Abstract
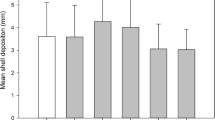
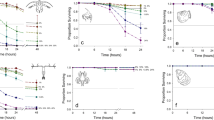
Effects of the herbicide Basamaïs (bentazon) and the fungicide Opus (epoxiconazole) on oyster spat (Crassostrea gigas) were assessed using in-situ microcosms in a field experiment lasting 13 days. Six-week-old hatchery spat (mean size 1.1 mm), previously collected on PVC plates, was immersed in glass bottles filled with 200 μm filtered seawater. Bottles were maintained underwater at 6 m depth and their water content changed every other day. Growth, measured as shell area index increase, was 126 ± 4% in the control bottles. While no growth differences were observed between control and individual pesticide treatments at 10 μg l−1, oysters treated with a mix of 10 μg l−1 Opus and 10 μg l−1 Basamaïs showed a 50% growth reduction compared with the control (P < 0.0001), suggesting a synergistic effect of these contaminants. Laboratory controls in microcosms maintained in a water bath with filtered natural light, were not significantly different from in-situ microcosm controls in the field, for organic weight content or growth. This in-situ experiment in microcosms allowed us to conclude that: (1) oyster spat can achieve significant growth in bottles immersed in situ without supplementary food; (2) this microcosm system is reliable and easy to use for environmental toxicity tests with C. gigas spat; (3) such microcosm systems can also be run in a laboratory water bath instead of more technically difficult immersed field experiments; (4) the synergistic effect observed here, at a concentration simulating a peak agricultural runoff event, suggests that the impacts of pesticides could be a real threat for oysters in estuarine areas.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiard-Triquet C, Altmann S, Amiard JC, Ballan-Dufrançais C, Baumard P, Budzinski H, Crouzet C, Garrigues P, His E, Jeantet AY, Menasria R, Mora P, Mouneyrac C, Narbonne JF, Pavillon JF (1998) Fate and effects of micropollutants in the Gironde estuary, France: a multidisciplinary approach. Hydrobiologia 373–374:259–279
Aminot A, Kérouel R (2004) Hydrologie des écosystèmes marins. Paramètres et analyses. Editions Ifremer, Plouzané, pp 172–194
Arnold GL, Luckenbach MW, Unger MA (2004) Runoff from tomato cultivation in the estuarine environment: biological effects of farm management practices. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 298(2):323–346
Auffret M, Oubella R (1997) Hemocyte aggregation in the oyster Crassostrea gigas: in vitro measurement and experimental modulation by xenobiotics. Comp Biochem Physiol 118A(3):705–712
Avery EL, Dunstan RH (1996) The detection of pollutant impact in marine environments: condition index, oxidative DNA damage, and their associations with metal bioaccumulation in the Sydney Rock oyster Saccostrea commercialis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 31(2):192–198
Banks KE, Turner PK, Wood SH, Matthews C (2005) Increased toxicity to Ceriodaphnia dubia in mixtures of atrazine and diazinon at environmentally realistic concentrations. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 60(1):28–36
Bendtsen J, Gustafsson KE, Petersen JK (2006) Modelling vertical mixing in the surface boundary layer using artificial age tracers. J Mar Syst 60:115–128
Bolton-Warberg M, Coen LD, Weinstein JE (2007) Acute toxicity and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio) and oysters (Crassostrea virginica) exposed to the organophosphate dichlorvos: laboratory and field studies. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52(2):207–216
Bouilly K, McCombie H, Leitão A, Lapègue S (2004) Persistence of atrazine impact on aneuploidy in Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas. Mar Biol 145(4):699–705
Bouilly K, Bonnard M, Gagnaire B, Renault T, Lapègue S (2007) Impact of diuron on aneuploidy and hemocyte parameters in Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52(1):58–63
Brown MR, McCausland MA (2000) Increasing the growth of juvenile Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas by supplementary feeding with microalgal and dried diets. Aquac Res 31(8–9):671–682
Brown M, Robert R (2002) Preparation and assessment of microalgal concentrates as feeds for larval and juvenile Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Aquaculture 207(3–4):289–309
