Abstract
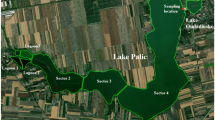
Lake Cajititlán is a shallow body of water located in an endorheic basin in western Mexico. This lake receives excess fertilizer runoff from agriculture and approximately 2.3 Hm3 per year of poorly treated wastewater from three municipal treatment plants. Thirteen water quality parameters were monitored at five sampling points within the lake over 9 years. The objective of this work was to characterize the spatial and temporal variations of the water quality and to identify the sources of data variability in order to assess the influence and the impact of different natural and anthropogenic processes. One-way ANOVA tests, principal component analysis (PCA), cluster analysis (CA), and discriminant analysis (DA) were implemented. The one-way ANOVA showed that biochemical oxygen demand and pH present statistically significant spatial variations and that alkalinity, total chloride, conductivity, chemical oxygen demand, total hardness, ammonia, pH, total dissolved solids, and temperature present statistically significant temporal variations. PCA results explained both natural and anthropogenic processes and their relationship with water quality data. The CA results suggested there is no significant spatial variation in the water quality of the lake because of lake mixing caused by wind. The most significant parameters for spatial variations were pH, NO3−, and NO2−, consistent with the configuration of point and nonpoint sources that affect the lake’s water quality. The temporal DA results suggested that conductivity, hardness, NO2−, pH, and temperature were the most significant parameters to discriminate between seasons. The temporal behavior of these parameters was associated with the transport pathways of seasonal contaminants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akan, J. C., Abbagambo, M. T., Chellube, Z. M., & Abdulrahman, F. I. (2012). Assessment of pollutants in water and sediment samples in Lake Chad, Baga, North Eastern Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Protection. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2012.311161.
Akpor, O. B., & Muchie, B. (2011). Environmental and public health implications of wastewater quality. African Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 2379–2387.
Andreopoulos, B. (2017). Clustering categorical data, Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online, https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118445112.stat07907.
Ávila Pérez, H., García Ibañez, S., & Rosas-Acevedo, J. L. (2015). Análisis de Componentes Principales, como herramienta parainterrelaciones entre variables fisicoquímicas y biológicas en un ecosistema léntico de Guerrero, México. Revista Iberoamericana de Ciencias, 2, 43–53.
AWWA. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (23rd ed.). In E. W. Rice, R. B. Baird, & A. D. Eaton (Eds.), American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation. ISBN: 9780875532875
Badillo-Camacho, J., Reynaga-Delgado, E., Barcelo-Quintal, I., del Valle, P. F. Z., López-Chuken, U. J., Orozco-Guareño, E., Álvarez-Bobadilla, J. I., & Gómez-Salazar, S. (2015). Water quality assessment of a tropical Mexican lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Environmental Protection. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2015.63022.
Bengraïne, K., & Marhaba, T. F. (2003). Using principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00104-3.
Bollmann, A., & Laanbroek, H. J. (2011). Nitrification in inland waters. In M. G. Klotz, B. B. Ward, & D. J. Arp (Eds.), Nitrification (pp. 385–403). Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology Press.
Cacoullos, T. (1973). Discriminant analysis and applications. Kent: Elsevier Science.
Campbell, N. A. (1978). The influence function as an aid in outlier detection in discriminant analysis. Applied Statistics. https://doi.org/10.2307/2347160.
CEA. (2018). Sistema de Calidad del Agua. Comisión Estatal del Agua del Estado de Jalisco, México [Resource Document]. http://info.ceajalisco.gob.mx/sca/. Accessed 25 Nov 2018.
CNA. (2016). Normas Mexicanas Vigentes del Sector Hídrico. Comisión Nacional del Agua. https://www.gob.mx/conagua/acciones-y-programas/normas-mexicanas-83266. Accessed 10 Feb 2019.
Costa, E., Pérez, J., & Kreft, J.-U. (2006). Why is metabolic labour divided in nitrification? Trends in Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2006.03.006.
de Anda, J., de J Díaz-Torres, J., Gradilla-Hernández, M. S., & de la Torre-Castro, L. M. (2019a). Morphometric and water quality features of Lake Cajititlán, Mexico. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7163-8.
de Anda, J., Gradilla-Hernández, M. S., Díaz-Torres, O., de Jesús Díaz-Torres, J., & de la Torre-Castro, L. M. (2019b). Assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments and sediment-water interface of Lake Cajititlán, Mexico. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7524-y.
Díaz Muñiz, C., García Nieto, P. J., Alonso Fernández, J. R., Martínez Torres, J., & Taboada, J. (2012). Detection of outliers in water quality monitoring samples using functional data analysis in San Esteban estuary (Northern Spain). Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.083.
Dillon, P. J., & Rigler, F. H. (1974). The phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes1,2: phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship. Limnology and Oceanography. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1974.19.5.0767.
