Abstract
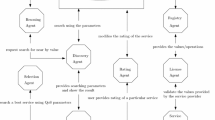
Cloud service searching technique is used to find relevant information on World Wide Web. Each search engine maintains following process in real time environment like web crawling, web scrapping, indexing and searching. The search engine over cloud is specially designed for cloud service discovery. This search engine mainly concentrates on discovering appropriate cloud services in effective and efficient manner. We proposed a technique named as Cognizant Clustering Algorithm that group service entries based on cloud user requirements that include functional, technical and cost specification. This search engine uses a similarity ontology that provides interrelationships between service entries. The similarity ontology has three kind of operation over cloud that includes perception, object entity and data type similarity reasoning. It uses Cognizant clustering matrix to calculate the number of service entries, distance and utilization per request. It improves the search result more effective and significantly increases the performance in service discovery over cloud environment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parhi, M., Pattanayak, B.K., Patra, M.R.: A multi-agent-based framework for cloud service description and discovery using ontology. In: Jain, L., Patnaik, S., Ichalkaranje, N. (eds.) Intelligent Computing, Communication and Devices, pp. 337–348. Springer, New York (2015)
Afify, Y.M., Moawad, I.F., Badr, N.L., Tolba, M.F.: A semantic-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) discovery and selection system. In: 2013 8th International Conference on Computer, Engineering Systems (ICCES), pp. 57–63 (2013)
Erl, T., Puttini, R., Mahmood, Z.: Cloud Computing: Percepts, Technology & Architecture. Pearson Education, US (2013)
Sim, K.M.: Complex and concurrent negotiations for multiple interrelated e-markets. IEEE Trans. Cybernet. 43, 230–245 (2013)
Gutierrez-Garcia, J.O., Sim, K.M.: Agent-based cloud service composition. Appl. Intell. 38, 436–464 (2013)
Dhanasekaran, S., Vasudevan, V.: A dynamic multi-intelligent agent system for enhancing the cloud service negotiation. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 10(43), 30469–30473 (2015)
Dhanasekaran, S., Vasudevan, V.: A smart logical multi agent system for consolidating suitable cloud services. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inform. Secur. 14(9), 517–522 (2016)
Dhanasekaran, S., Vasudevan, V.: Rational agent based multiple concurrent and complex concession for service composition and discovery. In: International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT), pp. 2797–2801 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanasekaran, S., Vasudevan, V. A Cognizant agent system for optimizing cloud service searching strategy. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 6), 13381–13386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1915-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1915-7