Abstract
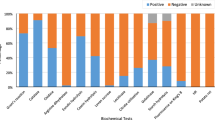
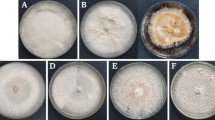
Skin blemishes of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers can cause severe economical losses to production. Some blemishes are due to known pathogens and others whose causes are unknown are called atypical blemishes. The present work aims at determining the origin of superficial atypical blemishes on a set of 204 tubers coming from 12 different French regions producing potato. The diversity of fungi and Streptomyces bacteria associated with blemishes was investigated by systematic isolation followed by identification by sequencing the internal transcribed spacer of the ribosomal DNA for fungi and by sequencing the 16S ribosomal DNA for bacteria. We found a high microbial diversity represented by 349 fungal isolates belonging to at least 47 different species and 21 bacterial strains of Streptomyces sp. The most represented fungi belonged to the genera Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, Alternaria, Penicillium, and Clonostachys. The pathogenicity of representative isolates was assessed in three bioassays; two bioassays based on single inoculations in previously sterilized potting mixture, and one bioassay based on both single and double inoculations under hydroponic conditions. We fulfilled the Koch’s postulates for Rhizoctonia solani AG 3 producing sclerotia. For other fungal and bacterial strains, our results did not show any causality or relationship between a single isolate or a complex and the occurrence of the blemishes. Moreover, the observation of irregular polygonal sunken corky lesions (polygonal lesions)—the most frequent atypical blemish—on non-inoculated tubers, suggested that the atypical blemishes could as well be a reaction of the plant to stressful environmental conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, N. A. (1982). The genetics and pathology of Rhizoctonia solani. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 20, 329–347.
Bouchek-Mechiche, K., Pasco, C., Andrivon, D., & Jouan, B. (2000). Differences in host range, pathogenicity to potato cultivars and response to soil temperature among Streptomyces species causing common and netted scab in France. Plant Pathology, 49, 3–10.
Braker, G., Ayala-del-Rio, H. L., Devol, A. H., Fesefeldt, A., & Tiedje, J. M. (2001). Community structure of denitrifiers, Bacteria, and Archaea along redox gradients in pacific northwest marine sediments by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of amplified nitrite reductase (nirS) and 16S rRNA genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 1893–1901.
Campion, C., Chatot, C., Perraton, B., & Andrivon, D. (2003). Anastomosis groups, pathogenicity and sensitivity to fungicides of Rhizoctonia solani isolates collected on potato crops in France. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 109, 983–992.
Cwalina-Ambroziak, B. (2002). Fungi colonizated of potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum L.) after harvest and after storage. Acta Agrobotanica, 55, 133–140.
Davide, R. G., & Zorilla, R. A. (1995). Evaluation of three nematophagous fungi and some nematicides for the control of potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Biocontrol, 1, 45–55.
Edwards, U., Rogall, T., Blocker, H., Emde, M., & Bottger, E. C. (1989). Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes - characterization of a gene coding for 16S-ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 17, 7843–7853.
El Bakali, A. M., & Martin, M. P. (2006). Black scurf of potato. Mycologist, 20, 130–132.
Fiers, M. (2010). Origins of the blemishes of potato tubers: from the soil microbiology to the pedoclimatic environment. Doctorate Thesis, Université de Bourgogne, (Dijon- France).
FNPPPT & GNIS. (2010). Le plant français de pomme de terre [cited 03 31 2010] Retrieved from www.plantdepommedeterre.org.
Gardes, M., & Bruns, T. D. (1993). ITS primers with enhanced specificity for Basidiomycetes - Application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Molecular Ecology, 2, 113–118.
Garrett, S. D. (1970). Pathogenic root-infecting fungi. Cambridge: Syndics of the Cambridge University Press.
GNIS & SOC. (2009). Echelle officielle française des maladies du tubercule de pomme de terre [cited 11 24 2009] Retrieved from www.plantdepommedeterre.org.
Gray, D. (1973). The growth of individual tubers. Potato Research, 16, 80–84.
Guillemaut, C., Edel-Hermann, V., Camporota, P., Alabouvette, C., Richard-Molard, M., & Steinberg, C. (2003). Typing of anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani by restriction analysis of ribosomal DNA. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 49, 556–568.
Hart, T. G. (1971). Fish scale or elephant hide on potatoes. The vegetarian newsletter, 71, 5.
