Abstract
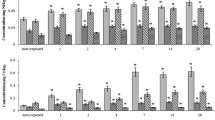
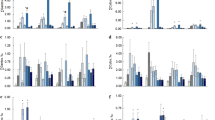
The aim of this research was to assess interactions between metals at low exposure concentrations (Maximum-Permissible-Concentrations accepted for the inland waters in EU) and to assess possible influence of background exposure (10-times reduced concentration of a single metal) on toxicological significance of selected biomarkers in Salmo salar after treatment with metal mixture (Zn – 0.1, Cu – 0.01, Ni – 0.01, Cr – 0.01, Pb – 0.005 and Cd – 0.005 mg/L). The tissue-specific bioaccumulation, genotoxicity and cytotoxicity responses (erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities assay) in peripheral blood, kidneys, gills and liver erythrocytes of fish to metal mixtures were assessed after 14 days treatment. Treatment with primary mixture (MIX) or two variants of this mixture (Cr↓ (10 times reduced Cr6+ concentration) and Cu↓ (10 times reduced Cu2+ concentration)) induced the strongest responses in genotoxicity and cytotoxicity endpoints. Exposure to these mixtures highly affected Zn, Cu and Cd bioaccumulation in liver tissue. The highest amount of Ni accumulated was measured after Cd↓ treatment in all tissues. Treatments with reduced concentration of non-essential metal resulted in an increased accumulation of Pb, Ni, or Cd; treatments with reduced concentration of essential metal resulted in a reduced accumulation of certain metals (especially Cd and Pb) in tissues compared between treatments. Glucose content in blood and behavioural endpoints were evaluated after short-term exposure to metal mixtures (MIX, Cr↓, Cu↓). Significant increase in blood glucose concentration was measured after all treatments. These metal mixtures elicit significant behavioural alterations in fish. Consequently, this research revealed a significant influence of background exposure considering mixture toxicity.
Highlights
-
10-fold reduction of mixtures components highly affected bioaccumulation of several metals in analysed tissues of Salmo salar.
-
Significant influence of background exposure considering mixture toxicity was detected.
-
Exposure to metal mixtures at environmentally relevant concentrations elicited genotoxicity and cytotoxicity.
-
Alterations in glucose content in blood and behavioural responses were observed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin DH, Tatara CP, Scholz NL (2011) Copper-induced olfactory toxicity in salmon and steelhead: Extrapolation across species and rearing environments. Aquat Toxicol 101:295–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.08.011
Baršienė J, Lazutka J, Syvokienė J, Dedonytė V, Rybakovas A, Bagdonas E, Bjornstad A, Andersen OK (2004) Analysis of micronuclei in blue mussels and fish from the Baltic and the North Seas. Environ Toxicol 19(4):365–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20031
Baršienė J, Dedonytė V, Rybakovas A, Andreikenaitė L, Andersen OK (2006) Investigation of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in peripheral blood and kidney of marine fish treated with crude oil. Aquat Toxicol 78S:S99–S104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.02.022
Baršienė J, Butrimavičienė L, Grygiel W, Lang T, Michailovas A, Jackūnas T (2014) Environmental genotoxicity and cytotoxicity in flounder (Platichthys flesus), herring (Clupea harengus) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) from chemical munitions dumping zones in the southern Baltic Sea. Mar Environ Res 96:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.08.012
Bartonkova J, Hyršl P, Vojtek L (2016) Glucose determination in fish plasma by two different moderate methods. Acta Vet Brno 85:349–353. https://doi.org/10.2754/avb201685040349
Barton B (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integ Comp Biol 42:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/42.3.517
Calabrese EJ, Mattson MP (2011) Hormesis provides a generalized quantitative estimate of biological plasticity. J Cell Commun Signal 5(1):25–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-011-0119-1
Cavas T, Garanko NN, Arkhipchuk VV (2005) Induction of micronuclei and binuclei in blood, gill and liver cells of fishes subchronically exposed to cadmium chloride and copper sulphate. Food Chem Toxicol 43(4):569–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2004.12.014
Cobbina SJ, Chen Y, Zhou Z, Wu X, Feng W, Wang W, Mao G, Xu H, Zhang Z, Wu X, Yang L (2015) Low concentration toxic metal mixture interactions: Effects on essential and non-essential metals in brain, liver, and kidneys of mice on sub-chronic exposure. Chemosphere 132:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.013
Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 496 16 December 2008 on environmental quality standards in the field of water 497 policy, amending and subsequently repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 498 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and amending Directive 499 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Official Journal of the European Communities L 500 348, p 0084–0097. Accessed 24 Dec 2008
Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. L. 276
Driessnack MK, Matthew AL, Raine JC, Niyogi S (2016) Interactive effects of chronic waterborne copper and cadmium exposure on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Comp Biochem Physiol C 179:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.10.009
Driessnack MK, Jamwal A, Niyogi S (2017a) Effects of chronic exposure to waterborne copper and nickel in binary mixture on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Chemosphere 185:964–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.100
Driessnack MK, Jamwal A, Niyogi S (2017b) Effects of chronic waterborne cadmium and zinc interactions on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.023
Eyer P, Worek F, Kiderlen D, Sinko G, Stuglin A, Simeon-Rudolf V, Reiner E (2003) Molar absorption coefficients for the reduced Ellman reagent: reassessment. Anal Biochem 312:224–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(02)00506-7
EEA (2012) European waters—assessment of status and pressures. Report No 8/2012, ISSN 1725-9177
Evans RM, Martin OV, Faust M, Kortenkamp A (2016) Should the scope of human mixture risk assessment span legislative/regulatory silos for chemicals? Sci Total Environ 543:757–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.162
Fabrin TMC, Diamante NA, Mota TFM, Ghisi NC, Prioli SMAP, Prioli AJ (2018) Performance of biomarkers metallothionein and ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase in aquatic environments: a meta-analytic approach. Chemosphere 205:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.069
Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E (2003) HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res 534:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00249-8
Gasulla J, Picco SJ, Carriquiriborde P, Dulout FN, Ronco AE, de Luca JC (2016) Genotoxic Effects Induced by Cd(+2), Cr(+6), Cu(+2) in the Gill and Liver of Odontesthes bonariensis (Piscies, Atherinopsidae). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96(5):591–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1774-y
Güner U, Muranlı FDG (2011) Micronucleus test, nuclear abnormalities and accumulation of Cu and Cd on Gambusia affinis (Baird & Girard, 1853). Turk. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 11:615–622. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v11_4_16
HELCOM (2011) Salmon and Sea Trout Populations and Rivers in the Baltic Sea—HELCOM assessment of salmon (Salmo salar) and sea trout (Salmo trutta) populations and habitats in rivers flowing to the Baltic Sea. Balt Sea Environ Proc No. 126A
Hendry K, Cragg-Hine D (2003) Ecology of the Atlantic Salmon. Conserving Natura 2000 Rivers Ecology Series No. 7. English Nature, Peterborough
Hylland K, Haux C, Hogstrand C (1992) Hepatic metallothionein and heavy metals in dad limanda limanda from the German Bight. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 91:89–96. https://doi.org/10.7773/cm.v31i12.89
ISO 6332 (1988) Water quality. Determination of iron—spectrometric method using 1.10-phenanthroline. ISO, the InternationalOrganization for Standardization
ISO 5814 (1990) Water quality. Determination of dissolved oxygen—electrotechnical probe method. SO, theInternational Organization for Standardization
ISO 9963-1 (1994) Water quality. Determination of alkalinity—Part 1: determination of total and composite alkalinity. ISO, the International Organization for Standardization
ISO 14911 (1998) Water quality. Determination of dissolved Li+, Na+, NH4 +, K+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ using ion chromatography—method for water and waste water. ISO, the International Organization for Standardization
ISO 15586 (2003) Water quality. Determination of trace elements using atomic absorption spectrometry with graphite furnace. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
ISO 10304-1 (2007) Water quality. Determination of dissolved anions by liquid chromatography of ions. Determination of bromide, chloride, fluoride, nitrate, nitrite, phosphate and sulfate. ISO, the International Organization for Standardization
ISO 10523 (2008) Water quality. Determination of pH. ISO, the International Organization for Standardization
Jia H, Ren H, Satoh S, Endo H, Hayashi T (2005) Comparison of pretreatment condition of cadmium in fish sample and diet by microwave digestion method for ICP-AES. J Tokyo Univ Mar Sci Technol 1:41–46
