Abstract
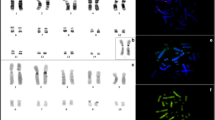
Laser microdissection was used for the preparation of whole chromosome painting probes in Silurana (Xenopus) tropicalis. Subsequent cross-species fluorescence in situ hybridization (Zoo-FISH) on its tetraploid relative Xenopus laevis revealed persistence of chromosomal quartets even after 50–65 million years of separate evolution. Their arrangement is in a partial concordance with previous experiments based on similarity of a high-resolution replication banding pattern. Further support for an allotetraploid origin of X. laevis was given by hybridization with a probe derived from the smallest X. tropicalis chromosome (Xt10). Here, pericentric areas of both arms of Xl 14 and 18 were stained, indicating intrachromosomal rearrangements. The positions of signals were not in agreement with the chromosomal quartets revealed by painting probes Xt 8 and 9 (Xl 11 + 14 and Xl 15 + 18, respectively). This suggests that both X. tropicalis chromosomes underwent non-reciprocal translocation of Xt10 separately in at least two different ancient ancestors. In addition, the observed translocation events could explain the origin of individuals with 18 chromosomes in diploid karyotypes, probably extinct after the genesis of the allotetraploid X. laevis (2n = 36).




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DOP-PCR:
-
degenerate oligonucleotide primed polymerase chain reaction
- FISH:
-
fluorescence in situ hybridization
- MYA:
-
million years ago
- NOR:
-
nucleolus organizer region
- SSR:
-
simple sequence repeat
- TSA:
-
tyramide signal amplification
- WCP:
-
whole chromosome painting
- WGA:
-
whole genome amplification
- Xl:
-
Xenopus laevis chromosome
- Xt:
-
Xenopus tropicalis chromosome
- Zoo-FISH:
-
cross-species fluorescence in situ hybridization
References
Chowdhary BP, Raudsepp T (2000) HSA4 and GGA4: remarkable conservation despite 300-Myr divergence. Genomics 15(1):102–105
Chowdhary BP, Raudsepp T (2001) Chromosome painting in farm, pet and wild animal species. Methods Cell Sci 23(1–3):37–55
Courtet M, Flajnik M, Du Pasquier L (2001) Major histocompatibility complex and immunoglobulin loci visualized by in situ hybridization on Xenopus chromosomes. Dev Comp Immunol 25(2):149–157
Evans BJ (2008) Genome evolution and speciation genetics of clawed frogs (Xenopus and Silurana). Front Biosci 1(13):4687–4706
Evans BJ, Kelley DB, Tinsley RC, Melnick DJ, Cannatella DC (2004) A mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of African clawed frogs: phylogeography and implications for polyploid evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 33(1):197–213
Fujiwara A, Abe S, Yamaha E, Yamazaki F, Yoshida MC (1998) Chromosomal localization and heterochromatin association of ribosomal RNA gene loci and silver-stained nucleolar organizer regions in salmonid fishes. Chromosome Res 6(6):463–471
Fukova I, Traut W, Vitkova M, Nguyen P, Kubickova S, Marec F (2007) Probing the W chromosome of the codling moth, Cydia pomonella, with sequences from microdissected sex chromatin. Chromosoma 116(2):135–145
Gribble S, Ng BL, Prigmore E, Burford DC, Carter NP (2004) Chromosome paints from single copies of chromosomes. Chromosome Res 12(2):143–151
Griffin DK, Robertson LB, Tempest HG et al (2008) Whole genome comparative studies between chicken and turkey and their implications for avian genome evolution. BMC Genomics 14(9):168
Guttenbach M, Nanda I, Feichtinger W, Masabanda JS, Griffin DK, Schmid M (2003) Comparative chromosome painting of chicken autosomal paints 1–9 in nine different bird species. Cytogenet Genome Res 103(1–2):173–184
Hellsten U, Khokha MK, Grammer TC, Harland RM, Richardson P, Rokhsar DS (2007) Accelerated gene evolution and subfunctionalization in the pseudotetraploid frog Xenopus laevis. BMC Biol 25(5):31
Hotz H, Uzzell T, Berger L (1997) Linkage groups of protein-coding genes in western palearctic water frogs reveal extensive evolutionary conservation. Genetics 147(1):255–270
Khokha MK, Krylov V, Reilly MJ et al (2009) Rapid gynogenetic mapping of Xenopus tropicalis mutations to chromosomes. Dev Dyn 238(6):1398–1406
