Abstract
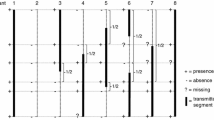
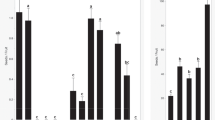
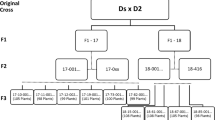
A balance of maternal and paternal genetic factors, conceptually named the endosperm balance number (EBN), is required for normal endosperm development in interspecific crosses in potato. We previously found that Solanum demissum (D), a hexaploid wild species widely used in potato breeding, has a slightly lower EBN than S. tuberosum (T). To explore the genetic nature of the EBN, the berry-setting rate, seed number/berry, and seed weight were evaluated in BC1 [(D × T) × T] plants, each possessing different portions of the S. demissum chromosomes, by reciprocal crosses with D and T, and a quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis was performed. At least 99 S. demissum-derived QTLs were detected, of which 29 were associated with differential responses to D and T. Three QTLs were possibly co-localized on chromosomes 7A and 10D1, while the remaining 23 QTLs were independently located. The QTLs in the three S. demissum homoeologous chromosomes exhibited three types of interaction: (1) positive, (2) negative, and (3) one positive and one negative effect on the same trait. We found that several major genes, one of which was localized in the S. demissum chromosome 9A, and many minor genes controlled the crossability of BC1 plants. The QTLs responsible for the differential responses to D and T were different between the BC1 plants used as male and female parents, indicating that different genes control the male and female EBNs. Consequently, we conclude that the EBN is represented by the sum of various genetic effects controlled by a large number of genes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla MMF, Hermsen JGTh (1972) Unilateral incompatibility: hypotheses, debate and its implications for plant breeding. Euphytica 21:32–47
Adams KL (2007) Evolution of duplicate gene expression in polyploid and hybrid plants. J Hered 98:136–141
Adams KL, Cronn R, Percifield R, Wendel JF (2003) Genes duplicated by polyploidy show unequal contributions to the transcriptome and organ-specific reciprocal silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4649–4654
Bamberg JB (1994) Allelism of endosperm balance number (EBN) in Solanum acaule Bitt. and other wild potato species. Theor Appl Genet 89:1682–1686
Bamberg JB, Hanneman RE Jr (1990) Allelism of Endosperm Balance Number (EBN) in Mexican tuber-bearing Solanum species. Theor Appl Genet 80:161–166
Bardil A, de Almeida JD, Combes MC, Lashermes P, Bertrand B (2011) Genomic expression dominance in the natural allopolyploid Coffea arabica is massively affected by growth temperature. New Phytol 192:760–774
Bedinger PA, Chetelat RT, McClure B, Moyle LC, Rose JKC, Stack SM, van der Knaap E, Baek YS, Lopez-Casado G, Covey PA, Kumar A, Li W, Nunez R, Cruz-Garcia F, Royer S (2011) Interspecific reproductive barriers in the tomato clade: opportunities to decipher mechanisms of reproductive isolation. Sex Plant Reprod 24:171–187
Bottley A, Xia GM, Koebner RMD (2006) Homoeologous gene silencing in hexaploid wheat. Plant J 47:897–906
Buck RW Jr (1960) Male sterility in interspecific hybrids of Solanum. J Hered 51:13–14
Burkart-Waco D, Josefsson C, Dilkes B, Kozloff N, Torjek O, Meyer R, Altmann T, Comai L (2012) Hybrid incompatibility in Arabidopsis is determined by a multiple-locus genetic network. Plant Physiol 158:801–812
Camadro EL, Masuelli RW (1995) A genetic model for the endosperm balance number (EBN) in the wild potato Solanum acaule Bitt. and two related diploid species. Sex Plant Reprod 8:283–288
Camadro EL, Peloquin SJ (1981) Cross-incompatibility between two sympatric polyploid Solanum species. Theor Appl Genet 60:65–70
Comai L (2005) The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nat Rev Genet 6:836–846
Comai L, Tyagi AP, Winter K, Holmes-Davis R, Reynolds SH, Stevens Y, Byers B (2000) Phenotypic instability and rapid gene silencing in newly formed Arabidopsis allotetraploids. Plant Cell 12:1551–1567