Cedergreen N, Kamper A, Streibig JC (2006) Is prochloraz a potent synergist across aquatic species? A study on bacteria, daphnia, algae and higher plants. Aquat Toxicol 78(3):243–252
Child AR, Laing I (1998) Comparative low temperature tolerance of small juvenile European, Ostrea edulis L., and Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas Thunberg. Aquac Res 29:103–113
Christl TJ, Pennington P, DeLorenzo M, Karnaky KJ, Scott GI (2004) Effect of multiple atrazine exposure profiles on hemocyte DNA integrity in the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73(2):404–410
Clara Reboucas do Amaral M, de Freitas Rebelo M, Paulo Machado Torres J, Christian Pfeiffer W (2005) Bioaccumulation and depuration of Zn and Cd in mangrove oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae, Guilding, 1828) transplanted to and from a contaminated tropical coastal lagoon. Mar Environ Res 59(4):277–285
Collet B, Boudry P, Thebault A, Heurtebise S, Morand B, Gerard A (1999) Relationship between pre- and post-metamorphic growth in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Aquaculture 175(3–4):215–226
da Cruz ACS, Couto BC, Nascimento IA, Pereira SA, Leite MBNL, Bertoletti E, Zagatto P (2007) Estimation of the critical effect level for pollution prevention based on oyster embryonic development toxicity test: the search for reliability. Environ Int 33(4):589–595
Damiens G, His E, Gnassia-Barelli M, Quiniou F, Romeo M (2004) Evaluation of biomarkers in oyster larvae in natural and polluted conditions. Comp Biochem Physiol 138C(2):121–128
de la Broise D, Palenik B (2007) Immersed in-situ microcosms: a tool for the assessment of pollution impact on phytoplankton. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 341(2):274–281
Fernandez-Alba AR, Guil LH, Lopez GD, Chisti Y (2001) Toxicity of pesticides in wastewater: a comparative assessment of rapid bioassays. Anal Chim Acta 426(2):289–301
Gagnaire B, Thomas-Guyon H, Renault T (2004) In vitro effects of cadmium and mercury on Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg), haemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 16(4):501–512
Geffard O, His E, Budzinski H, Seaman M, Garrigues P (2001) Qualité biologique de l’eau de mer évaluée in situ par le test embryo-larvaire de Crassostrea gigas et Mytilus galloprovincialis. In situ monitoring of sea water quality with the embryo-larval bioassay of Crassostrea gigas and Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comptes Rendus de l’Academie des Sciences - Series III - Sciences de la Vie 324(12):1149–1155
Geffard O, Geffard A, His E, Budzinski H (2003) Assessment of the bioavailability and toxicity of sediment-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals applied to Crassostrea gigas embryos and larvae. Mar Pollut Bull 46(4):481–490
Geffard O, His E, Budzinski H, Chiffoleau JF, Coynel A, Etcheber H (2004) Effects of storage method and duration on the toxicity of marine sediments to embryos of Crassostrea gigas oysters. Environ Pollut 129(3):457–465
Girard S, Perez-Agundez JA, Miossec L, Czerwinski N (2005) Recensement de la conchyliculture 2001. Cahiers (conchyliculture) n°1. Les productions Agreste, Paris
His E, Beiras R, Quiniou F, Parr ACS, Smith MJ, Cowling MJ, Hodgkiess T (1996) The non-toxic effects of a novel antifouling material on oyster culture. Water Res 30(11):2822–2825
His E, Budzinski H, Geffard O, Beiras R (1997) Action d’un sédiment pollué par les hydrocarbures sur la métamorphose de l’huître japonaise, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Effects of a hydrocarbon-polluted sediment on Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) metamorphosis. Comptes Rendus de l’Academie des Sciences - Series III - Sciences de la Vie 320(10):797–803
His E, Heyvang I, Geffard O, de Montaudouin X (1999) A comparison between oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) larval bioassays for toxicological studies. Water Res 33(7):1706–1718
Laing I, Chang RM (1998) Hatchery cultivation of Pacific oyster juveniles using algae produced in outdoor bloom-tanks. Aquac Int 6(4):303–315
Lehotey SJ, Harman-Fetcho JA, McConnell LL (1998) Agricultural pesticide residues in oysters and water from two Chesapeake bay tributaries. Mar Pollut Bull 37(1–2):32–34
