Abstract
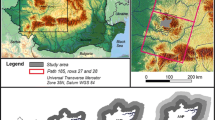
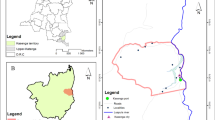
The investigation of land use changes by anthropic processes, spatially and temporally, is a fundamental tool to establish correlations between landscape patterns and processes and management of the buffer zone of Conservation Units. This study aimed to analyze the forest fragmentation and land use dynamics in the buffer zone of the Rio Doce State Park (PERD), located in Minas Gerais, Brazil, for the year 2015. Its buffer zone was delimited to a radius of 10 km, covering a total area of 128.893,36 ha. Land use classification was based on Landsat 8 image, orbit 217, point 73 and 74, and two types of ecosystems were identified: natural and anthropic. In the thematic mapping, the pressure of the anthropic use over the natural was notified, as well as the high number of forest fragments, which is a negative impact on the resilience required for the conservation of biodiversity and the local Atlantic forest. The fragments have different shapes and sizes and are distributed throughout the buffer zone of the PERD. There is a need to adopt conservation strategies, such as environmental education, reforestation techniques, recovery of degraded areas and ecological corridors. Even with a worrying current scenario, this finding makes it possible to establish an optimistic point for biodiversity conservation, associated with a tendency to reduce the forces of direct changes on natural systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AMLD. (2018). First vegetated viaduct built on federal highway can help save Golden Lion Tamarin in RJ. Golden Lion Tamarin Association. Retrieved December 14, 2018, from https://g1.globo.com/rj/regiao-dos-lagos/noticia/2018/12/19/primeiro-viaduto-vegetado-construido-em-rodovia-federal-pode-ajudar-a-salvar-mico-leao-dourado-no-rj.ghtml.
Britto, F. (2012). Ecological corridors: An integrative strategy in ecosystem management (2nd ed., p. 264). Florianópolis: EDUFSC.
Carroll, C., McRae, B. H., & Brookes, A. (2012). Use of linkage mapping and centrality analysis across habitat gradients to conserve connectivity of gray wolf populations in Western North America. Conservation Biology, 26(1), 78–87.
Carvalho, A. A. (2016). Environmental perception of rural producers in the surrounding area of the Rio Doce State Park (MG): Subsidies for environmental education. Dissertation (Master’s degree in Ecology, Conservation and Wildlife Management). Federal University of Minas Gerais/MG, 76 p.
De Oliveira, B. R., Da Costa, E. L., Carvalho-Ribeiro, S. M., & Maia-Barbosa, P. M. (2020). Land use dynamics and future scenarios of the Rio Doce State Park buffer zone, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 192(1), 1–12. Retrieved August 24, 2020, from https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8016-9.
EcoD. (2015). Meet the drone capable of planting up to 1 billion trees per year. Site online Eco Desenvolvimento Org. Retrieved September 28, 208, from http://www.ecodesenvolvimento.org/posts/2015/abril/conheca-o-drone-que-e-capaz-de-plantar-1-bilhao-de.
EPA of Jacroá. (2008). Management plan: Environmental protection area. Retrieved February 13, 2019, from http://www.universalisconsultoria.com.br/projetos/0029.pdf.
EPA of Jaguaraçu. (2008). Management plan: Environmental protection area. Retrieved February 13, 2019, from http://www.universalisconsultoria.com.br/projetos/0032.pdf.
ESRI. (2019). ArcGis Desktop—10.6.1 version. Redlands, CA: Environmental Systems Research Institute. Retrieved from http://www.esri.com/software/arcgis/arcgis-for-desktop.
Guerra, B. R. G., Andrade, D. S., Moura, M. O., & Rocha, I. C. C. (2016). Importance of animal-plant interaction in the recovery of degraded areas. XIII National environmental congress, 8 p. Retrieved September 20, 2018, from http://www.meioambientepocos.com.br/anais-2016/351.%20IMPORT%C3%82NCIA%20DA%20INTERA%C3%87%C3%83O%20ANIMAL-PLANTA%20NA%20%20%20RECUPERA%C3%87%C3%83O%20DE%20%C3%81REAS%20DEGRADADAS.pdf.
Haddad, N. M., Brudvig, L. A., Clobert, J., Davies, K. F., Gonzalez, A., Holt, R. D., et al. (2015). Habitat fragmentation and its lasting impact on Earth’s ecosystems. Applied Ecology, March, 1–9. Retrieved September 23, 2018, from https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1500052.
IEF. (1994). Priority research for the Rio Doce State Park, Brazil. Preliminary report. State Forestry Institute, Belo Horizonte, 35p.
