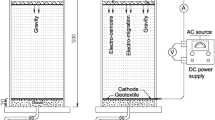
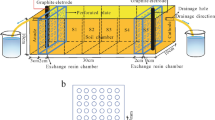
Abstract
A number of bench scale laboratory column tests were carried out using a newly designed and developed electrokinetic cell to investigate the fundamental behavior of zinc-spiked kaolin clay subjected to an electric field. Laboratory investigations focused on (i) zinc migration by the combined effects of electromigration and electro-osmosis and (ii) the electrically induced desorption characteristics of zinc-contaminated kaolin that occurred during processing. The correlations of the applied voltage gradient, electro-osmotic flow rate, and the development of a pH gradient were examined and evaluated. The results showed that the removal efficiency was high during the early stage of processing due to rapid desorption by electrokinetic effects in the cathode region. However, the majority of zinc migrating from the anode was precipitated due to the high pH environment in the cathode region.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar, Y. B., & Alshawabkeh, A. N. (1993). Principles of electrokinetic remediation. Environmental Science and Technology, 27(13), 2638–2647.
Acar, Y. B., Hamed, J. T., Alshawabkeh, A. N., & Gale, R. J. (1994). Removal of cadmium (II) from saturated kaolinite by the application of electrical current. Géotechnique, 44(2), 239–254.
Hamed, J., Acar, Y. B., & Gale, R. J. (1991). Pb(II) removal from kaolinite by electrokinetics. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 117(2), 241–271.
Rødsand, T., Acar, Y. B., & Breedveld, G. (1995). Electrokinetic extraction of lead from spiked Norwegian marine clay. Geoenvironment 2000, 2, 1518–1534.
Segall, B. A., O’Bannon, C. E., & Matthias, J. A. (1980). Electroosmosis chemistry and water quality. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 106(10), 1148–1152.
USEPA. (1986). Method 3050, Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soils. Test methods for evaluating solid wastes, SW846, (3rd ed.). Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Offices.
USEPA. (1987). Batch type adsorption procedures for estimating soil attenuation of chemicals. Washington, D.C: Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, EPA/530-SW-87-006.
Vangronsveld, J., & Cunningham, S. D. (1998). Metal-contaminated soils: in situ inactivation and phytorestoration, Springer.
Wood, P. A. (1997). Remediation methods for contaminated sites, Contaminated land and its reclamation, Issues in Environmental Science and Technology, The Royal Society of Chemistry, 47–71.
Yeung, A. T., Scott, T. B., Gopinath, S., Menon, R. M., & Hsu, C. (1997). Design, fabrication, and assembly of an apparatus for electrokinetic remediation studies. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 20(2), 199–210.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. H. Shimizu for his helpful assistance during the laboratory tests at the Disaster Prevention Research Institute (DPRI), Kyoto University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M., Kamon, M., Kim, S.S. et al. Desorption characteristics of kaolin clay contaminated with zinc from electrokinetic soil processing. Environ Geochem Health 29, 281–288 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-007-9100-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-007-9100-6