Dilkes BP, Comai L (2004) A differential dosage hypothesis for parental effects in seed development. Plant Cell 16:3174–3180
Dionne LA (1961) Cytoplasmic sterility in derivatives of Solanum demissum. Am Potato J 38:117–120
Dobzhansky T, Ayala FJ, Stebbins GL, Valentine JW (1977) Evolution. W. H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco
Ehlenfeldt MK, Hanneman RE Jr (1988) Genetic control of Endosperm Balance Number (EBN): three additive loci in a threshold-like system. Theor Appl Genet 75:825–832
Ehlenfeldt MK, Ortiz R (1995) Evidence on the nature and origins of endosperm dosage requirements in Solanum and other angiosperm genera. Sex Plant Reprod 8:189–196
Gebhardt C, Ritter E, Barone A, Debener T, Walkemeier B, Schachtschabel U, Kaufmann H, Thompson RD, Bonierbale MW, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD, Salamini F (1991) RFLP maps of potato and their alignment with the homoeologous tomato genome. Theor Appl Genet 83:49–57
Gopal J (1994) Flowering behaviour, male sterility and berry setting in tetraploid Solanum tuberosum germplasm. Euphytica 72:133–142
Grun P (1979) Evolution of the cultivated potato: a cytoplasmic analysis. In: Hawkes JG, Lester RN, Skelding AD (eds) The biology and taxonomy of the Solanaceae. Academic Press, London, pp 655–665
Grun P, Ochoa C, Capage D (1977) Evolution of cytoplasmic factors in tetraploid cultivated potatoes (Solanaceae). Am J Bot 64:412–420
Hanneman RE Jr (1994) Assignment of Endosperm Balance Numbers to the tuber-bearing Solanums and their close non-tuber-bearing relatives. Euphytica 74:19–25
Hanneman RE Jr (1999) The reproductive biology of the potato and its implication for breeding. Potato Res 42:283–312
Hanneman RE Jr, Peloquin SJ (1981) Genetic-cytoplasmic male sterility in progeny of 4x-2x crosses in cultivated potatoes. Theor Appl Genet 59:53–55
Hawkes JG (1990) The potato: evolution, biodiversity and genetic resources. Belhaven Press, London
Hawkes JG, Hjerting JP (1969) The potatoes of Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Oxford University Press, London
Hermsen JGTh, Sawicka E (1979) Incompatibility and incongruity in tuber-bearing Solanum species. In: Hawkes JG, Lester RN, Skelding AD (eds) The biology and taxonomy of the Solanaceae. Academic Press, London, pp 445–453
Howard HW, Swaminathan MS (1952) Species differentiation in the section Tuberarium of Solanum with particular reference to the use of interspecific hybridisation in breeding. Euphytica 1:20–28
Irikura Y (1968) Studies on interspecific crosses of tuber-bearing Solanums. 1. Overcoming cross-incompatibility between Solamum tuberosum and other Solanum species by mean of induced polyploids and haploids. Hokkaido Noshi Shuho 92:21–37
Iwanaga M, Ortiz R, Cipar MS, Peloquin SJ (1991) A restorer gene for genetic-cytoplasmic male sterility in cultivated potatoes. Am Potato J 68:19–28
Johnston SA, Hanneman RE Jr (1980) Support of the endosperm balance number hypothesis utilizing some tuber-bearing Solanum species. Am Potato J 57:7–14
Johnston SA, Hanneman RE Jr (1982) Manipulations of endosperm balance number overcome crossing barriers between diploid Solanum species. Science 217:446–448
Johnston SA, den Nijs TPM, Peloquin SJ, Hanneman RE Jr (1980) The significance of genetic balance to endosperm development in interspecific crosses. Theor Appl Genet 57:5–9
Josefsson C, Dilkes B, Comai L (2006) Parent-dependent loss of gene silencing during interspecies hybridization. Curr Biol 16:1322–1328
Katsiotis A, Hanneman RE Jr, Forsberg RA (1995) Endosperm Balance Number and the polar-nuclei activation hypotheses for endosperm development in interspecific crosses of Solanaceae and Gramineae, respectively. Theor Appl Genet 91:848–855
Köhler C, Scheid OM, Erilova A (2010) The impact of the triploid block on the origin and evolution of polyploidy plants. Trends Genet 26:142–148
Madlung A (2013) Polyploidy and its effect on evolutionary success: old questions revisited with new tools. Heredity 110:99–104
Marks GE (1965) Cytogenetic studies in tuberous Solanum species. III. Species relationships in some South and Central American species. New Phytol 64:293–306