Klein SL, Strausberg RL, Wagner L, Pontius J, Clifton SW, Richardson P (2002) Genetic and genomic tools for Xenopus research: the NIH Xenopus initiative. Dev Dyn 225(4):384–391
Krylov V, Mácha J, Tlapáková T, Takác M, Jonák J (2003) The c-SRC1 gene visualized by in situ hybridization on Xenopus laevis chromosomes. Cytogenet Genome Res 103(1–2):169–172
Krylov V, Tlapakova T, Macha J (2007) Localization of the single copy gene Mdh2 on Xenopus tropicalis chromosomes by FISH-TSA. Cytogenet Genome Res 116(1–2):110–112
Kubickova S, Cernohorska H, Musilova P, Rubes J (2002) The use of laser microdissection for the preparation of chromosome-specific painting probes in farm animals. Chromosome Res 10(7):571–577
Ocalewicz K, Penman DJ, Babiak I (2008) Variation in size and location of the Ag-NOR in the Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus). Genetica 133(3):261–267
Pollet N, Mazabraud A (2006) Insights from Xenopus genomes. Genome Dyn 2:138–153
Rab P, Rabova M, Pereira CS, Collares-Pereira MJ, Pelikanova S (2008) Chromosome studies of European cyprinid fishes: interspecific homology of leuciscine cytotaxonomic marker—the largest subtelocentric chromosome pair as revealed by cross-species painting. Chromosome Res 16(6):863–873
Schmid M, Steinlein C (1991) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XVI. High-resolution replication banding patterns in Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma 101(2):123–232
Schmid M, Steinlein C (2001) Sex chromosomes, sex-linked genes, and sex determination in the vertebrate class amphibia. EXS 91:143–176
Schmid M, Haaf T, Schempp W (1985) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. IX. The polyploid karyotypes of Odontophrynus americanus and Ceratophrys ornata (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Chromosoma 91(3–4):172–184
Shetty S, Griffin DK, Graves JA (1999) Comparative painting reveals strong chromosome homology over 80 million years of bird evolution. Chromosome Res 7(4):289–295
Smith JJ, Voss SR (2006) Gene order data from a model amphibian (Ambystoma): new perspectives on vertebrate genome structure and evolution. BMC Genomics 29(7):219
Teruel M, Cabrero J, Montiel EE, Acosta MJ, Sánchez A, Camacho JP (2009) Microdissection and chromosome painting of X and B chromosomes in Locusta migratoria. Chromosome Res 17(1):11–18
Tlapakova T, Krylov V, Macha J (2005) Localization, structure and polymorphism of two paralogous Xenopus laevis mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase genes. Chromosome Res 13(7):699–706
Tymowska J (1973) Karyotype analysis of Xenopus tropicalis Gray, Pipidae. Cytogenet Cell Genet 12(5):297–304
Tymowska J, Kobel HR (1972) Karyotype analysis of Xenopus muelleri (Peters) and Xenopus laevis (Daudin), Pipidae. Cytogenetics 11(4):270–278
Tymowska J, Fischberg M (1982) A comparison of the karyotype, constitutive heterochromatin, and nucleolar organizer regions of the new tetraploid species Xenopus epitropicalis Fischberg and Picard with those of Xenopus tropicalis Gray (Anura, Pipidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 34(1–2):149–157
Vitkova M, Fukova I, Kubickova S, Marec F (2007) Molecular divergence of the W chromosomes in pyralid moths (Lepidoptera). Chromosome Res 15(7):917–930
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant 304/07/P204 from the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic, by grant MSM0021620858 from the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic and by project MZE 0002716202 of the Grant Agency of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Walther Traut.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krylov, V., Kubickova, S., Rubes, J. et al. Preparation of Xenopus tropicalis whole chromosome painting probes using laser microdissection and reconstruction of X. laevis tetraploid karyotype by Zoo-FISH. Chromosome Res 18, 431–439 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-010-9127-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-010-9127-x