Summary
1. Aims: Brain vascular endothelial cells secret Adrenomedullin (AM) has multifunctional biological properties. AM affects cerebral blood flow and blood–brain barrier (BBB) function. We studied the role of AM on the permeability and tight junction proteins of brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMEC).
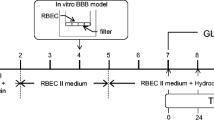
2. Methods: BMEC were isolated from rats and a BBB in vitro model was generated. The barrier functions were studied by measuring the transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) and the permeability of sodium fluorescein and Evans’ blue albumin. The expressions of tight junction proteins were analyzed using immunocytochemistry and immunoblotting.
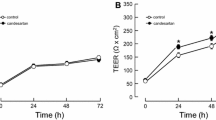
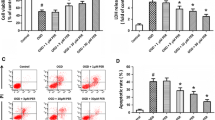
3. Results: AM increased TEER of BMEC monolayer dose-dependently. Immunocytochemistry revealed that AM enhanced the claudin-5 expression at a cell–cell contact site in a dose-dependent manner. Immunoblotting also showed an overexpression of claudin-5 in AM exposure.
4.Conclusions: AM therefore inhibits the paracellular transport in a BBB in vitro model through claudin-5 overexpression.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andras, I. E., Pu, H., Tian, J., Deli, M. A., Nath, A., Hennig, B., and Toborek, M. (2005). Signaling mechanisms of HIV-1 Tat-induced alterations of claudin-5 expression in brain endothelial cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 25:1159–1170.
Balabanov, R., and Dore-Duffy, P. (1998). Role of the CNS microvascular pericyte in the blood brain barrier. J. Neurosci. Res. 53:637–644.
Beltowski, J., and Jamroz, A. (2004). Adrenomedullin-what do we know 10 years since its discovery? Pol. J. Pharmacol. 56:5–27.
Chen, S. P., Zhou, B., Willis, B. C., Sandoval, A. J., Liebler, J. M., Kim, K. J., Ann, D. K., Crandall E. D., and Borok, Z. (2005). Effects of transdifferentiation and EGF on claudin isoform expression in alveolar epithelial cells. J. Appl. Physiol. 98:322–328.
Coyne, C. B., Vanhook, M. K., Gambling, T. M., Carson, J. L., Boucher, R. C., and Johnson, L. G. (2002). Regulation of airway tight junctions by proinflammatory cytokines. Mol. Biol. Cell 13:3218–3234.
Dehouck, M. P., Jolliet-Riant, P., Bree, F., Fruchart, J. C., Cecchelli, R., and Tillement, J. P. (1992). Drug transfer across the blood–brain barrier: correlation between in vitro and in vivo models. J. Neurochem. 58:1790–1807.
Deli, M. A., Abraham, C. S., Takahata, H., Katamine, S., and Niwa, M. (2000). Pentosan polysulfate regulates scavenger receptor-mediated, but not fluid-phase, endocytosis in immortalized cerebral endothelial cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 20:731–745.
Dohgu, S., Yamauchi, A., Takata, F., Naito, M., Tsuruo, T., Higuchi, S., Sawada, Y., and Kataoka, Y. (2004). Transforming growth factor-beta1 upregulates the tight junction and P-glycoprotein of brain microvascular endothelial cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 24:491–507.
Fernandez-Sauze, S., Delfino, C., Mabrouk, K., Dussert, C., Chinot, O., Martin, P. M., Grisoli, F., Ouafik, L., and Boudouresque, F. (2004). Effects of Adrenomedullin on endothelial cells in the multistep process of angiogenesis: Involvement of CRLR/RAMP2 and CRLR/RAMP3 receptors. Int. J. Cancer 108:797–804.
Florin, A., Maire, M., Bozec, A., Hellani, A., Chater, S., Bars, R., Chuzel, F., and Benahmed, M. (2005). Androgens and postmeiotic germ cells regulate claudin-11 expression in rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 146:1532–1540.
