Abstract
This work shows the effect of cellulose nanocrystal surface charge on the morphology, structure, thermal and dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites. CNCs extracted through sulfuric acid hydrolysis were modified using sodium hydroxide and cationization treatments to yield CNCs with zeta-potential values of − 26.1 ± 3.7 and − 4.4 ± 0.3 mV in comparison with the original highly-negative − 45.2 ± 1.1 mV. Nanocomposites where then obtained through doctor-blade casting followed by room temperature drying. CNC incorporation allows obtaining PVDF with 100% of γ-phase. An increase of the real dielectric constant ε′, dielectric loss tan δ and AC conductivity was observed by increasing CNC content. More importantly, these values are further boosted upon CNC surface-modification, suggesting the pivotal role of the CNC–PVDF interface. We conclude that the sulfate half-ester removal increase the amount of exposed –OH groups with increase the amount of accumulated charges at the PVDF–CNC interfaces.
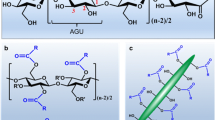
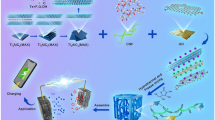
Graphic abstract
The effect of cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) surface charge on the morphology, structure, thermal and dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) nanocomposites is here shown. By removing the sulfate half-ester it is possible to increase the amount of exposed –OH groups, enhancing the accumulated charges at the PVDF–CNC interfaces and improving the electric performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Abdel-karim AM, Salama AH, Hassan ML (2018) Electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of nanofibrillated cellulose thin films from bagasse. J Phys Org Chem 31(9):e3851
Abitbol T, Marway H, Cranston E (2014) Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29:46–57
Alanis A, Valdés JH, María Guadalupe NV, Lopez R, Mendoza R, Mathew AP, Valencia L (2019) Plasma surface-modification of cellulose nanocrystals: a green alternative towards mechanical reinforcement of ABS. RSC Adv 9(30):17417–17424
Bai H, Wang X, Zhou Y, Zhang L (2012) Preparation and characterization of poly(vinylidene fluoride) composite membranes blended with nano-crystalline cellulose. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 22(3):250–257
Barnes E, Jefcoat JA, Alberts EM, McKechnie MA, Peel HR, Buchanan JP, Warner CM (2019) Effect of cellulose nanofibrils and TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils on the physical and mechanical properties of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/cellulose manofibril composites. Polymers 11(7):1091
Cai X, Lei T, Sun D, Lin L (2017) A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv 7(25):15382–15389
Cai X, Jiang Z, Zhang X, Gao T, Yue K, Zhang X (2018) Thermal property improvement of polytetrafluoroethylene nanocomposites with graphene nanoplatelets. RSC Adv 8(21):11367–11374
Chen RH, Chen LF, Chia CT (2007) Impedance spectroscopic studies on congruent LiNbO3single crystal. J Phys Condens Matter 19(8):086225
Cho SY, Lee ME, Kwak HW, Jin H-J (2018) Surface-modified cellulose nanocrystal-incorporated Poly(butylene succinate) nanocomposites. Fibers Polym 19(7):1395–1402
Cui Z, Hassankiadeh NT, Zhuang Y, Drioli E, Lee YM (2015) Crystalline polymorphism in poly(vinylidenefluoride) membranes. Prog Polym Sci 51:94–126
Dillon DR, Tenneti KK, Li CY, Ko FK, Sics I, Hsiao BS (2006) On the structure and morphology of polyvinylidene fluoride–nanoclay nanocomposites. Polymer 47(5):1678–1688
Dufresne A (2013) Nanocellulose: a new ageless bionanomaterial. Mater Today 16(6):220–227
Ferreira JCC, Monteiro TS, Lopes AC, Costa CM, Silva MM, Machado AV, Lanceros-Mendez S (2015) Variation of the physicochemical and morphological characteristics of solvent casted poly(vinylidene fluoride) along its binary phase diagram with dimethylformamide. J Non-Cryst Solids 412:16–23
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Godzhaev EM, Magerramov AM, Osmanova SS, Nuriev MA, Allakhyarov EA (2007) Charge state of composites based on polyethylene with semiconductor filler TlInSe2. Surf Eng Appl Electrochem 43(2):148–151
Gregorio R, Ueno EM (1999) Effect of crystalline phase, orientation and temperature on the dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). J Mater Sci 34(18):4489–4500
Habibi Y, Lucia LA, Rojas OJ (2010) Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Rev 110(6):3479–3500
