Abstract
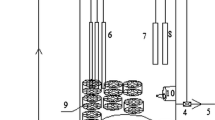
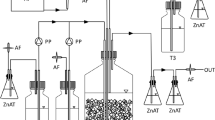
Arsenite (As(III)) was considered to be of great concern in acid mine drainage (AMD). A promising approach for cleaning up of arsenite from AMD is microbial oxidation of As(III) followed by adsorptions. However, there is virtually no research about the acidophilic bioreactor for As(III) oxidation so far. In this study, we formed a new biofilm bioreactor with a consortium of acidophilic As(III) oxidation bacteria. It is totally chemoautotrophic, with no need to add any carbon or other materials during the operations. It works well under pH 3.0–4.0, capable of oxidizing 1.0–20.0 mg/L As(III) in 3.0–4.5 h, respectively. A continuous operation of the bioreactor suggests that it is very stable and sustainable. Functional gene detection indicated that the biofilms possessed a unique diversity of As(III) oxidase genes. Taken together, this acidophilic bioreactor has great potential for industrial applications in the cleaning up of As(III) from AMD solution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment, and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145
Anawar HM (2015) Sustainable rehabilitation of mining waste and acid mine drainage using geochemistry, mine type, mineralogy, texture, ore extraction and climate knowledge. J Environ Manage 158:111–121
Bondu R, Cloutier V, Rosa E, Benzaazoua M (2017) Mobility and speciation of geogenic arsenic in bedrock groundwater from the Canadian Shield in western Quebec, Canada. Sci Total Environ 2017574:509–519
Chen LX, Huang LN, Méndez-García C, Kuang JL, Hua ZS, Liu J, Shu WS (2016) Microbial community, processes and functions in acid mine drainage ecosystems. Curr Opin Biotechnol 38:150–158
Chen X, Zeng XC, Kawa YK, Wu W, Zhu X, Ullah Z, Wang Y (2020) Microbial reactions and environmental factors affecting the dissolution and release of arsenic in the severely contaminated soils under anaerobic or aerobic conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:109946
Chen X, Zeng XC, Wang J, Deng Y, Ma T,E,G, Mu Y, Yang Y, Li H, Wang Y (2017) Microbial communities involved in arsenic mobilization and release from the deep sediments into groundwater in Jianghan plain, Central China. Sci Total Environ 579:989–999
Chen YT, Li JT, Chen LX, Hua ZH, Huang LN, Liu J, Xu BB, Liao B, Shu WS (2014) Biogeochemical processes governing natural pyrite oxidation and release of acid metalliferous drainage. Environ Sci Technol 48:5537–5545
Cheng H, Hu Y, Luo J, Xu B, Zhao J (2009) Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems. J Hazard Mater 165:13–26
Coudert L, Bondu R, Rakotonimaro TV, Rosa E, Guittonny M, Neculita CM (2019) Treatment of As-rich mine effluents and produced residues stability: current knowledge and research priorities for gold mining. J Hazard Mater 386:121920
Edwardson CF, Hollibaugh JT (2017) Metatranscriptomic analysis of prokaryotic communities active in sulfur and arsenic cycling in Mono Lake, California, USA. ISME J 11:2195–2208
Fernandez-Rojo L, Casiot C, Laroche E, Tardy V, Bruneel O, Delpoux S, Desoeuvre A, Grapin G, Savignac J, Boisson J, Morin G, Battaglia-Brunet F, Joulian C, Héry M (2019) A field-pilot for passive bioremediation of As-rich acid mine drainage. J Environ Manage 232:910–918
Grande JA, Santisteban M, de la Torre ML, Dávila JM, Pérez-Ostalé E (2018) Map of impact by acid mine drainage in the river network of The Iberian Pyrite Belt (Sw Spain). Chemosphere 199:269–277
Gutiérrez M, Mickus K, Camacho LM (2016) Abandoned Pb Zn mining wastes and their mobility as proxy to toxicity: A review. Sci Total Environ 565:392–400
Hierro A1, Olías M, Ketterer ME, Vaca F, Borrego J, Cánovas CR, Bolivar JP (2014) Geochemical behavior of metals and metalloids in an estuary affected by acid mine drainage (AMD). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:2611–2627
Hwang SK, Jho EH (2018) Heavy metal and sulfate removal from sulfate-rich synthetic mine drainages using sulfate reducing bacteria. Sci Total Environ 635:1308–1316
Johnson DB, Hallberg KB (2005) Acid mine drainage remediation options: a review. Sci Total Environ 338:3–14
Li H, Zeng XC, He Z, Chen X, E G, Han Y, Wang Y (2016) Long-term performance of rapid oxidation of arsenite in simulated groundwater using a population of arsenite-oxidizing microorganisms in a bioreactor. Water Res 101:393–401
Liu F, Zhou J, Zhou L, Zhang S, Liu L, Wang M (2015) Effect of neutralized solid waste generated in lime neutralization on the ferrous ion bio-oxidation process during acid mine drainage treatment. J Hazard Mater 299:404–411