Fujioka, M., Nishio, K., Sakaki, T., Minamino, N., and Kitamura, K. (2000). Adrenomedullin in patients with cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 31:3079–3083.
Furuse, M., Fujita, K., Hiiragi, T., Fujimoto, K., and Tsukita, S. (1998). Claudin-1 and -2: Novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J. Cell Biol. 141:1539–1550.
Furuse, M., Sasaki, A., and Tsukita, S. (1999). Manner of interaction of heterogeneous claudin species within and between tight junction strands. J. Cell Biol. 147:891–903.
Han, X., Fink, M. P., and Delude, R. L. (2003). Proinflammatory cytokines cause NO*-dependent and -independent changes in expression and localization of tight junction proteins in intestinal epithelial cells. Shock 19:229–237.
Hayashi, K., Nakao, S., Nakaoke, R., Nakagawa, S., Kitagawa, N., and Niwa, M. (2004). Effects of hypoxia on endothelial/pericytic co-culture model of the blood–brain barrier. Regul. Pept. 123:77–83.
Huber, J. D., Egleton, R. D., and Davis, T. P. (2001). Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions in the blood–brain barrier. Trends Neurosci. 24:719–725.
Ishizaki, T., Chiba, H., Kojima, T., Fujibe, M., Soma, T., Miyajima, H., Nagasawa, K., Wada, I., and Sawada, N. (2003). Cyclic AMP induces phosphorylation of claudin-5 immunoprecipitates and expression of claudin-5 gene in blood–brain-barrier endothelial cells via protein kinase A-dependent and -independent pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 290:275–288.
Kastin, A. J., Akerstrom, V., Hackler, L., and Pan, W. (2001). Adrenomedullin and the blood–brain barrier. Horm. Metab. Res. 33:19–25.
Kato, K., Yin, H., Agata, J., Yoshida, H., Chao, L., and Chao, J. (2003). Adrenomedullin gene delivery attenuates myocardial infarction and apoptosis after ischemia and reperfusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 285:H1506–1514.
Kis, B., Abraham, C. S., Deli, M. A., Kobayashi, H., Wada, A., Niwa, M., Yamashita, H., and Ueta, Y. (2001a). Adrenomedullin in the cerebral circulation. Peptides 22:1825–1834 Review.
Kis, B., Deli, M. A., Kobayashi, H., Abraham, C. S., Yanagita, T., Kaiya, H., Isse, T., Nishi, R., Gotoh, S., Kangawa, K., Wada, A., Greenwood, J., Niwa, M., Yamashita, H., and Ueta, Y. (2001b). Adrenomedullin regulates blood–brain barrier functions in vitro. Neuroreport 12:4139–4142.
Kis, B., Kaiya, H., Nishi, R., Deli, M. A., Abraham, C. S., Yanagita, T., Isse, T., Gotoh, S., Kobayashi, H., Wada, A., Niwa, M., Kangawa, K., Greenwood, J., Yamashita, H., and Ueta, Y. (2002). Cerebral endothelial cells are a major source of adrenomedullin. J. Neuroendocrinol. 14:283–293.
Kis, B., Abraham, C. S., Deli, M. A., Kobayashi, H., Niwa, M., Yamashita, H., Busija, D. W., and Ueta, Y. (2003a). Adrenomedullin, an autocrine mediator of blood–brain barrier function. Hypertens. Res. 26 (Suppl.):S61–70 Review.
Kis, B., Snipes, J. A., Deli, M. A., Abraham, C. S., Yamashita, H., Ueta, Y., and Busija, D. W. (2003b). Chronic adrenomedullin treatment improves blood–brain barrier function but has no effects on expression of tight junction proteins. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 86:565–568.
Kuribayashi, M., Wang, J., Fujiwara, O., Doi, Y., Nabae, K., Tamano, S., Ogiso, T., Asamoto, M., and Shirai, T. (2005). Lack of effects of 1439 MHz electromagnetic near field exposure on the blood–brain barrier in immature and young rats. Bioelectromagnetics 26:578–588.