INPE. (2015). Landsat images. Retrieved July 15, 2015, from www.dgi.inpe.br/CDSR/.
Lagos, M. C. C., & Marimon, B. S. (2012). Seed rain in a gallery forest in the Bacaba Park, in Nova Xavantine, Mato Grosso, Brazil. Revista Árvore, Viçosa-MG, 36(2), 311–320. Retrieved September 28, 2018, from http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rarv/v36n2/a12v36n2.pdf.
Lang, S., & Blaschke, T. (2009). Landscape analysis with GIS. São Paulo: Oficina de Textos.
Lima, B. C., Francisco, C. N., & Bohrer, C. B. A. (2017). Landslides and forest fragmentation in the mountain range region of Rio de Janeiro state. Ciência Florestal, Santa Maria, 27(4), 1283–1295.
Lima, R. N. S., & Rocha, C. H. B. (2011). Remote sensing techniques and landscape ecology metrics applied in the analysis of forest fragmentation in the municipality of Juiz de Fora, MG in 1987 and 2008. Anais XV Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto - SBSR, 2067–2074.
Magnago, L. F. S., Rocha, M. F., Meyer, L., Martins, S. V., & Meira-Neto, J. A. A. (2015). Microclimatic conditions at forest edges have significant impacts on vegetation structure in large Atlantic forest fragments. Biodiversity and Conservation, 24(9), 2305–2318. Retrieved September 14, 2018, from https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-015-0961-1.
Martines, M., & Toppa, R. (2018). Stepping-Stones Detection for connectivity planning at Local-Regional scale. Revista do Departamento de Geografia, 35, 49–57.
Martins, S. V. (2014). Recovery of riparian forests: in the context of the New Forest Code. 3rd edn., Viçosa/MG: Editora Aprenda Fácil, 1, 220 p.
Melo, A. M., Silva, F. T., Chaves, J., Lima, M. L. M., Scheid, P. F., & Botelho, T. P. (2017). Ecological Corridor Project: Uniting Forests and articulating forces. Minas Gerais. Retrieved September 20, 2018, from http://www.ief.mg.gov.br/images/stories/2017/PROGRAMAS_ACOES/Projeto_Corredor_Ecológico_-_Versao_1.pdf.
Metzger, J. P. (1999). Landscape structure and fragmentation: Bibliographic analysis. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 71(3–1), 445–462.
Metzger, J. P. (2001). What is landscape ecology? Biota Neotropica, 1(12), 1–9.
Metzger, J. P. (2009). Conservation issues in the Brazilian Atlantic forest. Biological Conservation, 142(6), 1138–1140. Retrieved September 25, 2018, from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2008.10.012.
Miccolis, A., Peneireiro, F. M., Marques, H. R., Vieira, D. L. M., Arco-Verde, M. F., Hoffmann, M. R., et al. (2016). Ecological restoration with agroforestry systems: How to reconcile conservation with production: Options for Cerrado and Caatinga. Embrapa Cerrados, 266 p. Retrieved September 20, 2018, from https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/1069767/restauracao-ecologica-com-sistemas-agroflorestais-como-conciliar-conservacao-com-producao-opcoes-para-cerrado-e-caatinga.
MMA. (2018). Ecological Corridors Project. Ministry of the Environment. Retrieved June 11, 2018, from http://www.mma.gov.br/areas-protegidas/programas-e-projetos/projeto-corredores-ecologicos.
Mosaico, C. (2012). Green corridors. Rio de Janeiro. Retrieved September 20, 2018, from http://www.rio.rj.gov.br/dlstatic/10112/4595787/4116261/corredores_verdes.pdf.
Novelli, F. Z., & Silva, A. G. (2013). The areas of permanent preservation as evidence of connectivity of forest fragments in the ecological corridor two mouths—Mestre Álvaro. Natureza Online, 11(3), 102–117. Retrieved August 24, 2020, from http://www.naturezaonline.com.br/natureza/conteudo/pdf/01_Novelli&Silva_102117.pdf.
OA&N. (2013). Eucalyptus trees Form ecological corridors in ES. Retrieved September 15, 2018, from http://www.olhardireto.com.br/agro/noticias/exibir.asp?id=12486¬icia=eucaliptos-formam-corredores-ecologicos-no-es.
Oliveira, B. R. (2019) Buffer zone of Rio Doce State Park, Minas Gerais, Brazil: Past, present and future. Thesis (Doctorate in Ecology, Conservation and Wildlife Management), Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte-MG, 86 p.