Duc Viet, N., Anh Bac, N., & Hoang, T. H. (2016). Dissolved oxygen as an indicator for eutrophication in freshwater lakes. Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Engineering and Management for Sustainable Development. 47.
Duda, R. O., Hart, P. E., & Stork, D. G. (2001). Pattern classification. New York: Wiley.
Everitt, B., & Hothorn, T. (2011). An introduction to applied multivariate analysis with R, Use R! New York: Springer-Verlag.
Fisher, R. A. (1936). The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Annals of Eugenics. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1936.tb02137.x.
Gnauck, A. (2004). Interpolation and approximation of water quality time series and process identification. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2799-3.
Gradilla-Hernández, M. S., de Anda-Sanchez, J., Ruiz-Palomino, P., Barrios-Piña, H., Senés-Guerrero, C., Del ToroBarbosa, M., & Vázquez-Toral, M. P. (2018). Estudio Preliminar del Índice de Calidad de Agua en el Lago de Cajitilán y su Potencial Predictivo de la Mortandad Masiva de Peces, In Memorias del congreso nacional de hidráulica 2018.
Guénoche, A., Hansen, P., & Jaumard, B. (1991). Efficient algorithms for divisive hierarchical clustering with the diameter criterion. Journal of Classification. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02616245.
Guo, W., Fu, Y., Ruan, B., Ge, H., & Zhao, N. (2014). Agricultural non-point source pollution in the Yongding River Basin. Ecological Indicators. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.07.012.
Hampel, J. J., McCarthy, M. J., Gardner, W. S., Zhang, L., Xu, H., Zhu, G., & Newell, S. E. (2018). Nitrification and ammonium dynamics in Taihu Lake, China: seasonal competition for ammonium between nitrifiers and cyanobacteria. Biogeosciences. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-15-733-2018.
Hennig, C. M., Meilă, M., Murtagh, F., & Rocci, R. (Eds.). (2016). Handbook of cluster analysis, Chapman & Hall/CRC handbooks of modern statistical methods. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group.
Hotelling, H. (1933). Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. Journal of Educational Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0071325.
Hotelling, H. (1936). Relations Between Two Sets of Variates. In S. Kotz & N. L. Johnson (Eds.), Breakthroughs in statistics: methodology and distribution (pp. 162–190). New York: Springer.
Huang, J. Z., & Stone, C. J. (2003). Extended linear modeling with splines. In D. D. Denison, M. H. Hansen, C. C. Holmes, B. Mallick, & B. Yu (Eds.), Nonlinear estimation and classification, lecture notes in statistics (pp. 213–233). New York: Springer.
Hubert, M., & Vandervieren, E. (2008). An adjusted boxplot for skewed distributions. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2007.11.008.
Huberty, C. J., & Olejnik, S. (2006). Applied MANOVA and discriminant analysis. New Jersey: Wiley.
Ibarra-Montoya, J. L., Rangel-Peraza, G., González-Farias, F. A., Anda, J. D., Zamudio-Reséndiz, M. E., Martínez-Meyer, E., & Macias-Cuellar, H. (2010). Modelo de nicho ecológico para predecir la distribución potencial de fitoplancton en la Presa Hidroeléctrica Aguamilpa, Nayarit. México. Ambiente & Água - An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Science. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.154.
Ibarra-Montoya, J. L., Rangel-Peraza, G., González-Farias, F. A., Anda, J. D., Martinez-Meyer, E., & Macias-Cuellar, H. (2012). Uso del modelado de nicho ecológico como una herramienta para predecir la distribución potencial de Microcystis sp (cianobacteria) en la Presa Hidroeléctrica de Aguamilpa, Nayarit, México. Ambiente & Água - An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Science. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.607.
IIEG Jalisco (2018). Municipal diagnosis: Tlajomulco de Zúñiga. [Resource Document]. https://iieg.gob.mx/contenido/Municipios/TlajomulcodeZuniga.pdf. Accessed 10 Apr 2019.
Jolliffe, I. T. (1986). Principal component analysis and factor analysis. In I. T. Jolliffe (Ed.), Principal component analysis (pp. 115–128). New York: Springer.
Jolliffe, I. T. (2002). Principal component analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Jolliffe, I. T., Trendafilov, N. T., & Uddin, M. (2003). A modified principal component technique based on the LASSO. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics. https://doi.org/10.1198/1061860032148.
Kazemi, E., Karyab, H., & Emamjome, M.-M. (2017). Optimization of interpolation method for nitrate pollution in groundwater and assessing vulnerability with IPNOA and IPNOC method in Qazvin plain. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-017-0287-x.