Liebner, S., Fischmann, A., Rascher, G., Duffner, F., Grote, E. H., Kalbacher, H., and Wolburg, H. (2000). Claudin-1 and claudin-5 expression and tight junction morphology are altered in blood vessels of human glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 100:323–331.
Lippoldt, A., Liebner, S., Andbjer, B., Kalbacher, H., Wolburg, H., Haller, H., and Fuxe, K. (2000). Organization of choroid plexus epithelial and endothelial cell tight junctions and regulation of claudin-1, -2 and -5 expression by protein kinase, C. Neuroreport 11:1427–1431.
Miyashita, K., Itoh, H., Sawada, N., Fukunaga, Y., Sone, M., Yamahara, K., Yurugi-Kobayashi, T., Park, K., and Nakao, K. (2003a). Adrenomedullin provokes endothelial Akt activation and promotes vascular regeneration both in vitro and in vivo. FEBS Lett. 544:86–92.
Miyashita, K., Itoh, H., Sawada, N., Fukunaga, Y., Sone, M., Yamahara, K., Yurugi, T., and Nakao, K. (2003b). Adrenomedullin promotes proliferation and migration of cultured endothelial cells. Hypertens. Res. 26(Suppl.):S93–98.
Morita, K., Furuse, M., Fujimoto, K., and Tsukita, S. (1999a). Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96:511–516.
Morita, K., Sasaki, H., Furuse, M., and Tsukita, S. (1999b). Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/ TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 147:185–194.
Nagoshi, Y., Kuwasako, K., Cao, Y. N., Imamura, T., Kitamura, K., and Eto, T. (2004). Tumor necrosis factor-α downregulates adrenomedullin receptors in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Peptides 25:1115–1121.
Serrano, J., Alonso, D., Encinas, J. M., Lopez, J. C., Fernandez, A. P., Castro-Blanco, S., Fernandez- Vizarra, P., Richart, A., Bentura, M. L., Santacana, M., Uttenthal, L. O., Cuttitta, F., Rodrigo, J., and Martinez, A. (2002). Adrenomedullin expression is up-regulated by ischemia-reperfusion in the cerebral cortex of the adult rat. Neuroscience 109:717–731.
Suzuki, Y., Horio, T., Nonogi, H., Hayashi, T., Kitamura, K., Eto, T., Kangawa, K., and Kawano, Y. (2004). Adrenomedullin as a sensitive marker for coronary and peripheral arterial complications in patients with atherosclerotic risks. Peptides 25:1321–1326.
Tahan, V., Avsar, E., Karaca, C., Uslu, E., Eren, F., Aydin, S., Uzun, H., Hamazaoglu, H. O., Besisik, F., Kalayci, C., Okten, A., and Tozun, N. (2003). Adrenomedullin in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. World J. Gastroenterol. 9:2325–2327.
Terata, K., Miura, H., Liu, Y., Loberiza, F., and Gutterman, D. D. (2000). Human coronary arteriolar dilation to adrenomedullin: role of nitric oxide and K(+). channels. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 279:H2620–2626.
Tsukita, S., and Furuse, M. (1999). Occludin and claudins in tight-junction strands: leading or supporting players? Trends Cell Biol. 9:268–273 Review.
Wijdicks, E. F. M., Heublein, D. M., and Burnett Jr., J. C. (2001). Increase and uncoupling of adrenomedullin from the natriuretic peptide system in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 94:252–256.
Wolburg, H., and Lippoldt, A. (2002). Tight junctions of the blood–brain barrier: development, composition and regulation. Vasc. Pharmacol. 38:323–337 Review.
Yi, X., Wang, Y., and Yu, F. S. (2000). Corneal epithelial tight junctions and their response to lipopolysaccharide challenge. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41:4093–4100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honda, M., Nakagawa, S., Hayashi, K. et al. Adrenomedullin Improves the Blood–Brain Barrier Function Through the Expression of Claudin-5. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 109–118 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9028-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9028-x