Abstract
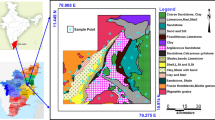
Hydrogeochemical investigations were carried out in Chithar River basin, Tamil Nadu, India to identify the major geochemical processes that regulate groundwater chemistry. For this study, long-term (1991–1997) and recent water quality data (2001–2002) for 30 groundwater wells spread over the study area were used to understand the groundwater geochemistry and hydrogeochemical process regulating groundwater quality. Groundwater quality data obtained from more than 400 water samples were employed. Results of electrical conductivity and chloride express large variation between minimum and maximum values and high standard deviation, which suggests that the water chemistry in the study region is not homogeneous and influenced by complex contamination sources and geochemical process. Nitrate and depth to water table expose the influences of surface contamination sources, whereas dissolved silica, fluoride and alkalinity strongly suggest the effect of rock–water interaction. In the study region, weathering of carbonate and silicate minerals and ion exchange reactions predominantly regulate major ion chemistry. Besides, the concentrations of sulphate, chloride and nitrate firmly suggest the impact of agricultural activities such as irrigation return flow, fertiliser application, etc on water chemistry in the study region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). Washington, DC: American public Health Association.
Apodaca, L. E., Jeffrey, B. B., & Michelle, C. S. (2002). Water quality in shallow alluvial aquifers, Upper Colorado River Basin, Colorodo. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 38, 133–143. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2002.tb01541.x.
Balasubramanian, A., & Sastri, J. C. V. (1994). Groundwater resources of Tamirabarani River basin, Tamil Nadu, India (pp. 484–501). India, Inland Water Resources.
Cederstorm, D. J. (1946). Genesis of groundwater in the coastal plain of Virginia. Environmental Geology, 41, 218–245.
Comly, H. H. (1945). Cyanosis in infants caused by nitrates in well water. Journal of the American Medical Association, 129, 12–114.
Das, B. K., & Kaur, P. (2001). Major ion chemistry of Renuka lake and weathering processes, Sirmaur district, Himachal Pradesh, India. Journal of Environmental Geology, 40, 908–917. doi:10.1007/s002540100268.
Datta, P. S., & Tyagi, S. K. (1996). Major ion chemistry of groundwater in Delhi area: Chemical weathering processes and groundwater regime. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 47, 179–188.
Devadas, D. J., Rao, N. S., Rao, B. T., Rao, K. V. S., & Subrahmanyam, A. (2007). Hydrogeochemistry of the Sarada river basin, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 52, 1331–1342. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0577-6.
Elango, L., Kannan, R., & Senthil Kumar, M. (2003). Major ion chemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes of groundwater in a part of Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu, India. Journal of Environmental Geoscience, 10, 157–166.
Fisher, S. R., & Mullican, W. F. (1997). Hydrogeochemical evolution of sodium-sulphate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the northern Chihuahua desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas, U.S.A. Hydrogeology Journal, 5, 4–16. doi:10.1007/s100400050102.
Garrels, R. M., & Mackenzie, F. T. (1971). Evolution of sedimentary rocks. New York: WW Norton.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science Journal, 170, 795–840.
Gilly, G., Corrao, G., & Favilli, S. (1984). Concentrations of nitrates in drinking water and incidence of gastric carcinomas. First descriptive study of the Piemonate Region, Italy. The Science of the Total Environment, 34, 35–37. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(84)90039-1.
GSI (1995). Geological and mineral map of Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry. Published in 1: 500,000 scale by the Director General, Geological Survey of India.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (3rd ed.). U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper, 2254, 263.
Holland, H. D. (1978). The chemistry of the atmosphere and ocean. New York: Wiley.
Jankowski, J., & Acworth, R. I. (1997). Impact of debris-flow deposits on hydrogeochemical process and the development of dry land salinity in the Yass River catchment, New South Wales, Australia. Hydrogeology Journal, 5, 71–88. doi:10.1007/s100400050119.
Jayananda, M., Janardhan, A. S., Sivasubramaniam, P., & Pencay, J. J. (1995). Geochronologic and istopic constraints on granulite formation in the Kodaikanal area, Southern India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 34, 373–390.
