Abstract
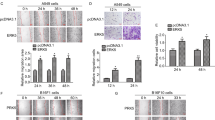
The murine EL4 lymphoma cell line exists in variants that are either sensitive or resistant to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). In sensitive cells, PMA causes Erk MAPK activation and Erk-mediated growth arrest. In resistant cells, PMA induces a low level of Erk activation, without growth arrest. A relatively unexplored aspect of the phenotypes is that resistant cells are more adherent to culture substrate than are sensitive cells. In this study, the roles of the protein tyrosine kinases FAK and Pyk2 in EL4 phenotype were examined, with a particular emphasis on the role of these proteins in metastasis. FAK is expressed only in PMA-resistant (or intermediate phenotype) EL4 cells, correlating with enhanced cell–substrate adherence, while Pyk2 is more highly expressed in non-adherent PMA-sensitive cells. PMA treatment causes modulation of mRNA for FAK (up-regulation) and Pyk2 (down-regulation) in PMA-sensitive but not PMA-resistant EL4 cells. The increase in Pyk2 mRNA is correlated with an increase in Pyk2 protein expression. The roles of FAK in cell phenotype were further explored using transfection and knockdown experiments. The results showed that FAK does not play a major role in modulating PMA-induced Erk activation in EL4 cells. However, the knockdown studies demonstrated that FAK expression is required for proliferation and migration of PMA-resistant cells. In an experimental metastasis model using syngeneic mice, only FAK-expressing (PMA-resistant) EL4 cells form liver tumors. Taken together, these studies suggest that FAK expression promotes metastasis of EL4 lymphoma cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- PMA:
-
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
References
Kramer CM, Sando JJ (1986) Substrates for protein kinase C in cytosol of EL4 mouse thymoma cells. Cancer Res 46:3040–3045
Meier KE, Licciardi KA, Haystead TAJ, Krebs EG (1991) Activation of messenger-independent protein kinases in wild-type and phorbol ester-resistant EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem 256:1914–1920
Baier-Bitterlich G, Uberall F, Bauer B, Fresser F, Wachter H, Grunicke H, Utermann G, Altman A, Baier G (1996) Protein kinase C-theta isoenzyme selective stimulation of the transcription factor complex AP-1 in T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol 16:1842–1850
Sansbury HM, Wisehart-Johnson AE, Qi C, Fulwood S, Meier KE (1997) Effects of protein kinase C activators on phorbol ester-sensitive and -resistant EL4 thymoma cells. Carcinogenesis 18:1817–1824
Richardson AF, Sando JJ (1995) Rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of an 85,000 M(r) protein after phorbol ester stimulation of EL4 thymoma cells. Cell Signal 7:17–30
Luo X, Sando JJ (1997) Deficient tyrosine phosphorylation of c-Cbl and associated proteins in phorbol ester-resistant EL4 mouse thymoma cells. J Biol Chem 272:12221–12228
Gause KC, Homma MK, Licciardi KA, Seger R, Ahn NG, Peterson MJ, Krebs EG, Meier KE (1993) Effects of phorbol ester on MAP kinase activator in wild-type and phorbol ester-resistant EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem 268:16124–16129
Bradshaw CD, Ella KM, Qi C, Sansbury HM, Wisehart-Johnson AE, Meier KE (1996) Effects of phorbol ester on phospholipase D and mitogen-activated protein kinase activities in T-lymphocyte cell lines. Immunol Lett 53:69–76
Resnick MS, Luo X, Vinton EG, Sando JJ (1997) Selective up-regulation of protein kinase C eta in phorbol ester-sensitive versus -resistant EL4 mouse thymoma cells. Cancer Res 57:2209–2215
Farrar JJ, Fuller-Farrar J, Simon PL, Hilfiker ML, Stadler BM, Farrar WL (1980) Thymoma production of T cell growth factor (interleukin 2). J Immunol 125:2555–2558
Sando JJ, Hilfiker ML, Piacentini MJ, Laufer TM (1982) Identification of phorbol ester receptors in T-cell growth factor-producing and -nonproducing EL4 mouse thymoma cells. Cancer Res 42:1676–1680
Pearlstein KT, Staiano-Coico L, Miller RA, Pelus LM, Kirch ME, Stutman O, Palladino MA (1983) Multiple lymphokine production by a phorbol ester-stimulated mouse thymoma: relationship to cell cycle events. J Natl Cancer Inst 71:583–590
Harrison JR, Lynch KR, Sando JJ (1987) Phorbol esters induce interleukin 2 mRNA in sensitive but not in resistant EL4 cells. J Biol Chem 262:234–238