Hasani M, Cranston ED, Westman G, Gray DG (2008) Cationic surface functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals. Soft Matter 4(11):2238
Hikosaka M, Rastogi S, Keller A, Kawabata H (1992) Investigations on the crystallization of polyethylene under high pressure: role of mobile phases, lamellar thickening growth, phase transformations, and morphology. J Macromol Sci Part B 31(1):87–131
Issa AA, Al-Maadeed M, Luyt AS, Mrlik M, Hassan MK (2016) Investigation of the physico-mechanical properties of electrospun PVDF/cellulose (nano)fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 133(26):43594
Jia N, Xing Q, Xia G, Sun J, Song R, Huang W (2015) Enhanced β-crystalline phase in poly(vinylidene fluoride) films by polydopamine-coated BaTiO3 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 139:212–215
Jiang Y, Ye Y, Yu J, Wu Z, Li W, Xu J, Xie G (2007) Study of thermally poled and corona charged poly(vinylidene fluoride) films. Polym Eng Sci 47(9):1344–1350
Jonscher AK (1977) The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267(5613):673–679
Kollmann FVA, Bazhenov: Piezoelectric Properties of Wood. Consultants Bureau, New York (1961) Zeitschrift für Elektrochemie, Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische. Chemie 66(6):522–523
Lin N, Dufresne A (2014) Surface chemistry, morphological analysis and properties of cellulose nanocrystals with gradiented sulfation degrees. Nanoscale 6:5384–5393
Lizundia E, Meaurio E, Vilas JL (2016) Chapter 3—grafting of cellulose nanocrystals. In: Multifunctional polymeric nanocomposites based on cellulosic reinforcements, pp 61–113
Lizundia E, Urruchi A, Vilas JL, Leon LM (2016) Increased functional properties and thermal stability of flexible cellulose nanocrystal/ZnO films. Carbohydr Polym 136:250–258
Lizundia E, Nguyen TD, Vilas JL, Hamad WY, MacLachlan MJ (2017) Chiroptical, morphological and conducting properties of chiral nematic mesoporous cellulose/polypyrrole composite films. J Mater Chem A 5(36):19184–19194
Lizundia E, Goikuria U, Vilas JL, Cristofaro F, Bruni G, Fortunati E, Armentano I, Visai L, Torre L (2018) Metal nanoparticles embedded in cellulose nanocrystal based films: material properties and post-use analysis. Biomacromol 19(7):2618–2628
Lopes AC, Costa CM, Tavares CJ, Neves IC, Lanceros-Mendez S (2011) Nucleation of the electroactive γ phase and enhancement of the optical transparency in low filler content poly(vinylidene)/clay nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C 115(37):18076–18082
Lopes AC, Costa CM, i Serra RS, Neves IC, Ribelles JLG, Lanceros-Méndez S (2013) Dielectric relaxation, ac conductivity and electric modulus in poly(vinylidene fluoride)/NaY zeolite composites. Solid State Ionics 235:42–50
Lucchini MA, Lizundia E, Moser S, Niederberger M, Nystrom G (2018) Titania-cellulose hybrid monolith for in-flow purification of water under solar illumination. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(35):29599–29607
Lv J, Zhang G, Zhang H, Zhao C, Yang F (2018a) Improvement of antifouling performances for modified PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with hydrophilic cellulose nanocrystal. Appl Surf Sci 440:1091–1100
Lv J, Zhang G, Zhang H, Yang F (2018b) Graphene oxide-cellulose nanocrystal (GO-CNC) composite functionalized PVDF membrane with improved antifouling performance in MBR: behavior and mechanism. Chem Eng J 352:765–773
Marega C, Marigo A (2003) Influence of annealing and chain defects on the melting behaviour of poly(vinylidene fluoride). Eur Polym J 39(8):1713–1720
Mendes SF, Costa CM, i Serra RS, Baldalo AA, Sencadas V, Gomez-Ribelles JL, Lanceros-Méndez S (2012) Influence of filler size and concentration on the low and high temperature dielectric response of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.47)O3 composites. J Polym Res 19(9):9967
Mendes-Felipe C, Oliveira J, Etxebarria I, Vilas-Vilela JL, Lanceros-Mendez S (2019) State-of-the-art and future challenges of UV curable polymer-based smart materials for printing technologies. Adv Mater Technol 4(3):1800618
Mujal-Rosas R, Marin Genesca M, Garcia Amoros J, Colom Fajula X, Salueña Berna X (2020) Comparison of the mechanical and dielectric characteristics of various polymers mixed with ground tired rubber (GTR) for its application as industrial work footwear insulator. DYNA 95:61–67
Nguyen TD, Sierra E, Eguiraun H, Lizundia E (2019) Iridescent cellulose nanocrystal films: the link between structural colour and Bragg’s law. Eur J Phys 39:045803