Oliveira, B. R., Carvalho-Ribeiro, S. M., & Maia-Barbosa, P. M. (2020). A multiscale analysis of land use dynamics in the buffer zone of Rio Doce State Park, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 63(5), 935–957. Retrieved August 24, 2020, from https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2019.1617681.
Oliveira, B. R., Oliveira, M. L., & Boti, J. B. (2013). Inventory of fruit species of Ifes campus Santa Teresa and its disperser fauna. Natureza Online, 11(3), 139–146. Retrieved September 20, 2018, from http://www.naturezaonline.com.br/natureza/conteudo/pdf/05_OliveiraBRetal_139146.pdf.
Passos, R. T. M. P., & Macedo, M. E. (2014). The importance of ecological corridors in reducing the number of roadkill of animals on highways. Acervo Da Iniciação Científica, 1, 10 p.
Pereira, V. H. C., & Cestaro, L. A. (2016). Ecological corridors in Brazil: Evaluation on the main criteria used for definition of potential areas. Caminhos de Geografia—Revista Online, 17(58), 16–33. Retrieved September 20, 2018, from http://www.seer.ufu.br/index.php/caminhosdegeografia/.
Pereira, M. A., Neves, N. A. G. S., & Figueiredo, D. F. C. (2007). Considerations on territorial fragmentation and networks of ecological corridors. Geografia (Universidade Estadual de Londrina), 16(2), 5–24.
Ribeiro, M. C., Metzger, J. P., Martensen, A. C., Ponzoni, F. J., & Hirota, M. M. (2009). The Brazilian Atlantic forest: How much is left, and how is the remaining forest distributed? Implications for conservation. Biological Conservation, 142(6), 1141–1153. Retrieved September 15, 2018, from http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2009.02.021.
Sandi, A. R. A. (2017). Medium and large sized mammals seed dispersors in forests along a degradation gradient in the eastern Amazon. Dissertation (Master in Ecology), National Institute of Amazonian Research/AM, 49 p. Retrieved September 14, 2018, from http://bdtd.inpa.gov.br/handle/tede/2254.
Saunders, D. A., Hobbs, R. J., & Margules, C. R. (1991). Biological consequences of ecosystem fragmentation: A review. Conservation Biology, 5(1), 18–32. Retrieved September 12, 2018, from https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.1991.tb00384.x.
SIAMIG. (2013). Green corridors demonstrate sustainability. SIAMIG, pp. 3–5. Retrieved September 13, 2018, from http://www.siamig.com.br/areainterna/cache/Canavial/setembro.pdf.
SOSMA & INPE. (2019). Atlas of forest remnants of the Atlantic rainforest period 2017–2018. Technical report, 63p. Retrieved September 16, 2018, from https://www.sosma.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Atlas-mata-atlanticaDIGITAL.pdf.
Tabarelli, M., Cardoso Da Silva, J. M., & Gascon, C. (2004). Forest fragmentation, synergisms and the impoverishment of neotropical forests. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13(7), 1419–1425. Retrieved September 12, 2018, from https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOC.0000019398.36045.1b.
Tabarelli, M., & Gascon, C. (2005). Lessons from fragmentation research: Refining management policies and guidelines for biodiversity conservation. Megadiversidade, 1(1), 181–188. Retrieved September 12, 2018, from http://www.unifap.br/ppgbio/doc/24_Tabarelli_Gascon.pdf.
WWF. (2017). Decree benefiting RPPNs is approved with support from WWF-Brasil. World Wild Fund. Retrieved September 18, 2018, from https://www.wwf.org.br/informacoes/?59622/Decreto-que-beneficia-as-RPPNs–aprovado-com-apoio-do-WWF-Brasil.
Zimbres, B. Q. C. (2016). Permanent Preservation Areas as ecological corridors for medium and large mammal fauna in southern Amazonia. Thesis (Doctorate in Zoology), University of Brasilia/DF, 119 p. Retrieved September 17, 2018, from http://repositorio.unb.br/bitstream/10482/22233/1/2016_BárbaradeQueirozCarvalhoZimbres.pdf.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Capes DS scholarship acquired by the student along with a doctorate in ecology (ECMVS – UFMG) in progress and in preparation with the structure of the Laboratory of Plankton Ecology (ICB – Institute of Biological Sciences) and Cartography laboratories (IGC – Institute of Geosciences), being part of the program The Long-Term Research Program- LTRP. Special thanks to the LTPR for the logistical, financial and scientific support and to the Rio Doce State Park (PERD) for the partnership throughout the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, B.R., Carvalho-Ribeiro, S.M. & Maia-Barbosa, P.M. Rio Doce State Park buffer zone: forest fragmentation and land use dynamics. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 8365–8376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00969-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00969-7