk: up to 9 years of follow-up of 361,859 recipients. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 17(1):27–36. doi:10.1002/pds.1507
Bonovas S, Filioussi K, Sitaras NM (2008) Statins are not associated with a reduced risk of pancreatic cancer at the population level, when taken at low doses for managing hypercholesterolemia: evidence from a meta-analysis of 12 studies. Am J Gastroenterol 103(10):2646–2651. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.02051.x
Vitek L (2009) Statins and pancreatic cancer: are all statins the same? Am J Gastroenterol 104(2):525. doi:10.1038/ajg.2008.103 (author reply 525)
Duncan RE, El-Sohemy A, Archer MC (2005) Statins and cancer development. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(8):1897–1898. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0027
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283(15):2008–2012
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2535
Lovastatin Study Groups I Through IV (1993) Lovastatin 5-year safety and efficacy study. Arch Intern Med 153(9):1079–1087
Olsen JH, Johansen C, Sorensen HT, McLaughlin JK, Mellemkjaer L, Steffensen FH, Fraumeni JF Jr (1999) Lipid-lowering medication and risk of cancer. J Clin Epidemiol 52(2):167–169
Higgins JP, Green S (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. http://www.cochrane-handbook.org/
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P (2012) The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
Bardou M, Barkun A, Martel M (2010) Effect of statin therapy on colorectal cancer. Gut 59(11):1572–1585. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.190900
Midgette AS, Wong JB, Beshansky JR, Porath A, Fleming C, Pauker SG (1994) Cost-effectiveness of streptokinase for acute myocardial infarction: a combined meta-analysis and decision analysis of the effects of infarct location and of likelihood of infarction. Med Decis Making 14(2):108–117
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(7109):629–634
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50(4):1088–1101
Clearfield M, Downs JR, Weis S, Whitney EJ, Kruyer W, Shapiro DR, Stein EA, Langendorfer A, Beere PA, Gotto AM (2001) Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study (AFCAPS/TexCAPS): efficacy and tolerability of long-term treatment with lovastatin in women. J Women’s Health Gender Based Med 10(10):971–981. doi:10.1089/152460901317193549
Serruys PW, de Feyter P, Macaya C, Kokott N, Puel J, Vrolix M, Branzi A, Bertolami MC, Jackson G, Strauss B, Meier B (2002) Fluvastatin for prevention of cardiac events following successful first percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 287(24):3215–3222
Strandberg TE, Pyorala K, Cook TJ, Wilhelmsen L, Faergeman O, Thorgeirsson G, Pederson TR, Kjekshus J (2004) Mortality and incidence of cancer during 10-year follow-up of the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 364(9436):771–777. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16936-5
Jacobs EJ, Newton CC, Thun MJ, Gapstur SM (2011) Long-term use of cholesterol-lowering drugs and cancer incidence in a large United States cohort. Cancer Res 71(5):1763–1771. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-10-2953
Marelli C, Gunnarsson C, Ross S, Haas S, Stroup DF, Cload P, Clopton P, DeMaria AN (2011) Statins and risk of cancer a retrospective cohort analysis of 45,857 matched pairs from an electronic medical records database of 11 million adult Americans. J Am Coll Cardiol 58(5):530–537. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.04.015
Haukka J, Sankila R, Klaukka T, Lonnqvist J, Niskanen L, Tanskanen A, Wahlbeck K, Tiihonen J (2010) Incidence of cancer and statin usage—record linkage study. Int J Cancer 126(1):279–284. doi:10.1002/ijc.24536
Sato S, Ajiki W, Kobayashi T, Awata N (2006) Pravastatin use and the five-year incidence of cancer in coronary heart disease patients: from the prevention of coronary sclerosis study. J Epidemiol 16(5):201–206
Graaf MR, Beiderbeck AB, Egberts ACG, Richel DJ, Guchelaar H-J (2004) The risk of cancer in users of statins. J Clin Oncol 22(12):2388–2394. doi:10.1200/jco.2004.02.027
Coogan PF, Rosenberg L, Strom BL (2007) Statin use and the risk of 10 cancers. Epidemiology 18(2):213–219. doi:10.1097/01.ede.0000254694.03027.a1
Pugh TE, Little MW, Carey FJ, Robinson RJ, Clark A, Metcalfe M, Ndokera R, Ing H, Dennison A, Hart A (2011) Aspirin, NSAIDS, calcium-channel blockers and statins in the aetiology of pancreatic cancer: preliminary results from a case-control study in two centres in the UK. Gut 60(Suppl 1):A81. doi:10.1136/gut.2011.239301.166
Dorais M TR, Rakel A, Lelorrier J, Panzini B (2007) Statins, nsaids and pancreatic cancer. Paper presented at the 4th Canadian therapeutics congress, Halifax, Nova Scotia, 10 May 2007. http://www.cjcp.ca/pubmed.php?articleId=113
Corsini A, Bellosta S, Baetta R, Fumagalli R, Paoletti R, Bernini F (1999) New insights into the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of statins. Pharmacol Ther 84(3):413–428
Moorman PG, Hamilton RJ (2007) Statins and cancer risk: what do we know and where do we go from here? Epidemiology 18(2):194–196. doi:10.1097/01.ede.0000254699.31405.e2
Brookhart MA, Patrick AR, Dormuth C, Avorn J, Shrank W, Cadarette SM, Solomon DH (2007) Adherence to lipid-lowering therapy and the use of preventive health services: an investigation of the healthy user effect. Am J Epidemiol 166(3):348–354. doi:10.1093/aje/kwm070
Boudreau DM, Yu O, Johnson J (2010) Statin use and cancer risk: a comprehensive review. Expert Opin Drug Saf 9(4):603–621. doi:10.1517/14740331003662620
Dale KM, Coleman CI, Henyan NN, Kluger J, White CM (2006) Statins and cancer risk: a meta-analysis. JAMA 295(1):74–80. doi:10.1001/jama.295.1.74
Kuoppala J, Lamminpaa A, Pukkala E (2008) Statins and cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer 44(15):2122–2132. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.06.025
Baigent C, Blackwell L, Emberson J, Holland LE, Reith C, Bhala N, Peto R, Barnes EH, Keech A, Simes J, Collins R (2010) Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: a meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 376(9753):1670–1681. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)61350-5
Shimoyama S (2011) Statins are logical candidates for overcoming limitations of targeting therapies on malignancy: their potential application to gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67(4):729–739. doi:10.1007/s00280-011-1583-2
Alsheikh-Ali AA, Karas RH (2009) The relationship of statins to rhabdomyolysis, malignancy, and hepatic toxicity: evidence from clinical trials. Curr Atheroscler Rep 11(2):100–104
Bocci G, Fioravanti A, Orlandi P, Bernardini N, Collecchi P, Del Tacca M, Danesi R (2005) Fluvastatin synergistically enhances the antiproliferative effect of gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer MIAPaCa-2 cells. Br J Cancer 93(3):319–330. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602720
Dimitroulakos J, Lorimer IA, Goss G (2006) Strategies to enhance epidermal growth factor inhibition: targeting the mevalonate pathway. Clin Cancer Res 12(14 Pt 2):4426s–4431s. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0089
Trial of Simvastatin and Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Cancer Patients (2012) http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00944463
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Gui Lv (Senior Lecturer in School of Foreign Studies, Southern Medical University) for her constructive comments and careful revision of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
There are no potential conflicts of interest among all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaobing Cui, Yue Xie and Min Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Xie, Y., Chen, M. et al. Statin use and risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 23, 1099–1111 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-012-9979-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-012-9979-9