Abstract
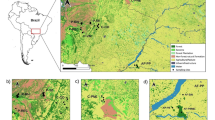
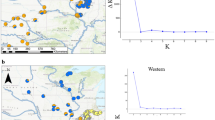
Little is known about the population biology of midget faded rattlesnakes, a sensitive subspecies of the Western Rattlesnake, despite conservation efforts to protect them. We conducted a molecular genetic study of midget faded rattlesnakes in southwestern Wyoming to investigate population genetic structure in this area, particularly with reference to Flaming Gorge Reservoir and its associated human activities, and to document levels of genetic diversity. We genotyped 229 snakes from 11 sampling sites using 9 microsatellite loci. We found significant levels of genetic structure among sites that were better explained by geographic region and isolation by distance than by position relative to waterways. Sites on either side of the reservoir at its widest point were not significantly different. Six of the sites showed signatures of a population bottleneck using an alpha value of 0.05. Three of these bottlenecked sites (the three most northern) were the most genetically distinct and occur in areas of greatest impact from human activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton KG (1999) Shedding aggregations of Crotalus viridis concolor. Herpetol Rev 30:211–213
Ashton KG (2003) Movements and mating behavior of adult male midget faded rattlesnakes, Crotalus oreganos concolor, in Wyoming. Copeia 2003:190–194
Ashton KG, de Queiroz A (2001) Molecular systematics of the Western Rattlesnake, Crotalus viridis (Viperidae), with comments on the utility of the D-loop in phylogenetic studies of snakes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 21:176–189
Ashton KG, Patton TM (2001) Movement and reproductive biology of female Midget Faded Rattlesnakes, Crotalus viridis concolor, in Wyoming. Copeia 2001:229–234
Baxter GT, Stone MD (1985) Amphibians and reptiles of Wyoming, 2nd edn. Wyoming Game and Fish Department, Cheyenne
Bonnet X, Shine R, Lourdais O (2002) Taxonomic chauvinism. Trends Ecol Evol 17:1–3
Bowcock AM, Ruiz-Linares A, Tomfohrde J, Minch E, Kidd JR, Cavalli-Sforza LL (1994) High-resolution of human evolutionary trees with polymorphic microsatellites. Nature 368:455–457
Cavalli-Sforza LL, Edwards AWF (1967) Phylogenetic analysis: models and estimation procedures. Am J Hum Genet 19:233–257
Clark RW, Brown WS, Stechert R, Zamudio KR (2008) Integrating individual behaviour and landscape genetics: the population structure of timber rattlesnake hibernacula. Mol Ecol 17:719–730
Cornuet JM, Luikart G (1997) Description and power analysis of two tests for detecting recent population bottlenecks from allele frequency data. Genetics 144:2001–2014
Douglas ME, Douglas MR, Schuett GW, Porras LW, Holycross AT (2002) Phylogeography of the Western Rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis) complex, with emphasis on the Colorado Plateau. In: Schuett GW, Hoggren M, Douglas ME, Greene HW (eds) Biology of the vipers. Eagle Mountain Publishing, Eagle Mountain, pp 11–50
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Gibbs HL, Prior KA, Weatherhead PJ, Johnson G (1997) Genetic structure of populations of the threatened eastern massauga rattlesnake, Sestrurus c. catenatus: evidence from microsatellite DNA markers. Mol Ecol 6:1123–1132
Goudet J (1995) Fstat version 1.2: a computer program to calculate F statistics. J Hered 86:485–486
Guo SW, Thompson EA (1992) Performing the exact test of Hardy–Weinberg proportions for multiple alleles. Biometrics 48:361–372
Haig SM (1998) Molecular contributions to conservation. Ecology 79:413–425
Kahn NW, Braun CE, Young JR, Wood S, Mata DR, Quinn TW (1999) Molecular analysis of genetic variation among large- and small-bodied Sage Grouse using mitochondrial control-region sequences. Auk 116:819–824
Klauber LM (1972) Rattlesnakes: their habits, life histories, and influence on mankind, vol 2, 2nd edn. University of California Press, Berkeley
MacKessy SP, Williams K, Ashton KG (2003) Ontogenetic variation in venom composition and diet of Crotalus oreganos concolor: a case of venom paedomorphosis? Copeia 2003:769–782
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Minch E, Ruiz-Linares A, Goldstein D, Feldman M, Cavalli-Sforza LL (1995) Microsat (version 1.4d): a computer program for calculating various statistics on microsatellite allele data. http://hpgl.stanford.edu/projects/microsat/
Oyler-McCance SJ, Leberg PL (2005) Conservation genetics in wildlife management. In: Braun CE (ed) Techniques for wildlife investigations and management, 6th edn. The Wildlife Society, Bethesda, pp 632–657
Oyler-McCance SJ, St John J, Parker JM, Anderson SH (2005) Characterization of microsatellite loci isolated in midget faded rattlesnakes (Crotalus viridis concolor). Mol Ecol Notes 5:452–453
Page RDM (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Parker JM (2003) The ecology and behavior of the midget faded rattlesnake [sic] in Wyoming. Dissertation, University of Wyoming
Parker JM, Anderson SH (2007) Ecology and behavior of the midget faded rattlesnake (Crotalus oreganus concolor) in Wyoming. J Herpetol 41:41–51
Pook CE, Wuster W, Thorpe RS (2000) Historical biogeography of the Western Rattlesnake (Serpentes: Viperidae: Crotalus viridis), inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequence information. Mol Phylogenet Evol 15:269–282
Pool WR, Bieber AL (1981) Fractionation of Midget-Faded Rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis concolor) venom: lethal fractions and enzymatic activities. Toxicon 19:517–527
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly PJ (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Raymond M, Rousset F (1995) GENEPOP (version 1.2): population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. J. Hered 86:248–249
Rubio M (1998) Rattlesnake: portrait of a predator. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) ARLEQUIN, version 2.000: a: software for population genetics data analysis. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, University of Geneva, Switzerland
Smouse PE, Long JC, Sokal RR (1986) Multiple-regression and correlation extensions of the Mantel Test of matrix correspondence. Syst Zool 35:627–632
Takezaki N, Nei M (1996) Genetic distances and reconstruction of phylogenetic trees from microsatellite DNA. Genetics 144:389–399
Travsky A, Beauvais GP (2004) Species assessment for the midget faded rattlesnake (Crotalus viridis concolor) in Wyoming. US Department of the Interior Report, Cheyenne
Villarreal X, Bricker J, Reinert HK, Gelbert L, Bushar LM (1996) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci for use in population genetic analysis in the Timber Rattlesnake, Crotalus horridus. J Hered 87:152–155
Acknowledgements
The use of any trade, product, or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. We thank J. St. John, T. Falley-Farnham, and S. Mullner for helpful comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oyler-McCance, S.J., Parker, J.M. A population genetic analysis of the midget faded rattlesnake in Wyoming. Conserv Genet 11, 1623–1629 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-009-0043-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-009-0043-6