Rayter SI, Woodrow M, Lucas SC, Cantrell DA, Downward J (1992) p21ras mediates control of IL-2 gene promoter function in T cell activation. EMBO J 11:4549–4556
Desrivieres S, Volarevic S, Mercep L, Ferrari S (1997) Evidence for different mechanisms of growth inhibition of T-cell lymphoma by phorbol esters and concanavalin A. J Biol Chem 272:2470–2476
Ku H, Meier KE (2000) Phosphorylation of paxillin via the ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem 275:11333–11340
Han S, Knoepp SM, Hallman M, Meier KE (2007) RasGRP confers the phorbol ester-sensitive phenotype to EL4 lymphoma cells. Mol Pharm 71:314–322
Chahal MS, Brauner D, Meier KE (2010) Effects of phospholipase D2 on EGF receptor response in EL4 lymphoma cells. Pharmaceuticals 3:2045–2058
Sansbury HM (1997) Phorbol ester responsiveness of sensitive and resistant EL4 thymoma cells. Dissertation, Medical University of South Carolina
Kisielow P, van Boehmer H (1995) Development and selection of T cells: facts and puzzles. Adv Immunol 58:87–209
Fine JS, Kruisbeek AM (1991) The role of LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions during murine T lymphocyte development. J Immunol 147:2852–2859
Cary LA, Guan JL (1999) Focal adhesion kinase in integrin-mediated signaling. Front Biosci 4:D102–D113
Boudreau N, Sympson CJ, Web Z, Bissell MJ (1995) Suppression of ICE and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Science 267:891–893
Wary KK, Mainiero F, Isakoff SJ, Marcantonio EE, Giancotti FG (1996) The adaptor protein Shc couples a class of integrins to the control of cell cycle progression. Cell 87:733–743
Cardone MH, Salveson GS, Widmann C, Johnson G, Frisch SM (1997) The regulation of anoikis: MEKK-1 activation requires cleavage by caspases. Cell 90:315–323
Schaller MD, Parsons JT (1994) Focal adhesion kinase and associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:705–710
Frisch SM, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E, Chan-Hui P-Y (1996) Control of adhesion-dependent cell survival by focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol 134:793–799
Schlaepfer DD, Hauck CR, Sieg DJ (1999) Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 7:435–478
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, Ilic D, Klingbeil CK, Schaefer E, Damsky CH, Schlaepfer DD (2000) FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 2:249–256
Frisch SM, Ruoslahti E (1997) Integrins and anoikis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:701–706
Sonoda Y, Matsumoto Y, Funakoshi M, Yamamoto D, Hanks SD, Kasahara T (2000) Anti-apoptotic role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Induction of inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins and apoptosis suppression by the overexpression of FAK in a human leukemic cell line, HL-60. J Biol Chem 275:116309–116315
Aoudjit F, Vuori K (2000) Engagement of the alpha2beta1 integrin inhibits Fas ligand expression and activation-induced cell death in T cells in a focal adhesion kinase-dependent manner. Blood 95:2044–2051
Siesser PMF, Hanks SK (2006) The signaling and biological implications of FAK overexpression in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:3233–3237
Shibue T, Weinberg RA (2009) Integrin β1-focal adhesion kinase signaling directs the proliferation of metastatic cancer cells disseminated in the lungs. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:10290–10295
Pirone DM, Liu WF, Ruiz SA, Gao L, Raghavan S, Lemmon CA, Romer LH, Chen CS (2006) An inhibitory role for FAK in regulating proliferation: a link between limited adhesion and RhoA-ROCK signaling. J Cell Biol 174:277–288
Choi K, Kennedy M, Keller G (1993) Expression of a gene encoding a unique protein-tyrosine kinase within specific fetal- and adult-derived hematopoietic lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5747–5751
Iwata S, Ohashi Y, Kamiguchi K, Morimoto C (2000) Beta 1-integrin-mediated cell signaling in T lymphocytes. J Dermatol Sci 23:75–86
Whitney GS, Chan PY, Blake J, Cosand WL, Neubauer MG, Aruffo A, Kanner SB (1993) Human T and B lymphocytes express a structurally conserved focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK. DNA Cell Biol 2:823–830
Recher C, Ysebaert L, Beyne-Rauzy O, Mansat-De Mas V, Ruidavets J-B, Cariven P, Demur C, Payrastre B, Laurent G, Racaud-Sultan C (2004) Expression of focal adhesion kinase in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with enhanced blast migration, increased cellularity, and poor prognosis. Cancer Res 64:3191–3197