Ponnamma D, Parangusan H, Tanvir A, AlMa'adeed MAA (2019) Smart and robust electrospun fabrics of piezoelectric polymer nanocomposite for self-powering electronic textiles. Mater Des 184:108176
Ram F, Ambone T, Sharma A, Murugesan R, Shanmuganathan K (2018) Fluorinated nanocellulose-reinforced all-organic flexible ferroelectric nanocomposites for energy generation. J Phys Chem C 122(29):16540–16549
Ribeiro C, Costa CM, Correia DM, Nunes-Pereira J, Oliveira J, Martins P, Lanceros-Méndez S (2018) Electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based structures for advanced applications. Nat Protoc 13(4):681–704
Rincon-Iglesias M, Lizundia E, Lanceros-Mendez S (2019) Water-soluble cellulose derivatives as suitable matrices for multifunctional materials. Biomacromol 20(7):2786–2795
Sadi MS, Yang M, Luo L, Cheng D, Cai G, Wang X (2020) Direct screen printing of single-faced conductive cotton fabrics for strain sensing, electrical heating and color changing. Cellulose 26(10):6196–6188
Satapathy S, Pawar S, Gupta PK, Rvarma KB (2011) Effect of annealing on phase transition in poly(vinylidene fluoride) films prepared using polar solvent. Bull Mater Sci 34(4):727–733
Sencadas V, Gregorio R, Lanceros-Méndez S (2009) α to β phase transformation and microestructural changes of PVDF films induced by uniaxial stretch. J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 48(3):514–525
Sengupta R, Bhattacharya M, Bandyopadhyay S, Bhowmick AK (2011) A review on the mechanical and electrical properties of graphite and modified graphite reinforced polymer composites. Prog Polym Sci 36(5):638–670
Tan Z, Fu C, Gao Y, Qian J, Li W, Wu X, Ran X (2018) Modifications of Gamma poly(vinylidene fluoride) (γ-PVDF) films by high-energy electron beam irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 153:258–268
Tang XG, Hou M, Zou J, Truss R (2011) Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/microcrystalline cellulose nanocomposites with enhanced compatibility and properties. Key Eng Mater 471–472:355–360
Tang CW, Li B, Sun L, Lively B, Zhong WH (2012) The effects of nanofillers, stretching and recrystallization on microstructure, phase transformation and dielectric properties in PVDF nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 48(6):1062–1072
Wang X, Cheng W, Wnag D, Ni X, Han G (2019) Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride-based fibrous nanocomposite membranes reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals for efficient separation of water-in-oil emulsions. J Membr Sci 575:71–79
Yun G-Y, Kim J-H, Kim J (2009) Dielectric and polarization behaviour of cellulose electro-active paper (EAPap). J Phys D Appl Phys 42(8):082003
Zhang G, Lv J, Yang F (2019) Optimized anti-biofouling performance of bactericides/cellulose nanocrystals composites modified PVDF ultrafiltration membrane for micro-polluted source water purification. Water Sci Technol 79:1437–1446
Zhao Z, Zheng W, Yu W, Long B (2009) Electrical conductivity of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/carbon nanotube composites with a spherical substructure. Carbon 47(8):2118–2120
Zheng M, Tajvidi M, Tayeb AH, Stark NM (2020) Effects of bentonite on physical, mechanical and barrier properties of cellulose nanofibril hybrid films for packaging applications. Cellulose 26(9):5363–5379
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the FCT (Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia) for financial support under the framework of Strategic Funding Grants UID/FIS/04650/2019, UID/EEA/04436/2013 and UID/QUI/0686/ 2016; and Projects Nos. PTDC/BTM-MAT/28237/2017; PTDC/EMD-EMD/28159/2017 and PTDC/FIS-MAC/28157/2017. The authors also thank the FCT for financial Support under grants SFRH/BPD/121526/2016 (D.M.C.) and SFRH/BPD/112547/2015 (C.M.C.) as well POCH and European Union. Financial support from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO) through Project MAT2016- 76039-C4-3-R (AEI/FEDER, UE) (including FEDER financial support) and from the Basque Government Industry and Education Departments under the ELKARTEK, HAZITEK and PIBA (PIBA-2018-06) programs, respectively, is also acknowledged
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rincón-Iglesias, M., Lizundia, E., Correia, D.M. et al. The role of CNC surface modification on the structural, thermal and electrical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites. Cellulose 27, 3821–3834 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03067-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03067-z