Machodi MJ, Daramola MO (2019) Synthesis and performance evaluation of PES/chitosan membranes coated with polyamide for acid mine drainage treatment. Sci Rep 9:17657
Moreno-González R, Cánovas CR, Olías M, Macías F (2020) Seasonal variability of extremely metal rich acid mine drainages from the Tharsis mines (SW Spain). Environ Pollut 259:113829
Naidu G, Ryu S, Thiruvenkatachari R, Choi Y, Jeong S, Vigneswaran S (2019) A critical review on remediation, reuse, and resource recovery from acid mine drainage. Environ Pollut 247:1110–1124
Ngegla JV, Zhou X, Chen X, Zhu X, Liu Z, Feng J, Zeng XC (2020) Unique diversity and functions of the arsenic-methylating microorganisms from the tailings of Shimen Realgar Mine. Ecotoxicology 29:86–96
Ozoko DC (2015) Heavy metal geochemistry of acid mine drainage in Onyeama Coal Mine, Enugu, Southeastern Nigeria. J Environ Earth Sci 5:120–127
Park I, Tabelin CB, Jeon S, Li X, Seno K, Ito M, Hiroyoshi N (2019) A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 219:599–606
Shi W, Wu W, Zeng XC, Chen X, Zhu X, Cheng S (2018) Dissimilatory arsenate-respiring prokaryotes catalyze the dissolution, reduction and release of arsenic from paddy soils into groundwater: implication for the effect of sulfate. Ecotoxicology 27:1126–1136
Sun J, Hong Y, Guo J, Yang J, Huang D, Lin Z, Jiang F (2019) Arsenite removal without thioarsenite formation in a sulfidogenic system driven by sulfur reducing bacteria under acidic conditions. Water Res 151:362–370
Sun R, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Chen GH, Jiang F (2018) Realizing high-rate sulfur reduction under sulfate-rich conditions in a biological sulfide production system to treat metal-laden wastewater deficient in organic matter. Water Res 131:1343–1354
Sun W, Sierra-Alvarez R, Field JA (2011) Long term performance of an arsenite-oxidizing-chlorate-reducing microbial consortium in an upflow anaerobic sludge bed (UASB) bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 102:5010–5016
Villegas-Plazas M, Sanabria J, Junca H (2019) A composite taxonomical and functional framework of microbiomes under acid mine drainage bioremediation systems. J Environ Manage 251:109581
Wang J, Zeng XC, Zhu X, Chen X, Zeng X, Mu Y, Yang Y, Wang Y (2017) Sulfate enhances the dissimilatory arsenate-respiring prokaryotes-mediated mobilization, reduction and release of insoluble arsenic and iron from the arsenic-rich sediments into groundwater. J Hazard Mater 339:409–417
Wang X, Jiang H, Fang D, Liang J, Zhou L (2019) A novel approach to rapidly purify acid mine drainage through chemically forming schwertmannite followed by lime neutralization. Water Res 151:515–522
Yang Y, Mu Y, Zeng XC, Wu W, Yuan J, Liu Y,E,G, Luo F, Chen X, Li H, Wang J (2017) Functional genes and thermophilic microorganisms responsible for arsenite oxidation from the shallow sediment of an untraversed hot spring outlet. Ecotoxicology 26:490–501
Zeng XC,E,G, Wang J, Wang N, Chen X, Mu Y, Li H, Yang Y, Liu Y, Wang Y (2016) Functions and Unique Diversity of Genes and Microorganisms Involved in Arsenite Oxidation from the Tailings of a Realgar Mine. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:7019–7029
Zeng XC, Yang Y, Shi W, Peng Z, Chen X, Zhu X, Wang Y (2018) Microbially Mediated Methylation of Arsenic in the Arsenic-Rich Soils and Sediments of Jianghan Plain. Front Microbiol 6:1389
Zhang X, Tang S, Wang M, Sun W, Xie Y, Peng H, Zhong A, Zhang X, Yu H, Giesy JP, Hecker M (2019) Acid mine drainage affects the diversity and metal resistance gene profile of sediment bacterial community along a river. Chemosphere 217:790–799
Zhu X, Zeng XC, Chen X, Wu W, Wang Y (2019) Inhibitory effect of nitrate/nitrite on the microbial reductive dissolution of arsenic and iron from soils into pore water. Ecotoxicology 28:528–538
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the General Programs and the Foundations for Innovative Research Groups from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 41472219 and 41521001), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (grant no. CUGCJ1702).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Li, H. & Zeng, XC. A novel biofilm bioreactor derived from a consortium of acidophilic arsenite-oxidizing bacteria for the cleaning up of arsenite from acid mine drainage. Ecotoxicology 30, 1437–1445 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02283-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02283-4