Katz, B. G., Gopalan, T. B., Bullen, T. D., & Davis, J. H. (1998). Use of chemical and isotopic tracers to characterise the interaction between groundwater and surface water in mantled karst. Groundwater Journal, 35, 1014–1028.
Mayo, A. L., & Loucks, M. D. (1995). Solute and isotopic geochemistry and groundwater flow in the Central Wasatch Range, Utah. Journal of Hydrology (Amsterdam), 172, 31–59. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(95)02748-E.
Mohan, R., Singh, A. K., Tripathi, J. K., & Chowdhary, G. C. (2000). Hydrochemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in Naini industrial area, Allahabad District, Uttar Pradesh. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 55, 77–89.
Möller, P., Rosenthal, E., Geyer, S., Guttman, J., Dulski, P., Rybakov, M., et al. (2007). Hydrochemical processes in the lower Jordan valley and in the Dead Sea area. Chemical Geology, 239, 27–49. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.12.004.
PWD (2002). Groundwater perspectives: A profile of Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu, India (pp. 53–65). India: Public Works Department, Government of Tamil Nadu.
PWD (2004). Groundwater quality data of Tirunelveli District for the period 1991–2003 collected from state ground and surface water resources data centre. India: Public Works Department, Government of Tamil Nadu.
Rammohan, H. S. (1984). A climatological assessment of water recourses of Tamil Nadu. Indian Journal of Power and River Valley Development, 34, 58–63.
Salama, R. B., Tapley, I., Ishii, T., & Hawkes, G. (1994). Identification of areas of recharge and discharge using Landsat-TM satellite imagery and aerial photography mapping techniques. Journal of Hydrology (Amsterdam), 162, 119–141. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(94)90007-8.
Sami, K. (1992). Recharge mechanisms and geochemical processes in a semi-arid sedimentary basin, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Journal of Hydrology (Amsterdam), 139, 27–48. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(92)90193-Y.
Sarin, M. M., Krishnaswamy, S., Dilli, K., Somayajulu, B. L. K., & Moore, W. S. (1989). Major ion chemistry of the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system: Weathering process and fluxes to the Bay of Bengal. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53, 997–1009. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(89)90205-6.
Schoeller, H. (1965). Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In Methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development (pp. 54–83). UNESCO.
Schoeller, H. (1967). Geochemistry of groundwater—an international guide for research and practice (Chap. 15, pp. 1–18). UNESCO.
Sikdar, P. K., Sarkar, S. S., & Palchoudhury, S. (2001). Geochemical evolution of groundwater in the quaternary aquifer of Calcutta and Howrah, India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 19, 579–594. doi:10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00056-0.
Stallard, R. F., & Edmond, J. M. (1983). Geochemistry of the Amazon, the influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88, 9671–9688. doi:10.1029/JC088iC14p09671.
Subramani, T. (2005). Hydrogeology and identification of geochemical processes in Chithar River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Ph.D. Thesis, Anna University, Chennai, India.
Subramani, T., Elango, L., & Damodarasamy, S. R. (2005a). Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Chithar River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Journal of Environmental Geology, 47, 1099–1110. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-1243-0.
Subramani, T., Elango, L., Srinivasalu, S., & Marikio, T. (2005b). Geological setting and groundwater chemistry in Chithar River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Journal of Indian Mineralogist, 39, 108–119.
Tesoriero, A. J., Spruill, T. B., & Eimers, L. (2004). Geochemistry of shallow ground water in coastal plain environments in the southeastern United States: Implications for aquifer susceptibility. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 1471–1482. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.01.021.
Yoshida, M. (1992). Precambrian tectonothermal events in east Gondwana land crustal fragments and their correlation (IGCP-288), In R. Tsudhi (Ed.), Japan contribution to the IGCP (pp. 51–62). Osaka.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramani, T., Rajmohan, N. & Elango, L. Groundwater geochemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes in a hard rock region, Southern India. Environ Monit Assess 162, 123–137 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0781-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0781-4