Keinath, A. P., Fravel, D. R., & Papavizas, G. C. (1991). Potential of Gliocladium roseum for biocontrol of Verticillium dahliae. Phytopathology, 81, 644–648.
Kuninaga, S., Carling, D. E., Takeuchi, T., & Yokosawa, R. (2000). Comparison of rDNA-ITS sequences between potato and tobacco strains in Rhizoctonia solani AG-3. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 66, 2–11.
Lambert, D. H., & Loria, R. (1989). Streptomyces scabies sp-nov, nom-rev. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 39, 387–392.
Lehtonen, M. J., Rantala, H., Kreuze, J. F., Bang, H., Kuisma, L., Koski, P., et al. (2004). Occurrence and survival of potato scab pathogens (Streptomyces species) on tuber lesions: quick diagnosis based on a PCR-based assay. Plant Pathology, 53, 280–287.
Lutaladio, N., & Castaidi, L. (2009). Potato: The hidden treasure. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 22, 491–493.
Park, H. S., & Kilbane, J. J. (2006). Rapid detection and high-resolution discrimination of the genus Streptomyces based on 16S-23S rDNA spacer region and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 33, 289–297.
Pasco, C., Jouan, B., & Andrivon, D. (2005). Resistance of potato genotypes to common and netted scab-causing species of Streptomyces. Plant Pathology, 54, 383–392.
Peever, T. L., Su, G., Carpenter-Boggs, L., & Timmer, L. W. (2004). Molecular systematics of citrus-associated Alternaria species. Mycologia, 96, 119–134.
Pieta, D., & Patkowska, E. (2003). Antagonistic bacteria and fungi limiting potato infection by soil-borne pathogenic fungi. Journal of Plant Protection Research, 43, 97–104.
Radtke, W., & Rieckmann, W. (1991). Diseases and pests of the potato. Maladies et ravageurs de la pomme de terre., 168pp.
Rapilly, F. (2001). Champignons des plantes: les premiers agents pathogènes reconnus dans l’histoire des sciences. C.R. Academie des Sciences de Paris, Science de la vie/Life Sciences, 324, 893–898.
Schroers, H. J., Samuels, G. J., Seifert, K. A., & Gams, W. (1999). Classification of the mycoparasite Gliocladium roseum in Clonostachys as C. rosea, its relationship to Bionectria ochroleuca, and notes on other Gliocladium-like fungi. Mycologia, 91, 365–385.
Sexton, P. (2003). Some thoughts on elephant hide. Spudline, December.
Stevenson, W. R., Loria, R., Franc, G. D., & Weingartner, D. P. (2001). Compendium of potato diseases. St. Paul: The American Phytopathological Society.
Theron, D. J. (1991). Dry rot of potatoes caused by Gliocladium roseum. Plant Pathology, 40, 302–305.
Wanner, L. A. (2004). Field isolates of Streptomyces differ in pathogenicity and virulence on radish. Plant Disease, 88, 785–796.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In M. A. Innis, D. H. Gelfand, J. J. Sninsky, & T. J. White (Eds.), PCR protocols. A guide to methods and applications (pp. 315–322). San Diego: Academic.
Woodhall, J. W., Lees, A. K., Edwards, S. G., & Jenkinson, P. (2007). Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani from potato in Great Britain. Plant Pathology, 56, 286–295.
Woodhall, J. W., Lees, A. K., Edwards, S. G., & Jenkinson, P. (2008). Infection of potato by Rhizoctonia solani: Effect of anastomosis group. Plant Pathology, 57, 897–905.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all technical partners, namely Pom’ Alliance and Germicopa Seed Production, for supplying tuber samples, Bretagne Plants for supplying strains T FSa and T FSC1 and INRA, Station de Pathologie Végétale, Le Rheu (France) for supplying the strains 9529b and i4 (9729-1). We also thank H. Friberg for comments on the manuscript.
Marie Fiers was financially supported by a PhD funding from the National Association of Technical Research (ANRT) (CIFRE n°1085/2006).
This work was part of a wider project: Program of Collaborative Research (PRC) between Bretagne Biotechnologie Végétale (BBV), Bretagne Plants and Germicopa, funded by the Region Brittany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiers, M., Chatot, C., Edel-Hermann, V. et al. Diversity of microorganisms associated with atypical superficial blemishes of potato tubers and pathogenicity assessment. Eur J Plant Pathol 128, 353–371 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-010-9657-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-010-9657-2