Salgia R, Avraham S, Pisick E, Li JL, Raja S, Greenfield EA, Sattler M, Avrahan H, Griffin JD (1996) The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase forms a complex with paxillin in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem 271:31222–31226
Mazaki Y, Uchida H, Hino O, Hashimoto S, Sabe H (1998) Paxillin isoforms in mouse. Lack of the gamma isoform and developmentally specific beta isoform expression. J Biol Chem 273:22435–22441
Berg NN, Ostergaard HL (1997) T cell receptor engagement induces tyrosine phosphorylation of FAK and Pyk2 and their association with Lck. J Immunol 159:1753–1757
Ganju RK, Hatch WC, Avraham H, Ona MA, Druker B, Avraham S, Groopman JE (1997) RAFTK, a novel member of the focal adhesion kinase family, is phosphorylated and associates with signaling molecules upon activation of mature T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 185:1055–1063
Ostergaard H, Lysechko TL (2005) Focal adhesion kinase-related protein tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in T-cell activation and function. Immunol Res 31:267–282
Rodriguez-Fernandez JL, Gomez M, Luque A, Hogg N, Sanchez-Madrid F, Cabanas C (1999) The interaction of activated integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 with ligand intercellular adhesion molecule 1 induces activation and redistribution of focal adhesion kinase and proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 in T lymphocytes. Mol Biol Cell 10:1891–1907
van Seventer GA, Mullen MM, van Seventer JM (1998) Pyk2 is differentially regulated by beta1 integrin- and CD28-mediated co-stimulation in human CD4+ T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 28:3867–3877
Hatch WC, Ganju RK, Hiregowdara D, Avraham S, Groopman JE (1998) The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase (RAFTK) is tyrosine phosphorylated and participates in colony-stimulating factor-1/macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling in monocyte-macrophages. Blood 91:3967–3973
Li X, Hunter D, Morris J, Haskill JS, Earp HS (1998) A calcium-dependent tyrosine kinase splice variant in human monocytes. Activation by a two-stage process involving adherence and a subsequent intracellular signal. J Biol Chem 273:9361–9364
Avraham H, Park SY, Schinkmann K, Avraham S (2000) RAFTK/Pyk2-mediated cellular signalling. Cell Signal 12:123–133
Benbernou N, Muegge K, Durum SK (2000) Interleukin (IL)-7 induces rapid activation of Pyk2, which is bound to Janus kinase 1 and IL-7Ralpha. J Biol Chem 275:7060–7065
McLeod SJ, Shum AJ, Lee RL, Takei F, Gold MR (2004) The Rap GTPases regulate integrin-mediated adhesion, cell spreading, actin polymerization and Pyk2 tyrosine phosphorylation in B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 279:12009–12019
Seufferlein T, Rozengurt E (1995) Sphingosylphosphorylcholine rapidly induces tyrosine phosphorylation of p125FAK and paxillin, rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton and focal contact assembly. J Biol Chem 270:24343–24351
Renshaw MW, Price LS, Schwartz MA (1999) Focal adhesion kinase mediates the integrin signaling requirement for growth factor activation of MAP kinase. J Cell Biol 147:611–618
De Nichilo MO, Katz BZ, O’Connell B, Yamada KM (1999) De novo expression of pp125 FAK in human macrophages regulates CSK distribution and MAP kinase activation but does not affect focal contact structure. J Cell Physiol 178:164–172
Litvak V, Tian D, Shaul YD, Lev S (2000) Targeting of PYK2 to focal adhesions as a cellular mechanism for convergence between integrins and G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades. J Biol Chem 275:32736–32746
Andreev J, Galisteo ML, Kranenburg O, Logan SK, Ghiu ES, Okigaki M, Cary LA, Moolenaar WH, Schlessinger J (2001) Src and Pyk2 mediate G-protein-coupled receptor activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) but are not required for coupling to the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling cascade. J Biol Chem 276:20130–20135
Small CL, Shima JE, Uzumcu M, Skinner MK, Griswold MD (2005) Profiling gene expression during the differentiation and development of the murine embryonic gonad. Biol Reprod 72:492–501
Zhang H, Zhang S, Cheung NK, Ragupathi G, Livingston PO (1998) Antibodies against GD2 ganglioside can eradicate syngeneic cancer micrometastases. Cancer Res 58:2844–2849
