Summary
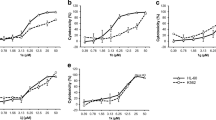
The cytotoxicity in vitro and antitumor activity in vivo of the organotin compound tri-n-butyltin(IV)lupinylsulfide hydrogen fumarate (IST-FS 35) have been investigated. The IC50 values obtained in a panel of tumor cell lines were compared to those of the parental compound IST-FS 29 in the same cells. IST-FS 35 resulted significantly more active than IST-FS 29 with IC50 values in the range 0.16–1.8 μM. Toxicity studies in vivo, after intravenous administration of escalating concentrations of IST-FS 35, provided the identification of the maximal tolerated dose (3.5 mg/kg) which was employed as therapeutic dose in the antitumor activity experiments. Preliminary results, in transplanted murine tumor models, revealed that both the P388 myelomonocytic leukaemia and the B16-F10 melanoma, implanted subcutaneously in BDF1 mice, were inhibited about 96% in their tumor volume at day 11, following a single intravenous injection of the compound. Additional studies are mandatory to unravel the mechanism of action for the development of IST-FS 35 as potential antitumor drug.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keppler BK, Berger MR, Klenner T, Heim ME (1990) Metal complexes as antitumor agents. Adv Drug Res 19:243–310
Respondek J, Engel J (1996) Organometallics in medicine. Drugs Future 21:391–408
Louie AY, Meade TJ (1999) Metal complexes as enzyme inhibitors. Chem Rev 99:2711–2734, doi:10.1021/cr9804285
Ho YP, Au-Yeung SCF, To KKW (2003) Platinum-based anticancer agents: innovative design strategies and biological perspectives. Med Res Rev 23:633–655, doi:10.1002/med.10038
Timerbaev AR, Hartinger CG, Aleksenko SS, Keppler BK (2006) Interactions of antitumor metallodrugs with serum protein: advances in characterization using modern analytical methodology. Chem Rev 106:2224–2248, doi:10.1021/cr040704h
Amtmann E, Zöller M, Wesch H, Schilling G (2001) Antitumoral activity of a sulfur-containing platinum complex with an acidic pH optimum. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 47:461–466, doi:10.1007/s002800000261
Friebolin W, Schilling G, Zöller M, Amtmann E (2004) Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of novel antitumoral platinum xanthate complexes. J Med Chem 47:2256–2263, doi:10.1021/jm0309405
Ang WH, Khalaila I, Allardyce CS, Juillerat-Jeanneret LP, Dyson J (2005) Rational design of platinum (IV) compounds to overcome glutathione-S-transferase mediated drug resistance. J Am Chem Soc 127:1382–1383, doi:10.1021/ja0432618
Hall MD, Mellor HR, Callaghan R, Hambley TW (2007) Basis for design and development of platinum (IV) anticancer complex. J Med Chem 50:3403–3411, doi:10.1021/jm070280u
Friebolin W, Schilling G, Zöller M, Amtmann E (2005) Antitumoral activity of non-platinum xanthate complexes. J Med Chem 48:7925–7931, doi:10.1021/jm040899l
Cagnoli M, Alama A, Barbieri F, Novelli F, Bruzzo C, Sparatore F (1998) Synthesis and biological activity of gold and tin compounds in ovarian cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 9:603–610, doi:10.1097/00001813-199808000-00005
Barbieri F, Viale M, Sparatore F, Favre A, Cagnoli M, Bruzzo C et al (2000) Cytotoxicity in vitro and preliminary antitumor activity in vivo of a novel organotin compound. Anticancer Res 20:977–980
Barbieri F, Sparatore F, Cagnoli M, Bruzzo C, Novelli F, Alama A (2001) Antiproliferative, activity and interactions with cell-cycle related proteins of organotin compound triethyltin(IV)lupinylsulfide hydrochloride. Chem Biol Interact 134:27–39, doi:10.1016/S0009-2797(00)00249-0
Barbieri F, Sparatore F, Bonavia R, Bruzzo C, Schettini G, Alama A (2002) Chemosensitivity of glioblastoma cells during treatment with the organo-tin compound triethyltin(IV)lupinyl sulfide hydrochloride. J Neurooncol 60:109–116, doi:10.1023/A:1020630214549
Barbieri F, Viale M, Sparatore F, Schettini G, Favre A, Bruzzo C et al (2002) Antitumor activity of a new orally active organotin compound: a preliminare study in murine tumor models. Anticancer Drugs 13:599–604, doi:10.1097/00001813-200207000-00006
Penninks AH, Bol-Schoenmakers M, Seinen W (1990) Cellular interactions of organo-tin compounds in relation to their antitumor activity. In: Gielen M (ed) Tin-based antitumor drugs. Sringer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 169–190
Cardarelli NF, Quitter BM, Allen A, Dobbins E, Libby EP, Hager P et al (1984) Organo-tin implications in anticarcinogenesis. Background and thymus involvement. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 62:199–208, doi:10.1038/icb.1984.20
de Vos D, Willem R, Gielen M, van Wingerden KE, Nooter K (1998) The development of novel organotin anti-tumor drugs: structure and activity. Metal-Based Drugs 5:179–188, doi:10.1155/MBD.1998.179
Gielen M, Biesemans M, de Vos D, Willem R (2000) Synthesis, characterization and in vitro antitumor activity of di- and tri-organotin derivatives of polyoxa- and biologically relevant carboxylic acids. J Inorg Biochem 79:139–145, doi:10.1016/S0162-0134(99)00161-0
Gitlitz MH, Moran MK (1983) Tin compounds. In: Kirk–Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. J Wiley Sons N Y 23:42–77
Novelli F, Recine M, Sparatore F, Juliano C (1999) Triorganotin compounds as antimicrobial agents. Farmaco 54:237–241, doi:10.1016/S0014-827X(99)00020-8
Stridh H, Orrenius S, Hampton MB (1999) Caspase involvement in the induction of apoptosis by the environmental toxicants tributyltin and triphenyltin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 156:141–146, doi:10.1006/taap.1999.8633
Aw TY, Nicotera P, Manzo L, Orrenius S (1990) Tributyltin stimulates apoptosis in rat thymocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 283:46–50, doi:10.1016/0003-9861(90)90610-B
Viviani B, Rossi AD, Chow SC, Nicotera P (1996) Triethyltin interferes with Ca2+ signaling and potentiates norepinephrine release in PC12 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 140:289–295, doi:10.1006/taap.1996.0224
Liu HG, Wang Y, Lian L, Xu LH (2006) Tributyltin induces DNA damage as well as oxidative damage in rats. Environ Toxicol 21:166–171, doi:10.1002/tox.20170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alama, A., Viale, M., Cilli, M. et al. In vitro cytotoxic activity of tri-n-butyltin(IV)lupinylsulfide hydrogen fumarate (IST-FS 35) and preliminary antitumor activity in vivo. Invest New Drugs 27, 124–130 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-008-9148-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-008-9148-x