Kittiwanich, J., Yamamoto, T., Kawaguchi, O., & Hashimoto, T. (2007). Analyses of phosphorus and nitrogen cyclings in the estuarine ecosystem of Hiroshima Bay by a pelagic and benthic coupled model. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning in Coastal and Transitional Waters. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2007.04.029.
Liebhold, A., Koenig, W. D., & Bjørnstad, O. N. (2004). Spatial synchrony in population dynamics. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.011802.132516.
Liu, Z., Hu, J., Zhong, P., Zhang, X., Ning, J., Larsen, S. E., Chen, D., Gao, Y., He, H., & Jeppesen, E. (2018). Successful restoration of a tropical shallow eutrophic lake: strong bottom-up but weak top-down effects recorded. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.09.007.
Loftis, J. C., Taylor, C. H., Newell, A. D., & Chapman, P. L. (1991). Multivariate trend testing of Lake Water quality. Journal of the American Water Resources Association. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1991.tb01446.x.
Mackey, L. W. (2009). Deflation methods for sparse PCA. In D. Koller, D. Schuurmans, Y. Bengio, & L. Bottou (Eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (Vol. 21, pp. 1017–1024). New York: Curran Associates, Inc..
Matson, P. A., Parton, W. J., Power, A. G., & Swift, M. J. (1997). Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5325.504.
Murphey, S. F. (2006). Water quality of Boulder Creek, Colorado. Reston: U.S. Geological Survey.
Murtagh, F. (1983). A survey of recent advances in hierarchical clustering algorithms. The Computer Journal. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/26.4.354.
North, R. P., & Livingstone, D. M. (2013). Comparison of linear and cubic spline methods of interpolating lake water column profiles: interpolation of lake profiles. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods. https://doi.org/10.4319/lom.2013.11.213.
Ouyang, Y., Nkedi-Kizza, P., Wu, Q. T., Shinde, D., & Huang, C. H. (2006). Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.08.030.
Parker, S. J., Butler, A. P., & Jackson, C. R. (2016). Seasonal and interannual behaviour of groundwater catchment boundaries in a Chalk aquifer: seasonal groundwater catchment dynamics. Hydrological Processes. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10540.
Pearson, K. (1901). On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440109462720.
Pejman, A. H., Bidhendi, G. R. N., Karbassi, A. R., Mehrdadi, N., & Bidhendi, M. E. (2009). Evaluation of spatial and seasonal variations in surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326086.
Pinto da Costa, J., & Soares, C. (2005). A weighted rank measure of correlation. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Statistics. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-842X.2005.00413.x.
Pollard, D. (1981). Strong consistency of K-means clustering. Ann. Statist. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176345339.
Potapova, M., & Charles, D. F. (2007). Diatom metrics for monitoring eutrophication in rivers of the United States. Ecological Indicators, 7, 48–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2005.10.001.
Qin, B., Gao, G., Zhu, G., Zhang, Y., Song, Y., Tang, X., & XU Hai1., Deng, J. (2013). Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response. Chinese Science Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5560-x.
Rencher, A. C. (2002). Methods of multivariate analysis. New York: Wiley.
Robinson, R. B., Chris, C., & Odom, K. (2005). Identifying outliers in correlated water quality data. Journal of Environmental Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2005)131:4(651.
Ryther, J. H., & Dunstan, W. M. (1971). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.171.3975.1008.
Savaresi, S. M., Boley, D. L., Bittanti, S., & Gazzaniga, G. (2002). Cluster selection in divisive clustering algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2002 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (pp. 299–314). Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2006.02.001.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Mohan, D., & Sinha, S. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011.
Smith, V. H., & Schindler, D. W. (2009). Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends in Ecology & Evolution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2008.11.009.
Stone, C. J., Hansen, M. H., Kooperberg, C., & Truong, Y. K. (1997). Polynomial splines and their tensor products in extended linear modeling. The Annals of Statistics, 25, 1371–1425.
Thornton, K. W., Kimmel, B. L., & Payne, F. E. (1990). Reservoir limnology: ecological perspectives. New York: Wiley.
Vega, M., Pardo, R., Barrado, E., & Debán, L. (1998). Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00138-9.
Yang, Y.-H., Zhou, F., Guo, H.-C., Sheng, H., Liu, H., Dao, X., & He, C.-J. (2010). Analysis of spatial and temporal water pollution patterns in Lake Dianchi using multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1242-9.
YSI. (2010). YSI 6600 V2 Sonde. YSI Incorporated. https://www.ysi.com/File%20Library/Documents/Specification%20Sheets/E52-6600V2.pdf. Accessed 31 Oct 2018.
Zelterman, D. (2015). Applied multivariate statistics with R, Statistics for biology and health. Cham: Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gradilla-Hernández, M.S., de Anda, J., Garcia-Gonzalez, A. et al. Multivariate water quality analysis of Lake Cajititlán, Mexico. Environ Monit Assess 192, 5 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7972-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7972-4