Han S, Meier KE (2009) Integrated modulation of phorbol ester-induced Raf activation in EL4 lymphoma cells. Cell Signal 21:793–800
Zhu X, Assoian RK (1995) Integrin-dependent activation of MAP kinase: a link to shape-dependent cell proliferation. Mol Biol Cell 6:273–282
Sieg DJ, Ilic D, Dones KC, Damsky CH, Hunter T, Schlaepfer DD (1998) Pyk2 and Src-family protein-tyrosine kinases compensate for the loss of FAK in fibronectin-stimulated signaling events but Pyk2 does not fully function to enhance FAK-cell migration. EMBO J 17:5933–5947
Ueki K, Mimura T, Nakamoto T, Sasaki T, Aizawa S, Hirai H, Yano S, Naruse T, Nojima Y (1998) Integrin-mediated signal transduction in cells lacking focal adhesion kinase. FEBS Lett 432:197–201
Knoepp SM, Chahal MS, Xie Y, Zhang Z, Brauner DJ, Hallman MA, Robinson SA, Han S, Imai M, Tomlinson S, Meier KE (2008) Effects of active and inactive phospholipase D2 on signal transduction, adhesion, migration, invasion, and metastasis in EL4 lymphoma cells. Mol Pharm 74:574–584
Schaller MD (2010) Cellular functions of FAK kinases: insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J Cell Sci 123:1007–1013
Bacon KB, Szabo MC, Yssel H, Bolen JB, Schall TJ (1996) RANTES induces tyrosine kinase activity of stably complexed p125FAK and ZAP-70 in human T cells. J Exp Med 184:873–882
Tsuchida M, Manthei ER, Alam T, Knechtle SJ, Hamawy MM (2000) Regulation of T cell receptor- and CD28-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the focal adhesion tyrosine kinases Pyk2 and Fak by protein kinase C—a role for protein tyrosine phosphatases. J Biol Chem 275:1344–1350
Corsi FM, Rouer E, Girault JA, Enslen H (2006) Organization and post-transcriptional processing of focal adhesion kinase gene. MBC Genomics 7:198
Golubovskaya V, Kaur A, Cance W (2004) Cloning and characterization of the promoter region of human focal adhesion kinase gene: nuclear factor kappa B and p53 binding sites. Biochim Biophys Acta 1678:111–125
Li S, Hua ZC (2008) FAK expression: regulation and therapeutic potential. Adv Cancer Res 101:45–61
Zheng C, Xing Z, Bian ZC, Guo C, Akbay A, Warner L, Guan J-L (1998) Differential regulation of Pyk2 and focal adhesion kinase (FAK). The C-terminal domain of FAK confers response to cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 273:2384–2389
Li X, Dy RC, Cance WG, Graves LM, Earp HS (1999) Interactions between two cytoskeleton-associated tyrosine kinases: calcium-dependent tyrosine kinase and focal adhesion tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 274:8917–8924
Le Boeuf F, Houle F, Sussman M, Huot J (2006) Phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) on Ser732 is induced by Rho-dependent kinase and is essential for proline-rich tyrosine kinase-1-mediated phosphorylation of FAK on Tyr407 in response to vascular endothelial growth factor. Mol Biol Cell 17:3508–3520
Roy S, Ruest PJ, Hanks SK (2002) FAK regulates tyrosine phosphorylation of CAS, paxillin, and PYK2 in cells expressing v-Src, but is not a critical determinant of v-Src transformation. J Cell Biochem 84:377–388
Du QS, Ren XR, Xie Y, Wang Q, Mei L, Xiong WC (2001) Inhibition of PYK2-induced actin cytoskeleton reorganization, PYK2 autophosphorylation and focal adhesion targeting by FAK. J Cell Sci 114:2977–2987
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (CA58640 and CA94144), National Science Foundation (EPS-9630167), U.S. Department of Defense (DAMD17-98-8524 and DAMD17-01-1-0730), the University Research Committee of the Medical University of South Carolina, and the Medical Scientist Training Program at the Medical University of South Carolina. We thank David Morris for supplying EL4 cells, Steven Hanks for supplying the FAK expression vector, David Cole for the Pyk2 expression vector, April Wisehart-Johnson for technical assistance, and Derek J. Pouchnik for assistance with the microarray analysis performed in the core facility supported by the Center for Biotechnology at WSU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Knoepp, S.M., Ku, H. et al. Differential expression of FAK and Pyk2 in metastatic and non-metastatic EL4 lymphoma cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis 28, 551–565 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-011-9391-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-011-9391-y