Javed M, Usmani N (2017) An overview of the adverse effects of heavy metal contamination on fish Health. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-017-0875-7
Knapen D, Reynders H, Bervoets L, Verheyen E, Blust R (2007) Metallothionein gene and protein expression as a biomarker for metal pollution in natural gudgeon populations. Aquat Toxicol 82:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.02.008
Kroon F, Streten C, Harries S (2017) A protocol for identifying suitable biomarkers to assess fish health: a systematic review. PLoS One 12(4):e0174762. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174762
Kulmala S, Haapasaari P, Karjalainen TP, Kuikka S, Pakarinenm T, Parkkila K, Romakkaniemi A et al. (2012) Ecosystem services provided by the Baltic salmon—a regional perspective to the socio-economic benefits associated with a keystone species, In Socio-economic importance of ecosystem services in the Nordic Countries—synthesis in the context of The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB), Copenhagen Nordic Council of Ministers, p 266–276
Makaras T, Svecevičius G, Kazlauskienė N, Montvydienė D (2018) Rapid detection of sublethal toxicity using locomotor activity of rainbow trout juveniles. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2244-x
Melvin SD, Petit MA, Duvignacg MC, Sumpter JP (2017) Towards improved behavioural testing in aquatic toxicology: acclimation and observation times are important factors when designing behavioural tests with fish. Chemosphere 180:430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.058
Min EY, Ahn TY, Ju-Chan Kang (2016) Bioaccumulation, alterations of metallothionein, and antioxidant enzymes in the mullet Mugil cephalus exposed to hexavalent chromium. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 19:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41240-016-0020-1
Mishra AK, Mohanty B (2008) Acute toxicity impacts of hexavalent chromium on behavior and histopathology of gill, kidney and liver of the freshwater fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26(2):136–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2008.02.010
Nys C, Versieren L, Cordery KI, Blust R, Smolders E, De Schamphelaere KAC (2017) Systematic evaluation of chronic metal-mixture toxicity to three species and implications for risk assessment. Environ Sci Technol 51(8):4615–4623. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05688
Palermo FF, Risso WE, Simonato JD, Martinez CBR (2015) Bioaccumulation of nickel and its biochemical and genotoxic effects on juveniles of the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 116:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.02.032
Perez-Benito JF (2006) Effects of chromium (VI) and vanadium (V) on the lifespan of fish. J Trace Elem Med Biol 20(3):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2006.04.001
Peixoto NC, Roza T, Flores EMM, Pereira ME (2003) Effects of zinc and cadmium on HgCl2-δ-ALA-D inhibition and Hg levels in tissues of suckling rats. Toxicol Lett 146:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.08.006
Price MHH (2013) Sub-lethal metal toxicity effects on salmonids: a review. Report prepared for Skeena Wild Conservation Trust. Smithers, BC p 64
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Ma J, Duan HY, Li X (2017) Effects of exposure to multiple heavy metals onbiochemical and histopathological alterations in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Fish Shellfish Immunol 70:461–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.08.013
Randall DJ, Perry SF (1992) Catecholamine. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Farrell TP (eds) Fish physiology 12. Academic Press, New York, NY
Saibu Y, Jamwal A, Feng R, Peak D, Niyogi S (2018) Distribution and speciation of zinc in the gills of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during acute waterborne zinc exposure: interactions with cadmium or copper. Comp Biochem Physiol C 206–207:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2018.02.004
Sampaio FG, Boijink CDL, Oba ET, Santos LRBD, Kalinin AL (2008) Antioxidant defenses and biochemical changes in pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) in response to single and combined copper and hypoxia exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol, Part C 147:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.07.009
Sandahl JF, Baldwin DH, Jenkins JJ, Scholz NL (2007) A sensory system at the interface between urban storm water runoff and salmon survival. Environ Sci Tech 41:2998–3004. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062287r