Li Q, Osada M, Takahashi K, Matsutani T, Mori K (1997) Accumulation and depuration of tributyltin oxide and its effect on the fertilization and embryonic development in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 58(3):489–496
Losso C, Novelli AA, Picone M, Marchetto D, Pantani C, Ghetti PF, Ghirardini AV (2007) Potential role of sulfide and ammonia as confounding factors in elutriate toxicity bioassays with early life stages of sea urchins and bivalves. Ecotox Environ Safe 66(2):252–257
Lyons BP, Pascoe CK, McFadzen IRB (2002) Phototoxicity of pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene to embryo-larval stages of the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Mar Environ Res 54(3–5):627–631
Nice HE, Thorndyke MC, Morritt D, Steele S, Crane M (2000) Development of Crassostrea gigas larvae is affected by 4-nonylphenol. Mar Pollut Bull 40(6):491–496
Nilsen JEO, Falck E (2006) Variations of mixed layer properties in the Norwegian sea for the period 1948–1999. Prog Oceanogr 70:58–90
Oliver LM, Fisher WS, Winstead JT, Hemmer BL, Long ER (2001) Relationships between tissue contaminants and defense-related characteristics of oysters (Crassostrea virginica) from five Florida bays. Aquat Toxicol 55(3–4):203–222
Oros DR, Jarman WM, Lowe T, David N, Lowe S, Davis JA (2003) Surveillance for previously unmonitored organic contaminants in the San Francisco estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 46:1102–1110
Paixão JF, Nascimento IA, Pereira SA, Leite MBL, Carvalho GC, Silveira JSC Jr, Reboucas M, Matias GRA, Rodrigues ILP (2007) Estimating the gasoline components and formulations toxicity to microalgae (Tetraselmis chuii) and oyster (Crassostrea rhizophorae) embryos: an approach to minimize environmental pollution risk. Environ Res 103(3):365–374
Ponis E, Robert R, Parisi G (2003a) Nutritional value of fresh and concentrated algal diets for larval and juvenile Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Aquaculture 221(1–4):491–505
Ponis E, Robert R, Parisi G, Tredici M (2003b) Assessment of the performance of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) larvae fed with fresh and preserved Pavlova lutheri concentrates. Aquac Int 11(1):69–79
Quiniou F, Damiens G, Gnassia-Barelli M, Geffard A, Mouneyrac C, Budzinski H, Romeo M (2007) Marine water quality assessment using transplanted oyster larvae. Environ Int 33(1):27–33
Riedel GF, Valette-Silver N (2002) Differences in the bioaccumulation of arsenic by oysters from Southeast coastal US and Chesapeake Bay: environmental versus genetic control. Chemosphere 49(1):27–37
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 3rd edn. W. H. Freeman and Co., NY
Steen RJCA, van der Vart J, Hiep M, Van Hattum B, Cofino WP, Brinkman UAT (2001) Gross fluxes and estuarine behaviour of pesticides in the Scheldt Estuary (1995–1997). Environ Pollut 115:65–79
Tanguy A, Boutet I, Laroche J, Moraga D (2005) Molecular identification and expression study of differentially regulated genes in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas in response to pesticide exposure. FEBS J 272(2):390–403
Wintermyer ML, Cooper KR (2007) The development of an aquatic bivalve model: evaluating the toxic effects on gametogenesis following 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (2,3,7,8-TCDD) exposure in the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Aquat Toxicol 81(1):10–26
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the “Ministère de l’Ecologie et du Développement Durable”, and the “Région Bretagne”, who financially supported this research. We thank the Capitainerie de Beg-Meil, city of Fouesnant and Patrick Le Coz for their technical assistance; Xavier Caisey, Pierre Mollo and Christian Mingant who provided assistance with spat settlement; Hansy Haberkorn, Gaël Durand, Geneviève Arzul, Louis Coroller, and Jacques Baron.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stachowski-Haberkorn, S., Quiniou, F., Nedelec, M. et al. In-situ microcosms, a tool for assessment of pesticide impacts on oyster spat (Crassostrea gigas). Ecotoxicology 17, 235–245 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0190-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0190-9