Matsubayashi M (1991) Phylogenetic relationships in the potato and its related species. In: Tsuchiya T, Gupta PK (eds) Chromosome engineering in plants: genetics, breeding, evolution, part B. Elsevier, New York, pp 93–118
Mori K, Mukojima N, Nakao T, Tamiya S, Sakamoto Y, Sohbaru N, Hayashi K, Watanuki H, Nara K, Yamazaki K, Ishii T, Hosaka K (2012) Germplasm release: Saikai 35, a male and female fertile breeding line carrying Solanum phureja-derived cytoplasm and potato cyst nematode resistance (H1) and Potato virus Y resistance (Ry chc) genes. Am J Potato Res 89:63–72
Moyle LC, Graham EB (2005) Genetics of hybrid incompatibility between Lycopersicon esculentum and L. hirsutum. Genetics 169:355–373
Moyle LC, Nakazato T (2008) Comparative genetics of hybrid incompatibility: sterility in two Solanum species crosses. Genetics 179:1437–1453
Nishiyama I, Yabuno T (1978) Causal relationships between the polar nuclei in double fertilization and interspecific cross-incompatibility. Cytologia 43:453–466
Ono S (2008) A cytogenetic study on the backcross populations from a wild hexaploid species Solanum demissum Lindl. and a common potato. BS thesis, Kobe University
Ono S, Sanetomo R, Hosaka K (2016) Genetic transmission of Solanum demissum (2n = 6x = 72) chromosomes from a pentaploid hybrid of S. tuberosum (2n = 4x = 48) into the aneuploid BC1 progeny. Euphytica 207:149–168
Ortiz R, Ehlenfeldt MK (1992) The importance of Endosperm Balance Number in potato breeding and the evolution of tuber-bearing Solanum species. Euphytica 60:105–113
Pandey KK (1962) Interspecific incompatibility in Solanum species. Amer J Bot 49:874–882
Phumichai C, Ikeguchi-Samitsu Y, Fujimatsu M, Kitanishi S, Kobayashi A, Mori M, Hosaka K (2006) Expression of S-locus inhibitor gene (Sli) in various diploid potatoes. Euphytica 148:227–234
Plaisted RL, Hoopes RW (1989) The past record and future prospects for the use of exotic potato germplasm. Am Potato J 66:603–627
Pushkarnath (1942) Studies on sterility in potatoes. 1. The genetics of self- and cross-incompatibilities. Indian J Genet Pl Breed 2:11–36
Ross H (1986) Potato breeding—problems and perspectives. Verlag Paul Parey, Berlin
Rudorf W (1950) Methods and results of breeding resistant strains of potatoes. Am Potato J 27:332–339
Sanetomo R, Ono S, Hosaka K (2011) Characterization of crossability in the crosses between Solanum demissum and S. tuberosum, and the F1 and BC1 progenies. Am J Potato Res 88:500–510
Spooner DM, van den Berg RG, Rodríguez A, Bamberg J, Hijmans RJ, Lara Cabrera SI (2004) Wild potatoes (Solanum section Petota; Solanaceae) of North and Central America. Syst Bot Monogr 68:1–209
Spooner DM, Ghislain M, Simon R, Jansky SH, Gavrilenko T (2014) Systematics, diversity, genetics, and evolution of wild and cultivated potatoes. Bot Rev 80:283–383
Stupar RM, Bhaskar PB, Yandell BS, Rensink WA, Hart AL, Ouyang S, Veilleux RE, Busse JS, Erhardt RJ, Buell CR, Jiang J (2007) Phenotypic and transcriptomic changes associated with potato autopolyploidization. Genetics 176:2055–2067
Udall JA, Swanson JM, Nettleton D, Percifield RJ, Wendel JF (2006) A novel approach for characterizing expression levels of genes duplicated by polyploidy. Genetics 173:1823–1827
Van Ooijen JW (2009) MapQTL® 6, software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations of diploid species. Kyazma B. V., Wageningen
Walia H, Josefsson C, Dilkes B, Kirkbride R, Harada J, Comai L (2009) Dosage-dependent deregulation of an AGAMOUS-LIKE gene cluster contributes to interspecific incompatibility. Curr Biol 19:1128–1132
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Shizuka Souma and Eri Kakuta for technical assistance. This research was supported by Calbee Inc., Hokkaido Potato Growers Association, Kewpie Corp., KENKO Mayonnaise Co., Ltd., and Japan Snack Cereal Foods Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosaka, K., Sanetomo, R. Effects of Solanum demissum chromosomes on crossability in the backcross progeny to Solanum tuberosum. Euphytica 214, 113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2186-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2186-3