Stankevičiūtė M, Butrimavičienė L, Valskienė R, Greiciūnaitė J, Baršienė J, Vosylienė Z, Svecevičius G (2016) Analysis of nuclear abnormalities in erythrocytes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) treated with Cu and Zn and after 4-, 8-, and 12-day depuration (post-treatment recovery). Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 797:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.01.003
Stankevičiūtė M, Sauliutė G, Svecevičius G, Kazlauskienė N, Baršienė J (2017) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity response to environmentally relevant complex metal mixture (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd) accumulated in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Part I: importance of exposure time and tissue dependence. Ecotoxicology 26(8):1051–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1833-0
Svecevičius G (2007) Avoidance response of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss to hexavalent chromium solutions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:596–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-003-0154-6
Svecevičius G (2009) Use of behavioral responses of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in identyfing sublethal exposure to hexavalent chromium. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:564–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9657-0
Tierney KB, Baldwin DH, Hara TJ, Ross PS, Scholz NL, Kennedy CJ (2010) Olfactory toxicity in fishes. Aquat Toxicol 96:2–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.09.019
US EPA (1998) Toxicological review of hexavalent chromium. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC, p 70
US EPA (2002) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 5th edn. Office of Water, Washington, DC
Valskienė R, Stankevičiūtė M, Butrimavičienė L, Greiciūnaitė J, Svecevičius G (2015) Induction of nuclear abnormalities in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after exposure to a model mixture of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Cd, Pb) at maximum permissible concentration. Proceedings of the 18th Conference for Junior Researchers “Science – Future of Lithuania”, aplinka 15:100–105
Velma V, Vutukuru SS, Tchounwou PB (2009) Ecotoxicology of hexavalent chromium in freshwater fish: a critical review. Rev Environ Health 24(2):129–145. https://doi.org/10.1515/REVEH.2009.24.2.129
Wah Chu K, Chow KL (2002) Synergistic toxicity of multiple heavy metals is revealed by a biological assay using a nematode and its transgenic derivative. Aquat Toxicol 61:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(02)00017-6
Wu H, Aoki A, Arimoto T, Nakano T, Ohnuki H, Murata M, Ren H, Endo H (2015) Fish stress become visible: A new attempt to use biosensor for real-time monitoring fish stress. Biosens Bioelectron 67:503–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.09.015
Zhang Y, Wang YJ, Yu RL, Zhang S, Wu ZB (2008) Effects of heavy metals Cd2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+ on DNA damage of loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Front Biol China 3(1):50–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-008-0012-3
Zhu B, Wu ZF, Li J, Wang GX (2011) Single and joint action toxicity of heavy metals on early developmental stages of Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74(8):2193–2202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.07.033
Zhu Y, Wang J, Bai Y, Zhang R (2004) Cadmium, chromium, and copper induce polychromatocyte micronuclei in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 72(1):78–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-003-0243-6
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the research infrastructure Open Access Centre for Nature Research at the initiative of the Open R&D Lithuania network. This study was funded by the Research Council of Lithuania through the project ACTIS S-MIP-17-10. Metallothionein determination was funded by the Research Council of Lithuania, Project No. MIP-108/2015. We are thankful to Dalia Baršytė Lovejoy (Toronto University) for the language check. We are thankful to Liutauras Savičius for the production of the experimental aquariums for behavioural assay. The authors are grateful to Dr Kęstutis Arbačiauskas and Dr Eglė Šidagytė for the suggestions in data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. LT 61-13-005; SR-432.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stankevičiūtė, M., Sauliutė, G., Makaras, T. et al. Responses of biomarkers in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) following exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of complex metal mixture (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd). Part II. Ecotoxicology 27, 1069–1086 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1960-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1960-2